The vibration frequency is one of the key factors that affect the microstructure and properties of castings produced by the vibration lost foam casting technology. Therefore, cast pig iron and Q235 steel are used as raw materials, 75 ferrosilicon and fesimg8re3 alloy are used as master alloys, and the treatment temperature of molten iron is 1510 ° C. Nodular cast iron was prepared by changing the vibration frequency in the process of vibration lost foam casting. The vibration frequencies were 0, 35, 50 and 100Hz respectively. The effects of vibration frequency on graphite morphology, matrix structure and mechanical properties of nodular cast iron were studied.
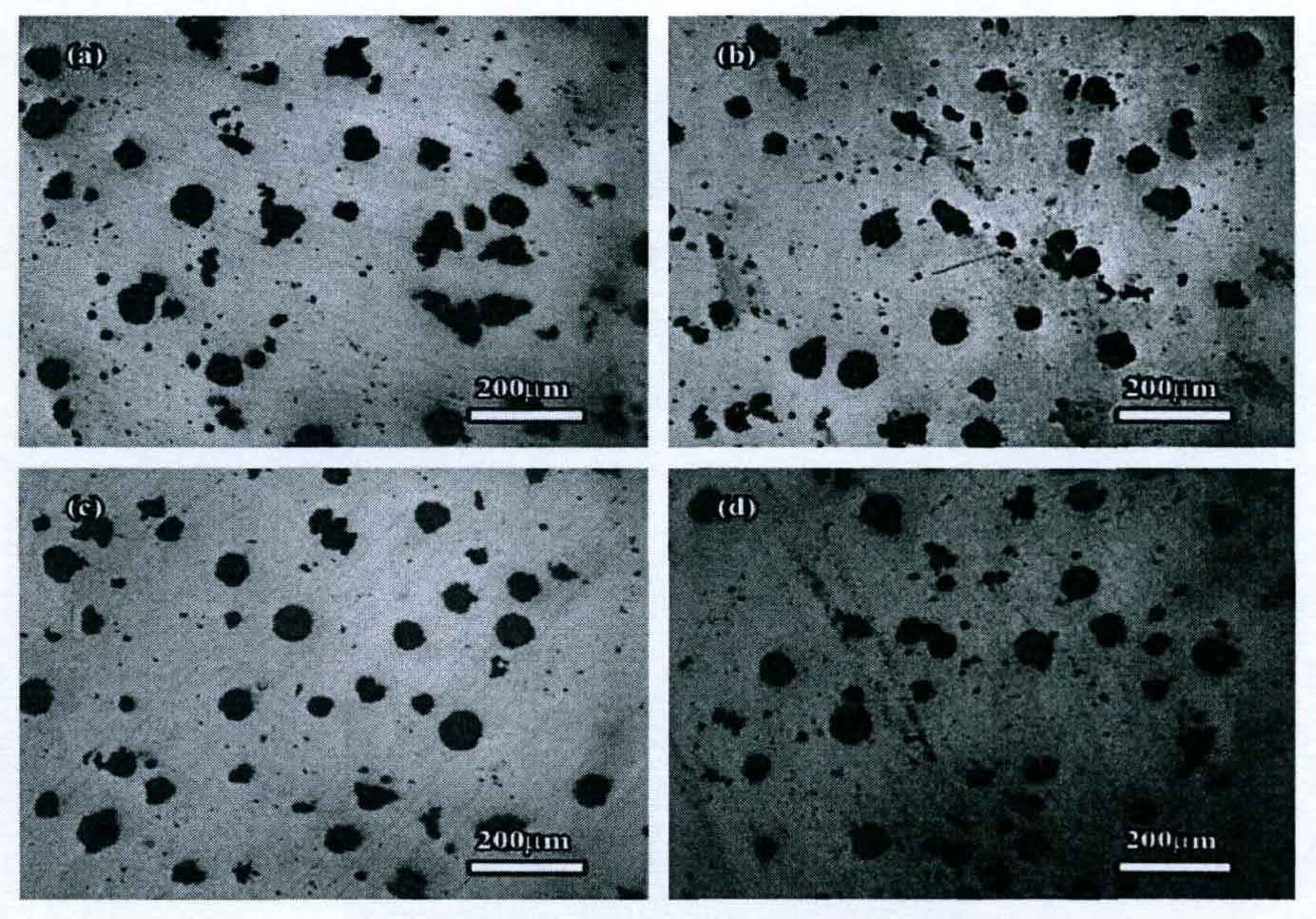
Figure 1 shows the graphite morphology of ductile iron in lost foam casting under the action of different vibration frequencies with an amplitude of 3mm. Figures 1 (a) – (d) show the graphite morphology of nodular cast iron prepared at vibration frequencies of 0, 35, 50 and 100Hz, respectively.
