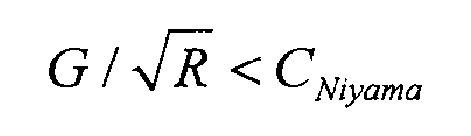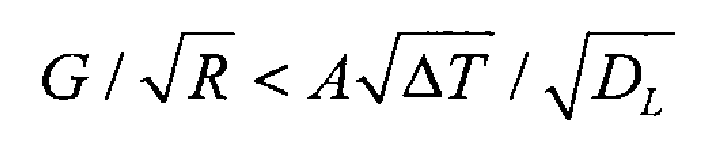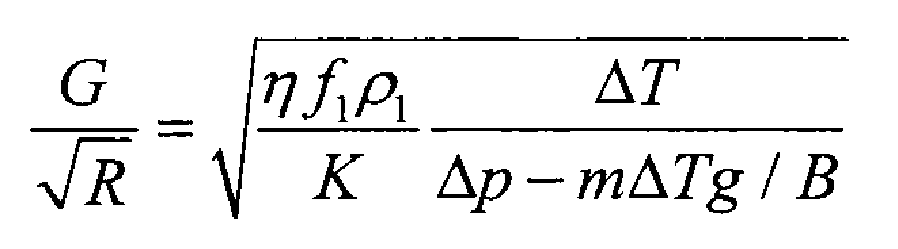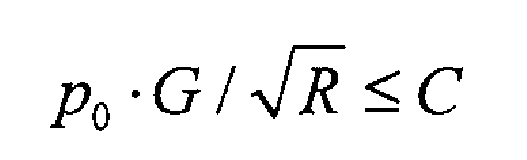The shrinkage porosity produced in the solidification process of castings is mainly predicted by using the shrinkage porosity criterion. There are many factors affecting the shrinkage porosity casting defects, such as the speed of solidification process, alloy composition or section size. Now foundry workers mainly use niyama criterion to predict shrinkage casting defects. The expression of the criterion is:
Since the niyama criterion itself does not consider the influencing factors of alloy composition, this criterion itself has certain limitations. In order to judge the shrinkage porosity produced in the solidification process of castings more accurately and make the criterion more rigorous, some casting researchers are committed to revising the criterion. The modified criterion considers more influencing factors, such as flow resistance between hot dendrites and pressure loss. Although the modified criterion is more complex, it makes the criterion more rigorous.
After considering the influence of dendrite growth factors on shrinkage porosity, Jia Baoqian et al. Obtained the following criteria, and its mathematical expression is:
Where, a is the correction coefficient, and its value is related to the dendrite morphology; Diffusion coefficient of solute in liquid metal at DL; Δ T is the temperature difference between liquidus and solidus.
Jia Baoqian et al. Also considered the feeding flow of dendrites and other factors, and derived the following criteria:
Where, B is the physical property parameter; F1 is the liquid fraction; M is the slope of liquidus; ρ 1 is the density of liquid phase; Δ T is the temperature difference between liquidus and solidus; η Is the liquidus viscosity coefficient.
Tian Xuelei et al. Believed that although the niyama criterion considered the influence of factors such as pressure difference, it did not consider the influence of pressure itself. On this basis, Tian Xuelei et al. Introduced the pressure factor and deduced a new criterion condition for shrinkage and porosity. Its expression is as follows:
Where P0 is the static pressure of the liquid; C is the critical value.