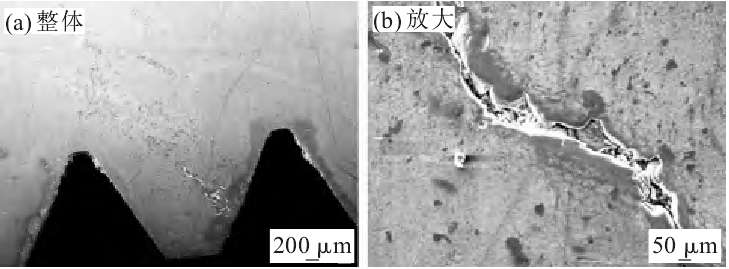
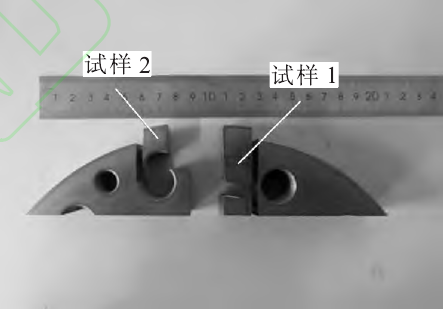
Cracks were found at the flange after machining, and the macro morphology of the cracks is shown in Fig. 1. After analysis, the location of crack source is indicated in Fig. 1. Samples are cut around the crack, and the sample numbers are sample 1 and 2. The sampling position is shown in Fig. 2.

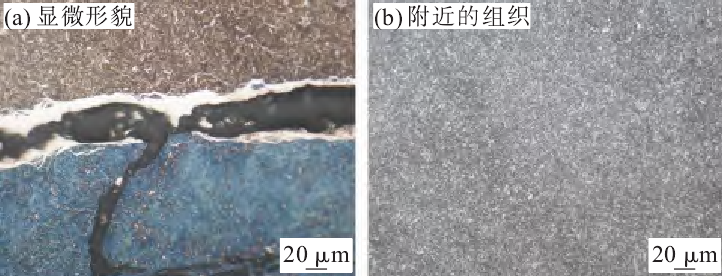
The chemical composition of sample 1 was detected by spectrd direct reading spectrometer. The results show that the content of C and S elements in sample 1 exceeds the requirements of GB / T 5216-2014. After polishing, the sample 1 was observed under the metallographic microscope. It was found that there were a lot of point and block inclusions in the material, as shown in Fig. 2. After corrosion, the metallographic structure of the crack and its vicinity was observed. The results show that there is no oxidation and decarburization in the crack, and there is a white bright layer on both sides of the crack produced by nitriding process, which is not produced by decarburization, as shown in Fig. 3 (a). The grain size near the crack is uniform without overburnt structure and grain boundary melting phenomenon, as shown in Fig. 3 (b).
The composition of point inclusion in sample 1 was analyzed by SEM, and the results are shown in Fig. 4. According to the result of composition analysis, the gray point inclusion is MNS, and the main component of white strip and block material is Fe3C.


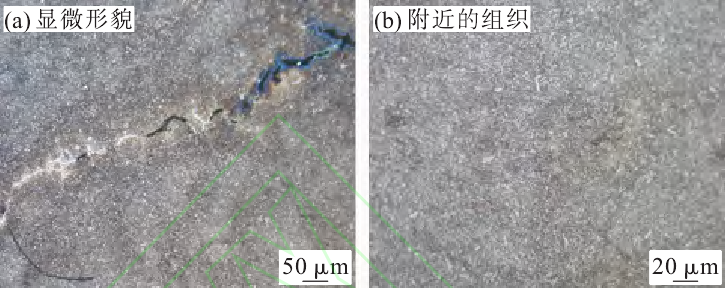
After polishing, the sample 2 was observed under the metallographic microscope, and a large number of point and block inclusions were found in the material, as shown in Fig. 5. After corrosion, the metallographic structure of the crack and its vicinity was observed. There was no oxidation or decarburization in the crack. There was a white bright layer produced by nitriding process on both sides of the crack, which was not produced by decarburization. The cracks were distributed intermittently in the form of teeth. The two ends of each intermittent crack were round and not sharp. They were transgranular cracks without decarburization, as shown in Fig. 6 (a). The metallographic structure near the crack is normal, as shown in Fig. The shrinkage porosity structure was found at the thread tooth of flange plate, and the morphology was deformed under the force. As shown in Fig. 7, the shrinkage porosity structure is the crack source.

The morphology of shrinkage porosity and inclusion structure of sample 2 is shown in Fig. 8. The sample 2 was re corroded with 10% sulfuric acid + 10% nitric acid solution. The problems of dendrite segregation shrinkage cavity, local carbide segregation and solidification liquid precipitation carbide were found under the metallographic microscope. As shown in Fig. 8, it is proved that the casting structure of the material has not been completely eliminated, and there are quality problems in the raw material.