Some typical samples were selected to analyze the distribution characteristics of casting defects.
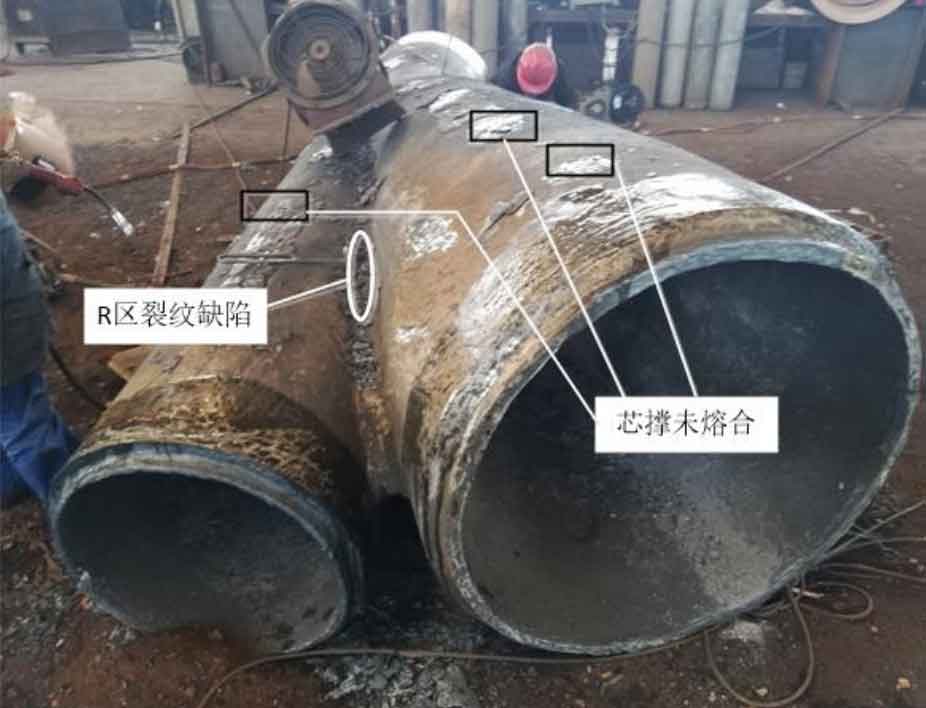
(1) ZG-03 is a multi pipe intersection node. Magnetic particle flaw detection was carried out for its R area and ultrasonic flaw detection was carried out for other areas. A total of 4 crack defects were detected at this node, and the types of casting defects detected were R-zone crack and incomplete fusion of core support. Figure 1 shows the location, shape and type of casting defects detected in the cast steel joint.
