According to the simulation results in the previous section, it is found that the feeding channel of riser neck is closed too early, resulting in many isolated molten pools in nodular cast iron at the later stage of solidification, which eventually leads to more shrinkage defects. Therefore, in order to prolong the solidification time of riser neck, the pouring temperature was increased from 1370 ℃ to 1400 ℃ and 1425 ℃, and the effects of different temperatures on the casting simulation of the original process scheme of automobile hub support were studied.
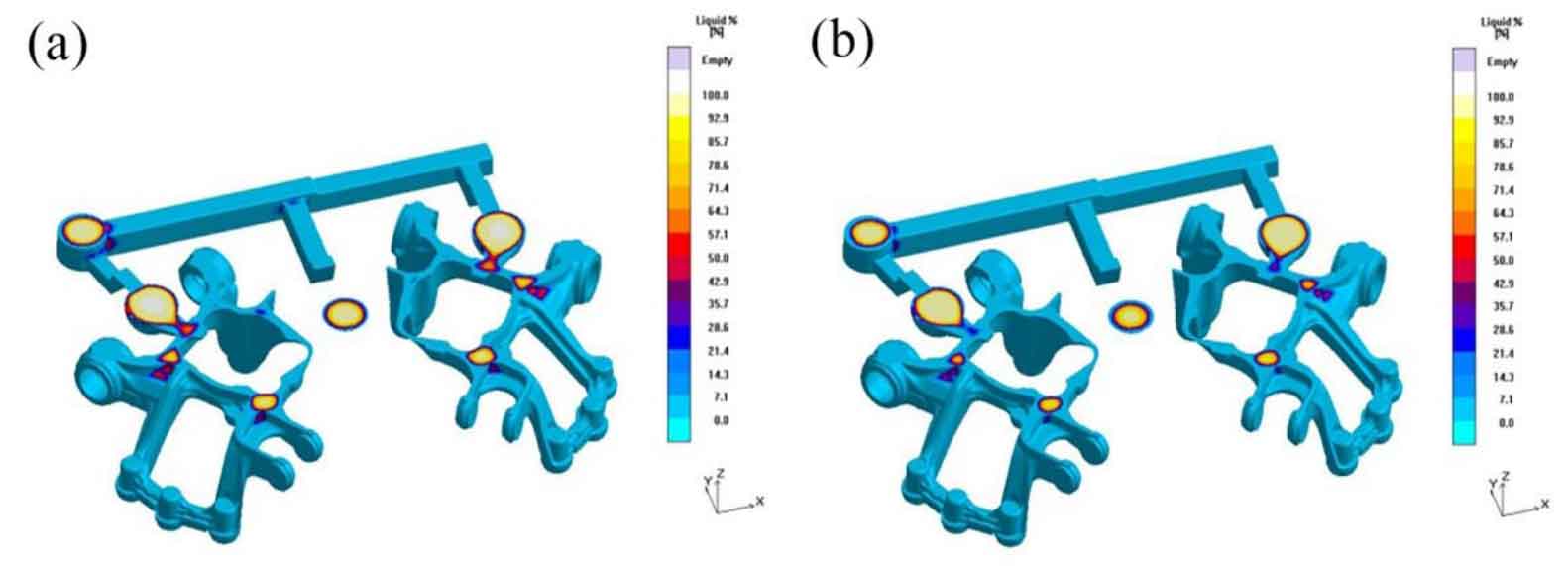
