A large amount of carbon in foam materials is the “arch criminal” of the carbon defect produced by EPC cast steel. Therefore, the selection of foam materials is an important factor affecting the quality of castings. The foam materials used for EPC in the market mainly include EPS (expandable polystyrene), PMMA (polymethyl methacrylate) and STMMA (methyl methacrylate and styrene copolymer resin), and the molecular structure of the three kinds of foams is shown.
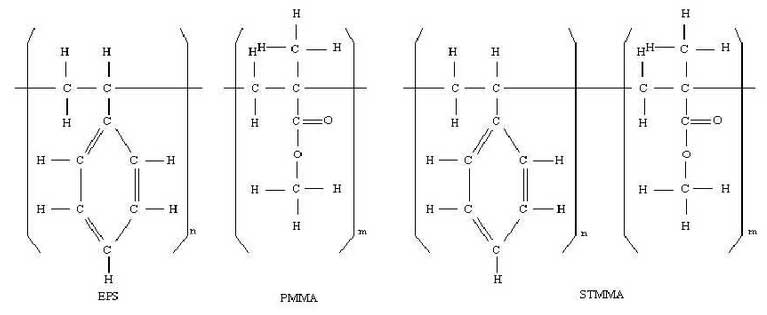
EPS is widely used in all kinds of EPC enterprises because of its convenient manufacture and low price. However, the carbon content of EPS is as high as 92%, and EPS is also widely used in EPC enterprises The decomposition process is a kind of disordered fracture type decomposition. A large amount of viscous liquid will be produced during the decomposition. These liquids will be in contact with the molten metal for a long time, which will crack the hydrocarbon bond in the benzene ring structure to generate carbon and hydrogen, which increases the chance of carbon being trapped by the liquid metal, resulting in the casting defects such as carburization and porosity Especially for the surface carburization of steel castings.
PMMA is an EPC foam material developed by DOW in 1986. Its molecular formula is C5O2H8, and its carbon content is only 60%. It can be seen from Fig. 2-6 that PMMA is mainly of straight chain structure, which can be decomposed more fully at high temperature casting. The products are mainly gas, and there are few liquid and solid products, which is conducive to eliminating carbon defects. However, the gas generation of PMMA during pyrolysis is large, which is easy to cause liquid metal reverse injection and porosity defects.
Stmma is a new kind of special material for lost foam pattern. It is a polymer composed of EPS and PMMA in different proportions, so it is also called copolymer. It has the advantages of both EPS and PMMA. When the ratio of EPS and PMMA is 3:7, the carbon content is 69.6%, and the carbon source of carbon defect is more than EPS It is a kind of “zipper” decomposition mode with many honeycomb structures inside, which increases the contact area between the material and air and accelerates the combustion of the material. Moreover, the molecular structure contains oxygen atoms. In the process of heating and combustion, oxygen atoms react with carbon to generate gas, so the residues are less.
This study is a low-carbon steel casting. In order to reduce the carbon defect, STMMA is used to simulate the two casting schemes and verify the production. When studying the influence of carbon defect on the quality of steel castings, two foam materials, EPS and STMMA, are selected for comparative tests.
