1. Design Preparation
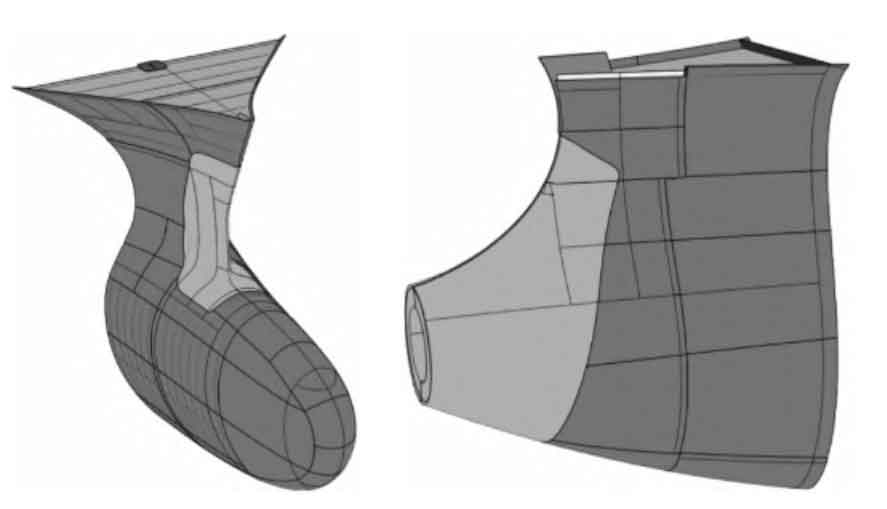
The design of ship steel castings is an important component of ship structure design, involving components such as outer plate linetype, regional deck, and rib plates. In general, the thickness of cast steel (or forged steel) connected to the hull structural join should be 25%~50% more than the thickness of the adjacent hull shell plate; The bow column is firmly connected to the side outer plate, bottom structure, and bottom plate deck, forming a watertight structure; The exposed parts and edges of the bow pillar should be fully rounded. In a three-dimensional environment, the design and modeling work of steel castings needs to be based on the design work of relevant structures such as the hull shell (surface), deck, and rib plates in the early stage. The picture shows the CATIA modeling effect of the steel castings for the bow column and stern shaft tube, and the steel castings should be segmented and docked with their adjacent structures.
2. General ideas for modeling the design of ship steel castings in CATIA
In CATIA, the modeling of steel castings is different from that of ship structures: due to the fact that most of the steel castings are solid surfaces with curved structures and their linear curvature changes greatly, it is not possible to use a plane as a support surface for modeling, like structural panels, brackets, and bulkheads; Due to the uneven thickness of steel castings, they cannot be endowed with the same shelf properties as the outer plate. Therefore, it is necessary to use key information such as points, lines, and surfaces to control the shape of steel castings. The modeled steel castings must have at least two directional profiles to achieve smooth linear connections.
1) The hull structure files and the smoothed hull shell surface files that need to be transferred into the preliminary work are used to establish the intersection lines between important docking components such as ribs, decks, and platform ribs and the hull shell, taking the ribs, decks, and platforms as profiles. These lines are used as the skeleton lines (the line connecting the outer plate surface) for the next step of the steel casting and the outer plate, as well as auxiliary lines for the design of the inner surface of the steel casting.
2) Steel castings need to be divided into different areas based on these line types and structural features, and their line types and surfaces need to be constructed separately. In CATIA, there are various ways to generate curves and surfaces: sketches can be drawn using any plane, and then projected onto the surface to form spatial curves; By directly intersecting, cutting, and offsetting spatial elements through points, lines, and surfaces, new elements can be generated, and useful elements can be recombined through filtering to form new three-dimensional curves.
3) Based on the generated three-dimensional curves, the outer surface of ship steel castings is generated by filling or multi section curves, and the closed envelope formed by the outer surface is filled, thus completing the preliminary design modeling of the ship steel casting structure. The geometric features of steel castings are mainly designed through the GWS (Generative Wire frame&Surface) module. Design and modeling process of bow column steel castings.
