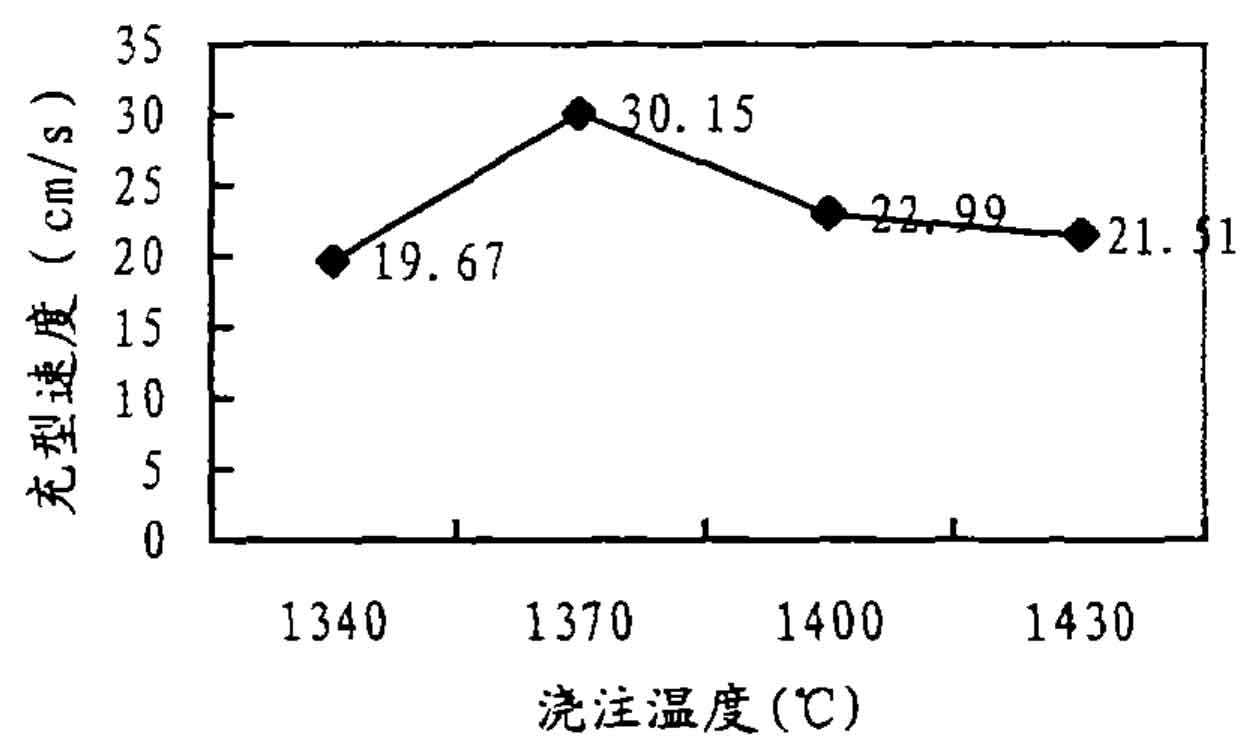
The test results are shown in the table:
| Pouring temperature (℃) | Total mold filling time (s) | Average filling speed (cm/s) |
| 1340 | 1.02 | 19.67 |
| 1370 | 0.66 | 30.15 |
| 1400 | 0.87 | 22.99 |
| 1430 | 0.93 | 21.51 |
The mold filling process of lost foam casting is completed by the pyrolysis of pattern materials, and the pouring temperature has a great influence on the pyrolysis of pattern materials, which determines the type, quantity and decomposition rate of pyrolysis products. The filling speed of molten metal depends on two aspects: heat and mass transfer. On the one hand, the thermal decomposition of the model material is an endothermic process. With the thermal decomposition of the model material, the front end of the liquid metal will be subject to a certain degree of chilling effect. The properties of the model material, including density, bead size, monomer mass, bead fusion degree, etc., have a considerable impact on its thermal decomposition characteristics. On the other hand, when the pattern material decomposes under the thermal action of liquid metal, The pressure promotes the thermal decomposition products to enter the nearby dry sand through the coating. The vacuum negative pressure in the sand box, the gas evolution speed and gas evolution of the model material, the permeability of the coating layer, the particle size of dry sand and its permeability will all have an important impact on this process.
In sand mold casting, the hydraulic formula for calculating the blocking cross-sectional area is:
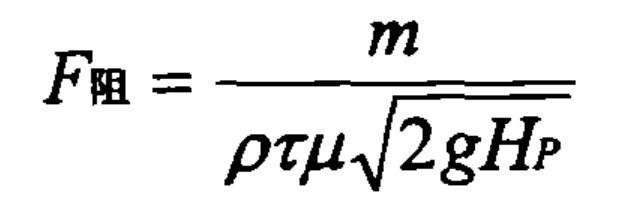
HP is the average calculated pressure head when filling the cavity.
In lost foam casting, due to the existence of thermal decomposition products of the model, the filling driving force of liquid metal decreases, the blocking cross-sectional area depends on the gas pressure in the gap between the average calculated pressure head and the liquid metal model, the effective static pressure head is used to represent its filling driving force, and the filling speed of liquid metal depends on its filling driving force.
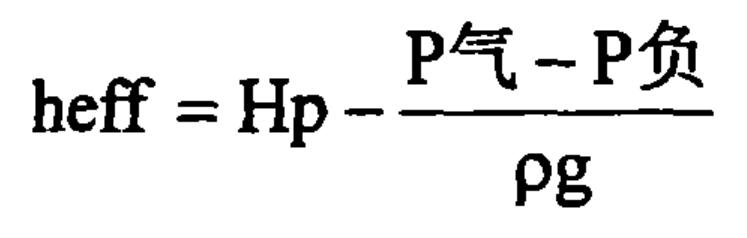
When other conditions are the same, the relationship curve between the average mold filling speed of molten metal and pouring temperature is shown in Figure 1. It can be seen from the figure that below 1370 ℃, the average mold filling speed of molten metal increases almost linearly with the increase of pouring temperature, and the average mold filling speed of molten metal reaches the maximum value of 30.15cm/s at 1370 ℃; Between 1370 ℃ and 1400 ℃, the average mold filling speed of molten metal decreases rapidly with the increase of pouring temperature. At 1400 ℃, the average mold filling speed of molten metal decreases to 22.99cm/s. Compared with 1370 ℃, the average mold filling speed decreases by 23.7%, higher than 1400 ℃. With the increase of pouring temperature, the average mold filling speed of molten metal decreases slowly, From 22.99cm/s at 1400 ℃ to 21.51cm/s at 1430 ℃, reaching a relatively stable average mold filling speed of molten metal.