Spheroidal Graphite Cast Iron is renowned for its superior mechanical properties, including high strength, ductility, and toughness. However, like all ferrous materials, it is susceptible to corrosion, which can significantly affect its performance and lifespan. Understanding the factors that influence the corrosion resistance of Spheroidal Graphite Cast Iron and employing appropriate protective measures, including heat treatment processes, is essential for enhancing its durability in corrosive environments. This article explores the corrosion resistance of Spheroidal Graphite Cast Iron and the methods to improve it.
Factors Affecting Corrosion Resistance in Spheroidal Graphite Cast Iron
The corrosion resistance of Spheroidal Graphite Cast Iron depends on several factors, including its chemical composition, microstructure, and the environment it is exposed to.
Key Factors
- Chemical Composition: The presence of certain elements can influence the corrosion behavior of Spheroidal Graphite Cast Iron.
- Microstructure: The distribution and morphology of graphite nodules and the matrix structure play a significant role in corrosion resistance.
- Environment: The type of corrosive medium (e.g., acidic, alkaline, saline) and exposure conditions (e.g., humidity, temperature) impact corrosion rates.
Table 1: Factors Affecting Corrosion Resistance
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Elements such as silicon, chromium, and nickel can enhance corrosion resistance |
| Microstructure | Graphite nodules and matrix phases influence corrosion behavior |
| Environment | Type of corrosive medium and exposure conditions impact corrosion rates |
Chemical Composition and Corrosion Resistance
The chemical composition of Spheroidal Graphite Cast Iron significantly affects its corrosion resistance. Adding specific alloying elements can enhance its ability to withstand corrosive environments.
Important Alloying Elements
- Silicon (Si): Silicon increases the passivity of the iron, forming a protective oxide layer on the surface that inhibits further corrosion.
- Chromium (Cr): Chromium enhances resistance to oxidation and pitting corrosion, especially in acidic environments.
- Nickel (Ni): Nickel improves overall corrosion resistance and toughness, particularly in marine and acidic environments.
- Molybdenum (Mo): Molybdenum provides additional resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion.
Table 2: Alloying Elements and Their Effects on Corrosion Resistance
| Element | Effect on Corrosion Resistance |
|---|---|
| Silicon (Si) | Forms protective oxide layer, enhances passivity |
| Chromium (Cr) | Improves resistance to oxidation and pitting |
| Nickel (Ni) | Enhances corrosion resistance and toughness |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | Provides resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion |
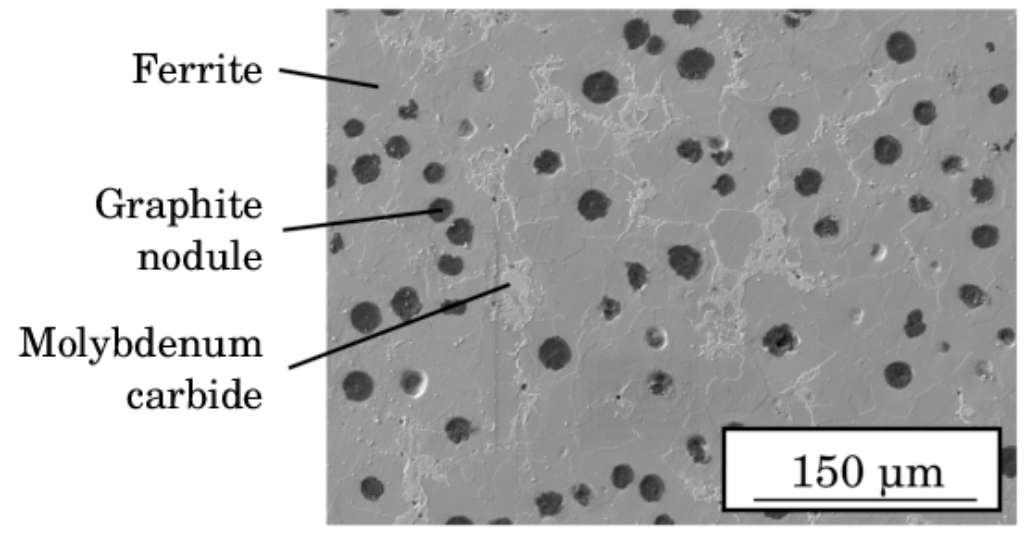
Microstructure and Corrosion Resistance
The microstructure of Spheroidal Graphite Cast Iron, including the shape and distribution of graphite nodules and the matrix structure, plays a crucial role in its corrosion resistance.