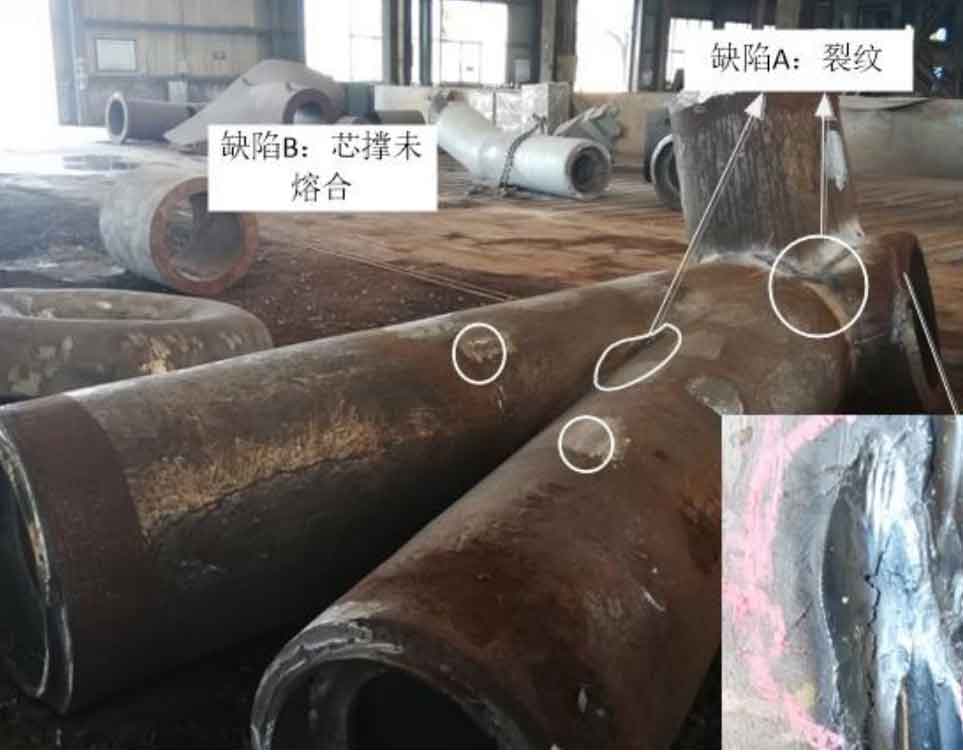
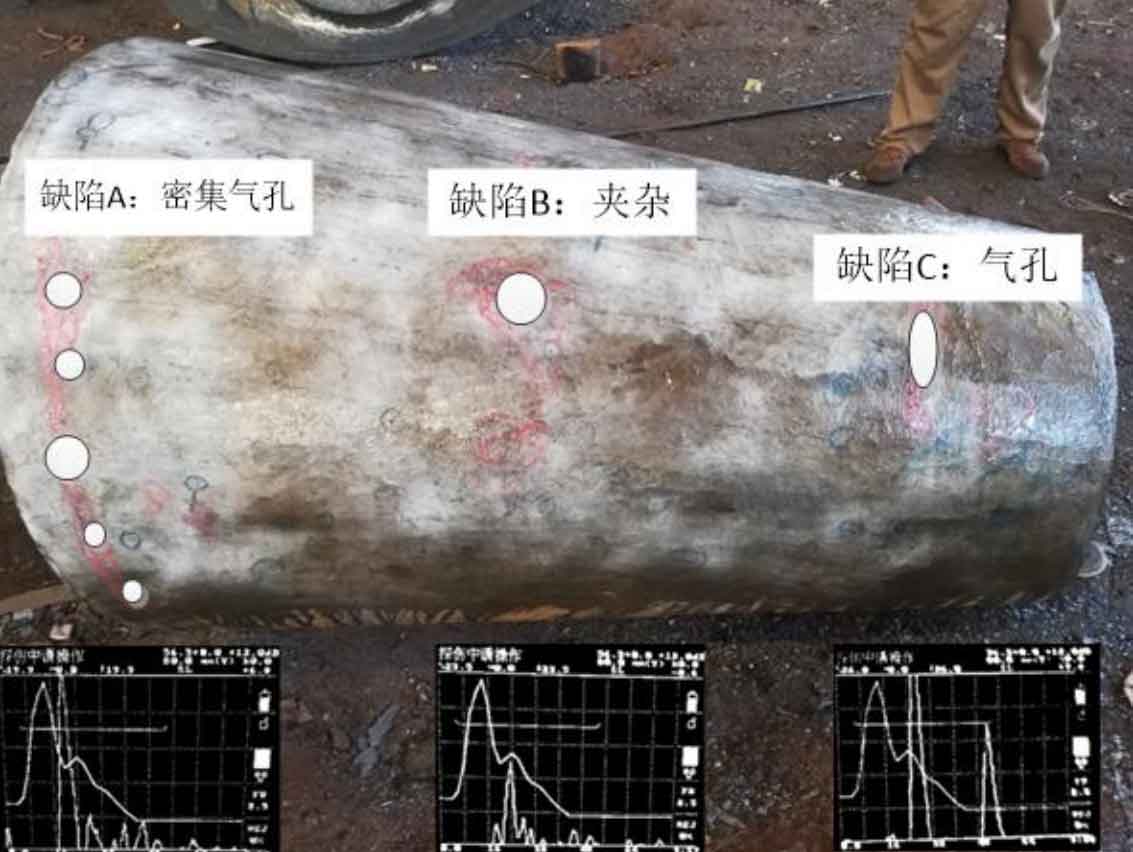
(2) ZG-08 is a three fork cast steel joint. Magnetic particle flaw detection was carried out for its R area and ultrasonic flaw detection was carried out for other areas. A total of 5 casting defects were detected at this node. The types of casting defects detected were dense pores at the nozzle, cracks in R-zone and incomplete fusion of core support. Figure 2 shows the location, shape and type of casting defects detected in the cast steel joint.