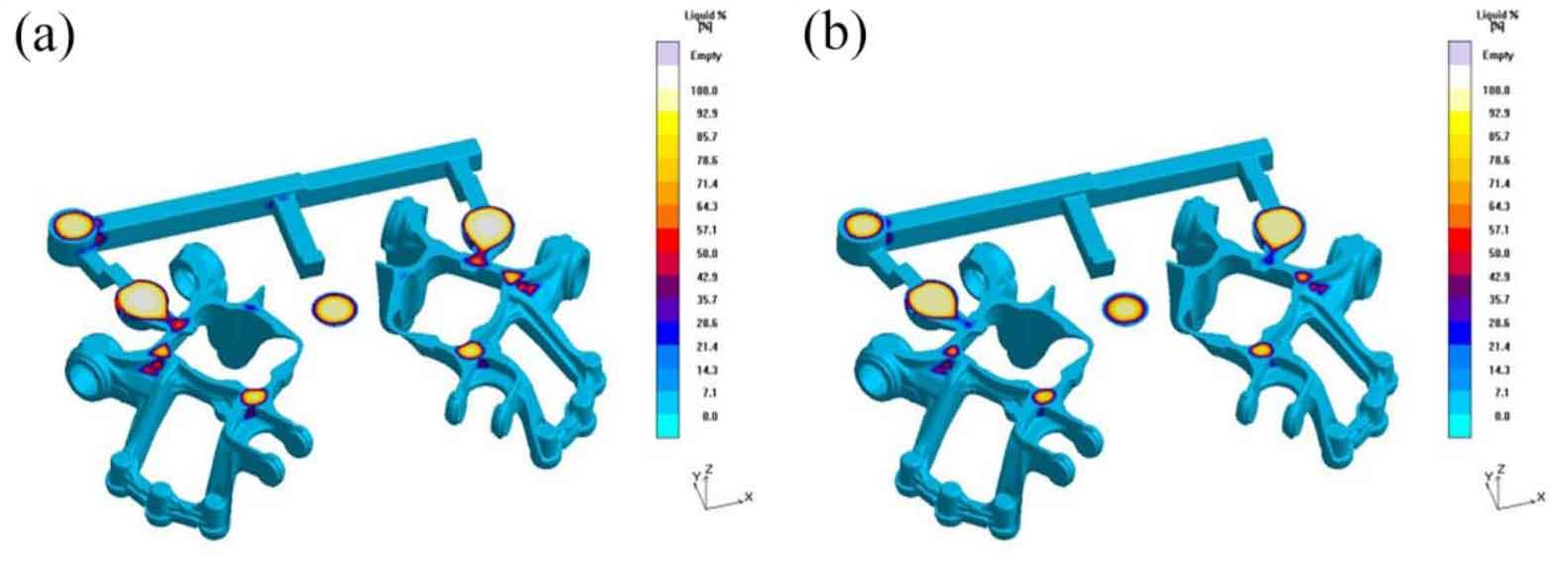
Figure 1 and Figure 2 show the liquid phase distribution in nodular cast iron at the later stage of solidification when the simulation is carried out at 1400 ℃ and 1425 ℃ respectively. Compared with Fig. 3, it is not difficult to find that when the liquid phase rate in nodular cast iron is about 23% and 18% respectively, with the increase of pouring temperature, the solidification time of nodular cast iron increases, and the solidification time of riser neck also extends to 168.19 s and 182.27 s, so that the riser can feed nodular cast iron for a longer time.