Microstructural Features
- Graphite Nodules: Spherical graphite nodules reduce stress concentrations and help in distributing corrosive effects more uniformly, thereby improving corrosion resistance compared to flake graphite in gray iron.
- Matrix Phases: The presence of ferrite, pearlite, or a bainitic matrix can influence corrosion behavior. A ferritic matrix generally offers better corrosion resistance than a pearlitic matrix due to its homogeneity and lower carbon content.
List 1: Microstructural Features Influencing Corrosion Resistance
- Spherical graphite nodules for uniform stress distribution.
- Ferritic matrix for better corrosion resistance.
Heat Treatment and Corrosion Resistance
Heat treatment processes can alter the microstructure of Spheroidal Graphite Cast Iron, thereby affecting its corrosion resistance. By optimizing heat treatment, the corrosion resistance can be significantly enhanced.
Key Heat Treatment Processes
- Annealing: Annealing can homogenize the microstructure, reducing internal stresses and improving corrosion resistance.
- Normalizing: Normalizing refines the grain structure and can enhance the uniformity of the matrix, improving overall corrosion resistance.
- Austempering: Austempering produces a bainitic structure, which can improve both mechanical properties and corrosion resistance.
- Surface Hardening: Processes such as induction hardening can increase surface hardness and improve resistance to corrosive wear.
Table 3: Heat Treatment Processes and Their Effects on Corrosion Resistance
| Process | Effect on Corrosion Resistance |
|---|---|
| Annealing | Homogenizes microstructure, reduces internal stresses |
| Normalizing | Refines grain structure, enhances uniformity |
| Austempering | Produces bainitic structure, improves properties |
| Surface Hardening | Increases surface hardness, improves resistance to corrosive wear |
Protective Coatings and Surface Treatments
In addition to heat treatment, applying protective coatings and surface treatments can further enhance the corrosion resistance of Spheroidal Graphite Cast Iron.
Common Protective Measures
- Paint Coatings: Applying paint or epoxy coatings to create a barrier against corrosive elements.
- Galvanizing: Coating with a layer of zinc to protect against rust and corrosion.
- Plating: Electroplating with materials such as nickel or chromium to enhance corrosion resistance.
- Chemical Treatments: Using inhibitors and corrosion-resistant chemicals to protect the iron surface.
List 2: Protective Measures for Enhancing Corrosion Resistance
- Paint or epoxy coatings for barrier protection.
- Galvanizing for zinc protection.
- Electroplating with nickel or chromium.
- Chemical treatments with corrosion inhibitors.
Case Study: Enhancing Corrosion Resistance in Marine Environments
A marine equipment manufacturer faced challenges with the corrosion resistance of Spheroidal Graphite Cast Iron components exposed to seawater. The following strategies were implemented to enhance the corrosion resistance.
Strategies Implemented
- Alloying with Nickel and Chromium: Added nickel and chromium to the iron to improve overall corrosion resistance.
- Austempering Heat Treatment: Applied austempering to achieve a bainitic microstructure with improved mechanical properties and corrosion resistance.
- Protective Coatings: Applied a combination of galvanizing and epoxy coatings for additional protection against seawater corrosion.
Table 4: Strategies and Benefits
| Strategy | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Alloying with Nickel and Chromium | Enhanced overall corrosion resistance |
| Austempering Heat Treatment | Improved mechanical properties and corrosion resistance |
| Protective Coatings | Additional protection against seawater corrosion |
Conclusion
Spheroidal Graphite Cast Iron, with its excellent mechanical properties, can be effectively protected against corrosion through careful control of its chemical composition, microstructure, and the application of appropriate heat treatment processes. By optimizing alloying elements, refining the microstructure through heat treatment, and applying protective coatings and surface treatments, the corrosion resistance of Spheroidal Graphite Cast Iron can be significantly enhanced. These measures ensure that Spheroidal Graphite Cast Iron components perform reliably in various corrosive environments, extending their service life and maintaining their mechanical integrity. As technology advances, further improvements in corrosion resistance are likely, broadening the applications and longevity of Spheroidal Graphite Cast Iron in demanding environments.