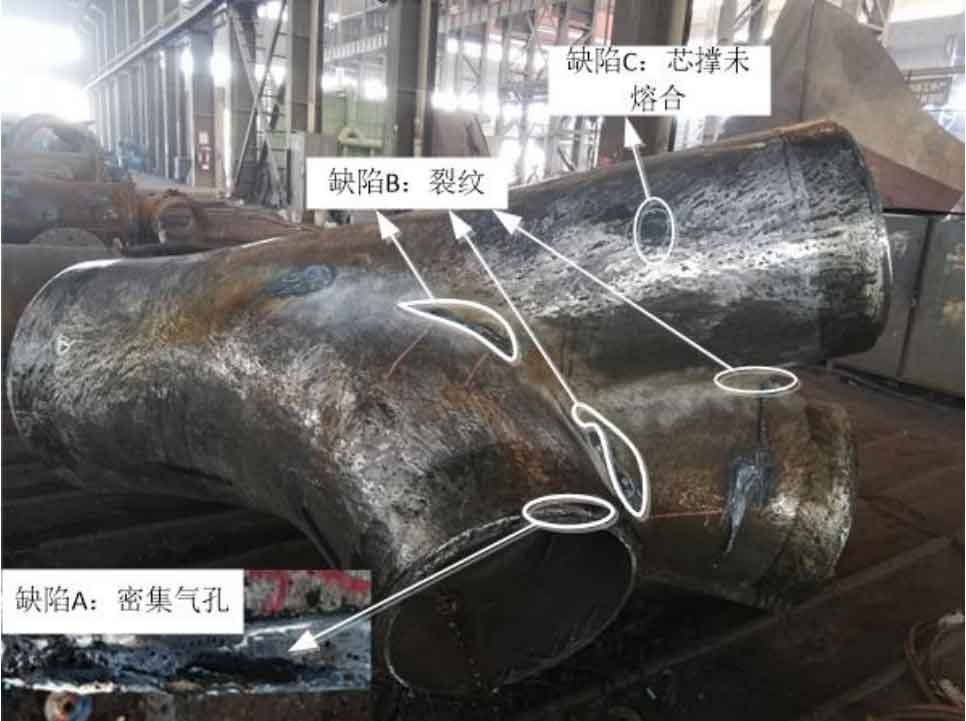
(3) ZG-09 is a three fork cast steel joint. Magnetic particle flaw detection was carried out for its R area and ultrasonic flaw detection was carried out for other areas. A total of 5 casting defects were detected at this node. The types of casting defects detected were dense pores at the nozzle, cracks in R-zone and incomplete fusion of core support. Figure 3 shows the location, shape and type of casting defects detected in the cast steel joint.