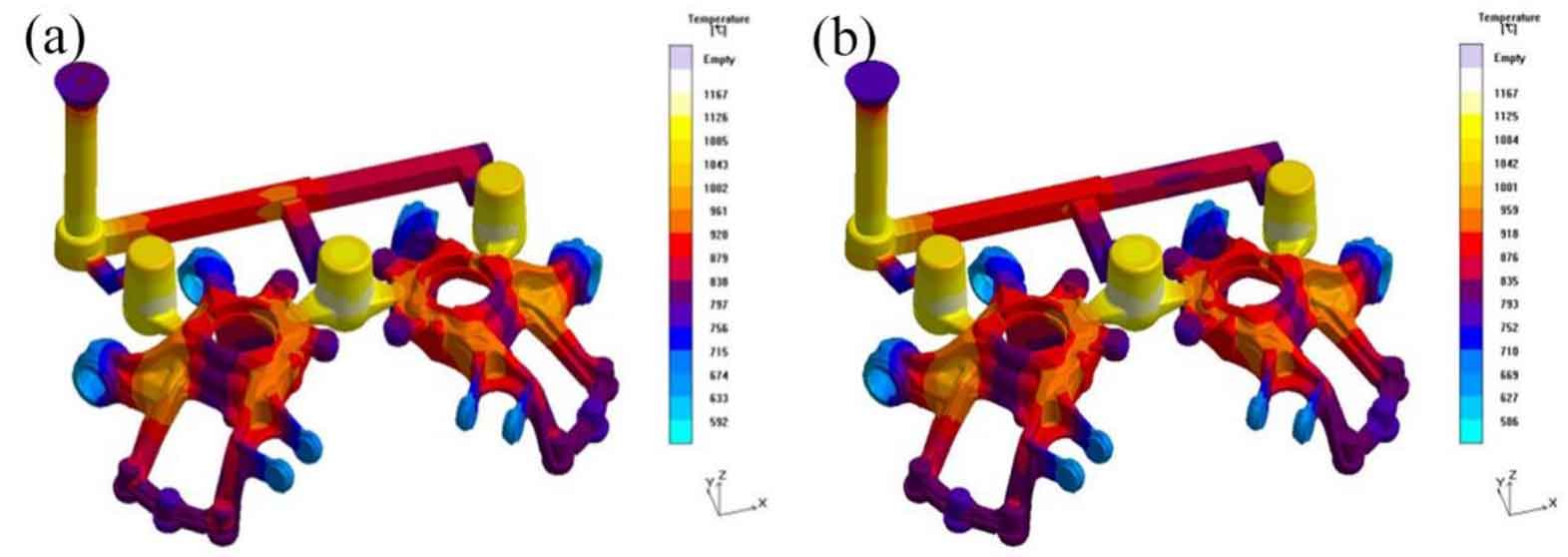
As can be seen from Fig. 4, the final setting time at 1400 ℃ is 316.33 s; The final setting time at 1425 ℃ is 340.81 s.
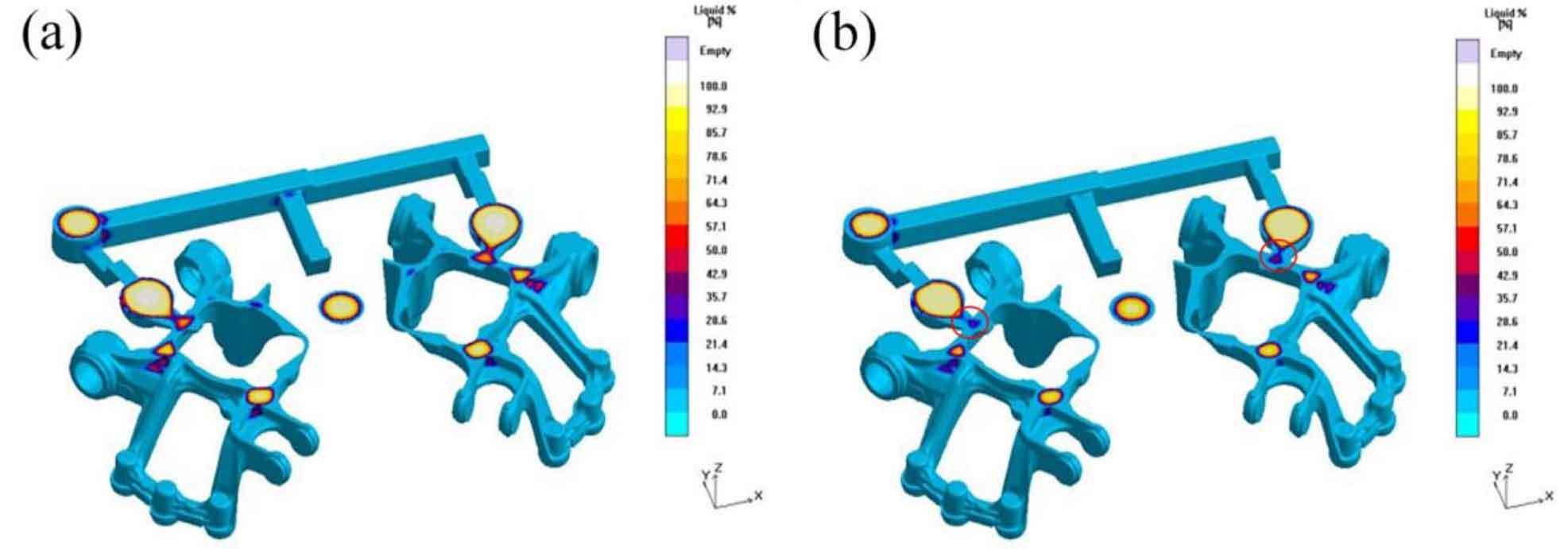
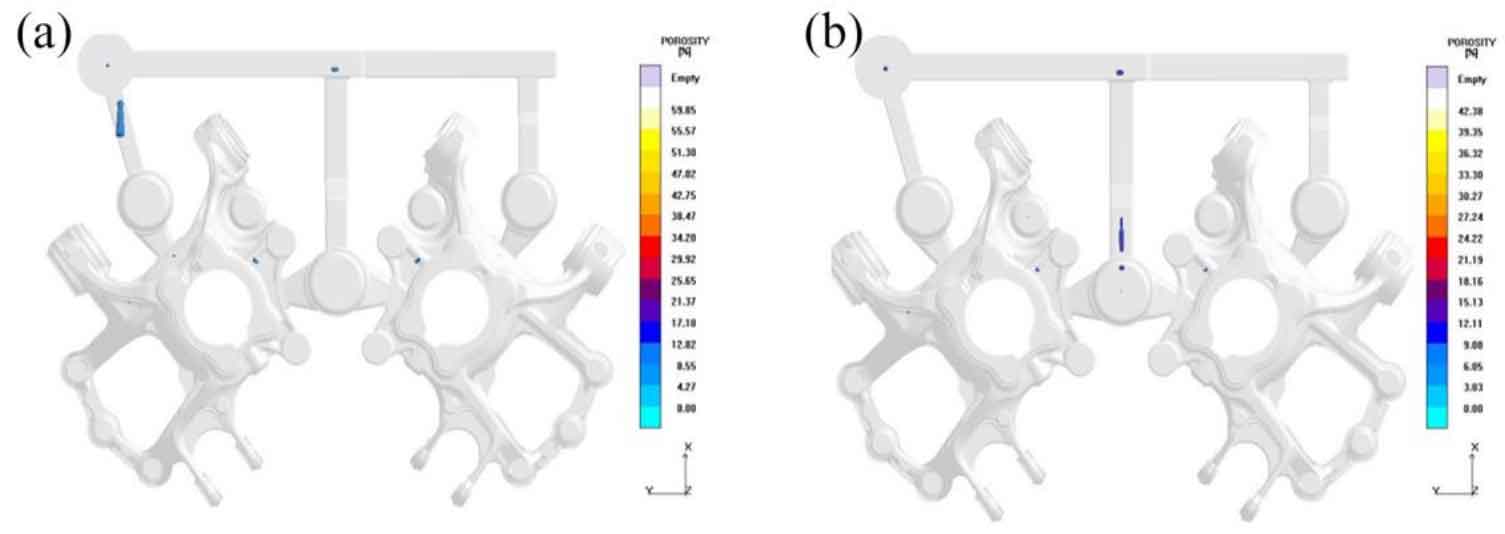
Figure 5 shows the simulated distribution of shrinkage porosity and shrinkage defects of nodular cast iron cast at 1400 ℃ and 1425 ℃. It can be seen that due to the extension of the solidification time of the feeding channel, the areas with insufficient feeding during pouring at 1370 ℃ are basically eliminated, and there are shrinkage porosity and shrinkage cavity defects on the inner side of the connection point between the sprue and the brake, and the defect positions in nodular cast iron are reduced to 5. With the increase of pouring temperature, the shrinkage volume of the same part decreases slightly. Therefore, according to the comparison of the three groups of simulation results, it shows that the higher pouring temperature is conducive to prolong the solidification time of the feeding channel, so that the riser can feed nodular cast iron for a longer time, so as to reduce the internal defects of nodular cast iron. Therefore, 1425 ℃ is selected as the best pouring temperature.