It can be seen from the figure that in the nodular cast iron without vibration, the number of graphite balls is small, the diameter of graphite balls is large, and the graphite morphology is poor. However, in the vibration lost foam casting ductile iron, the number of graphite balls is more and the diameter of graphite balls is smaller.
With the help of image analysis software, the graphite ball parameters of nodular graphite cast iron prepared under different vibration frequencies are statistically analyzed, and the analysis results are shown in the table.
| Vibration frequency | Number of graphite balls per square millimeter | Spheroidization rate |
| 0 | 77 | 0.83 |
| 35 | 84 | 0.87 |
| 50 | 91 | 0.89 |
| 100 | 107 | 0.85 |
It can be seen from the table that the number of graphite balls per unit area in the lost foam casting nodular cast iron without vibration is the least, and the number of graphite balls per unit area in the nodular cast iron prepared under the vibration frequency of 100Hz is the most. The spheroidization rate of nodular cast iron first increases and then decreases with the increase of vibration frequency. The spheroidization rate of graphite is the largest in the nodular cast iron prepared under the vibration frequency of 50Hz, that is, the distortion of graphite ball is the smallest, and the graphite morphology is the best. However, in the lost foam casting nodular cast iron without vibration, the spheroidization rate of graphite is low, the graphite morphology is poor, and there are more flocculent graphite.
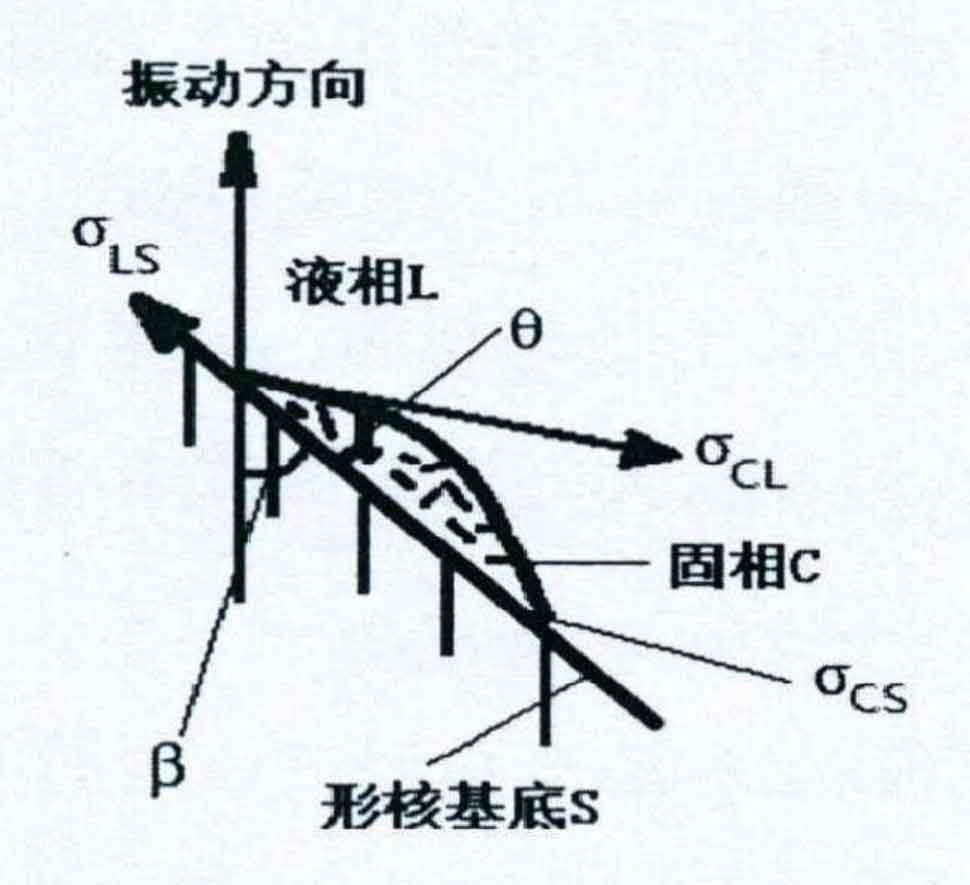
When nodularizing and inoculating nodular cast iron, a large number of non-metallic inclusions will be produced in the metal solution. The size of the primary inclusions is very small. In the subsequent pouring and solidification process, they will collide with each other, polymerize and become larger, float or sink, and become the nucleation core of graphite. The substances that can be used as the nucleation core of graphite include graphite, sulfide, carbide, nitride, oxide, intermetallic compound and gas, that is, graphite is formed by adhering to the interface of these nucleation substances. When vibration is applied during metal solidification, the introduction of periodic tensile pressure into the solidified metal will have an important impact on the metal solidification process. Its model is shown in Figure 2.