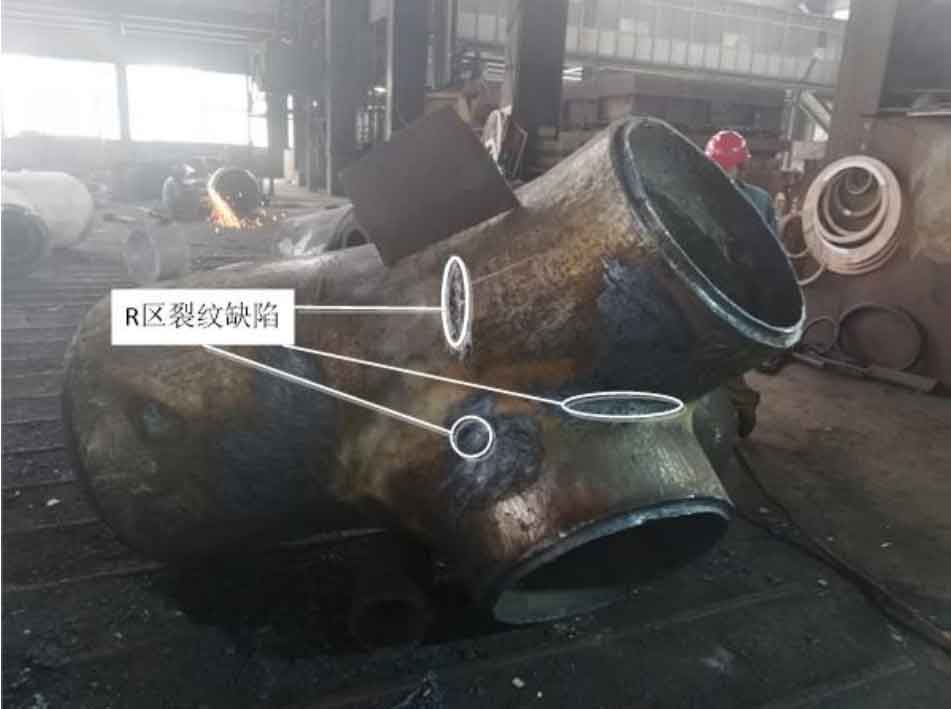
(4) ZG-10 is a two bifurcation cast steel joint. Magnetic particle flaw detection was carried out for its R area and ultrasonic flaw detection was carried out for other areas. Two kinds of casting defects were detected at this node: R-zone crack and incomplete fusion of core support. Figure 4 shows the location, shape and type of casting defects detected in the cast steel joint.
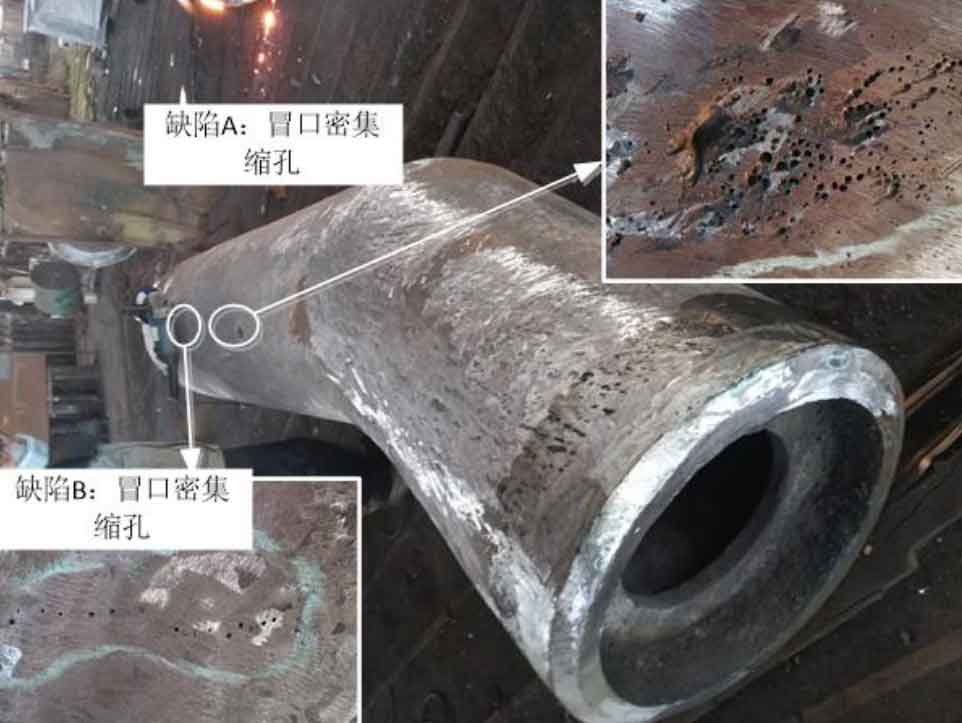
(5) ZG-06 is a non bifurcated cast steel joint, which has been subject to ultrasonic flaw detection. The joint has simple shape and smooth transition. A total of 2 casting defects are detected at the joint, all of which are riser shrinkage defects. Figure 5 shows the location, shape and type of casting defects detected in the cast steel joint.
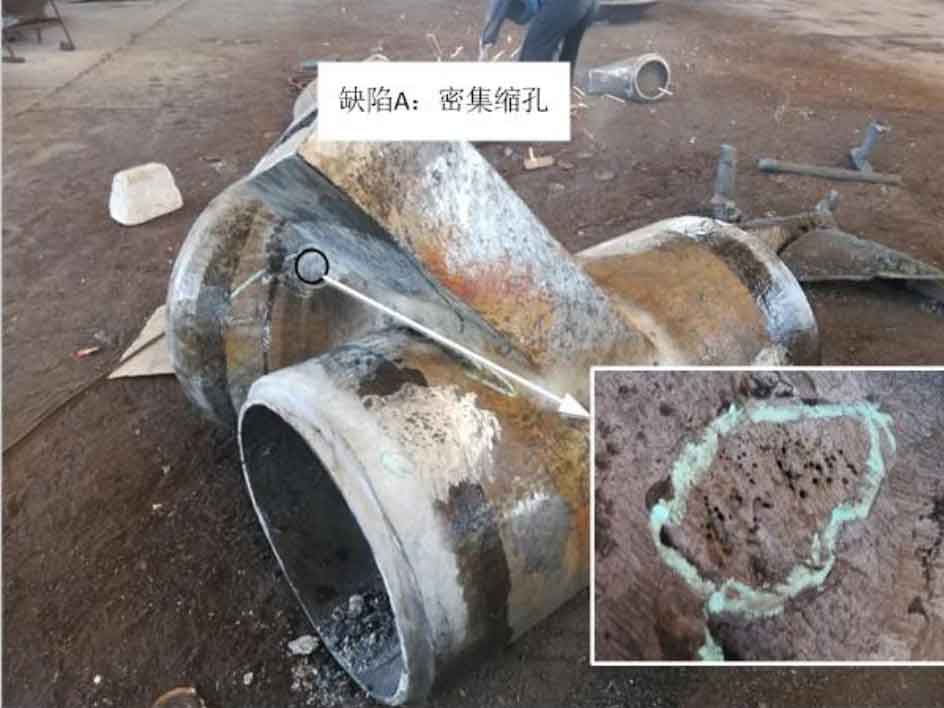
(6) ZG-07 is a multi pipe intersection node. Magnetic particle flaw detection was carried out for its R area and ultrasonic flaw detection was carried out for other areas. A total of one casting defect is detected at this node, and the detected casting defect type is shrinkage defect. Figure 6 shows the location, shape and type of casting defects detected in the cast steel joint.
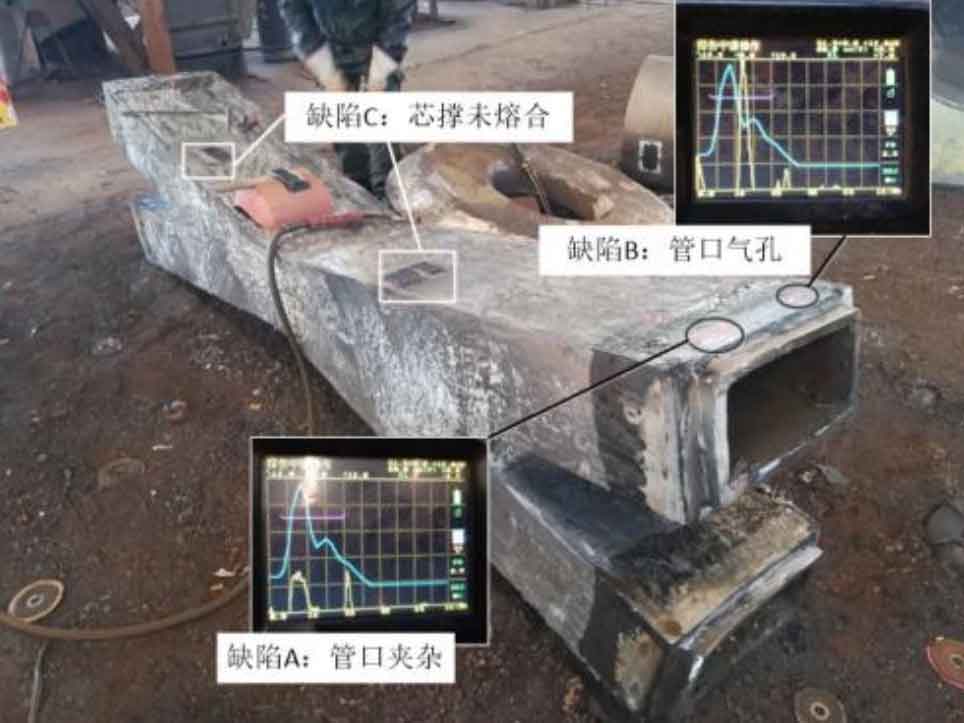
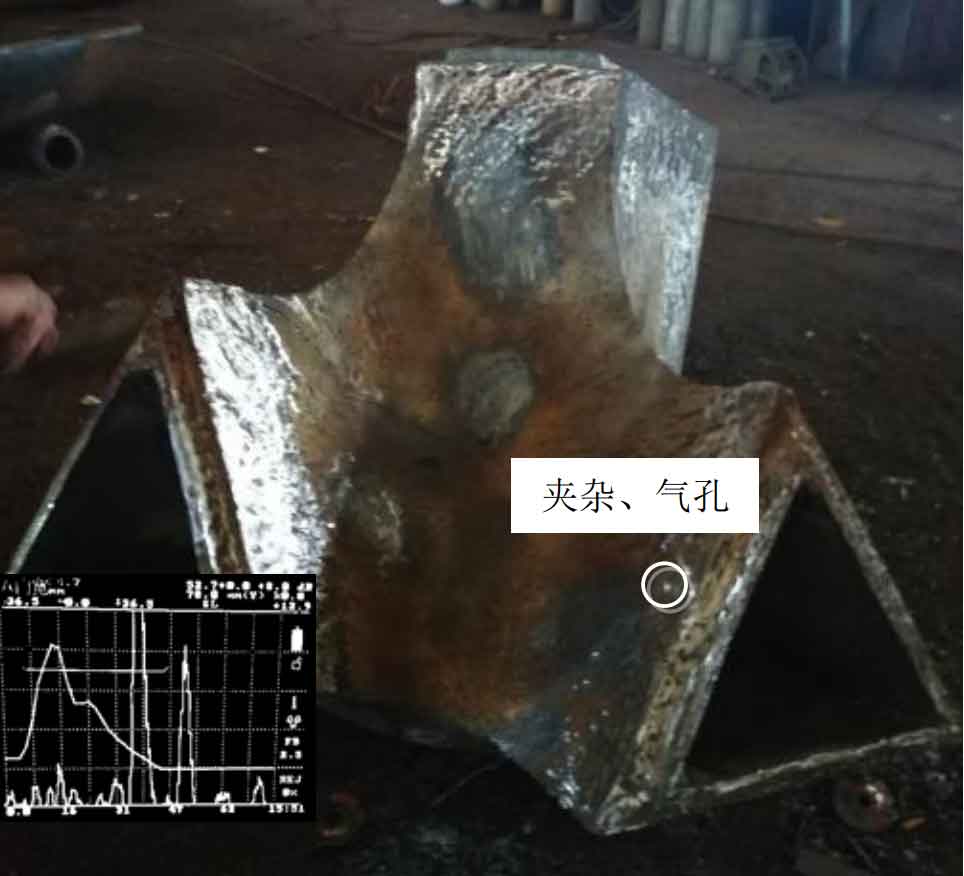
(7) ZG-21 is an X-type cast steel joint. Ultrasonic flaw detection was carried out on the whole. Three kinds of casting defects were detected in this node. In addition to the lack of fusion of the surface core support, the types of casting defects detected by ultrasound were nozzle inclusions and nozzle pores, and the over standard defects were nozzle pores. See Figure 7 for node photos.
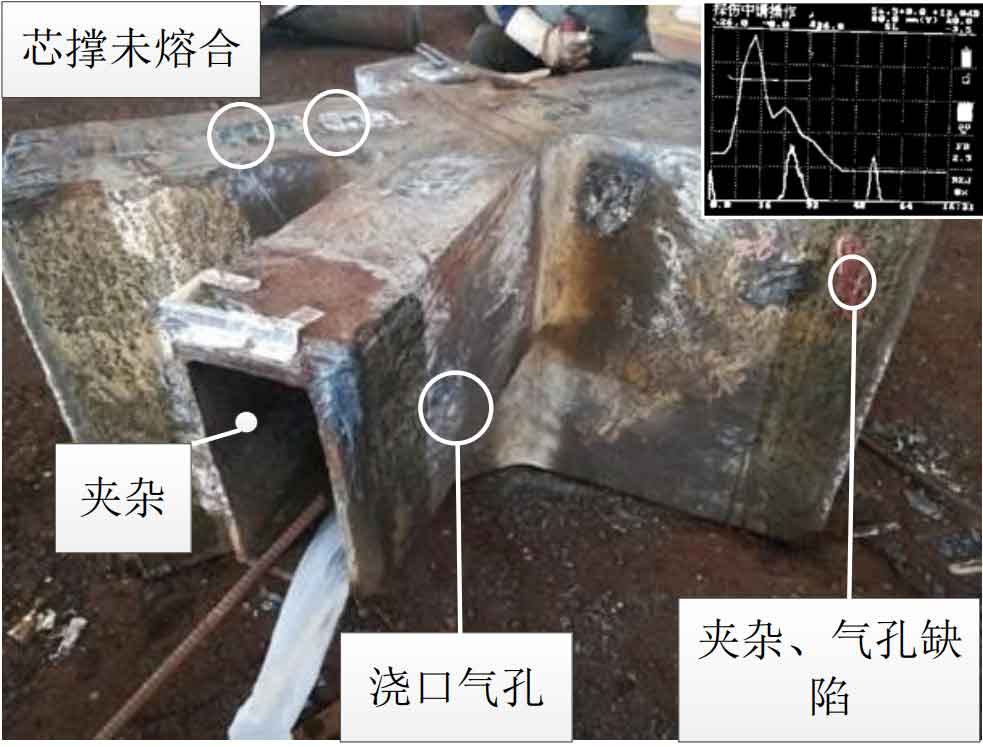
(8) ZG-24 is a cast steel joint of square pipe intersection. Magnetic particle flaw detection was carried out for its R area and ultrasonic flaw detection was carried out for other areas. Typical casting defects include dense pores near the gate, lack of fusion of core support on the casting surface, inclusions near the gate, pores and inclusions near the nozzle. See Figure 8 for node photos.
(9) ZG-11 carried out ultrasonic flaw detection. There are many inclusion defects at the nozzle of the cast steel joint, and there are serious pore defects, which need to be repaired by welding. See Figure 9 for node photos.
(10) ZG-17 carried out ultrasonic flaw detection. There are many inclusions, pores and other defects at the gate of the cast steel joint, all of which are beyond the standard and need to be repaired. See Figure 10 for node photos.