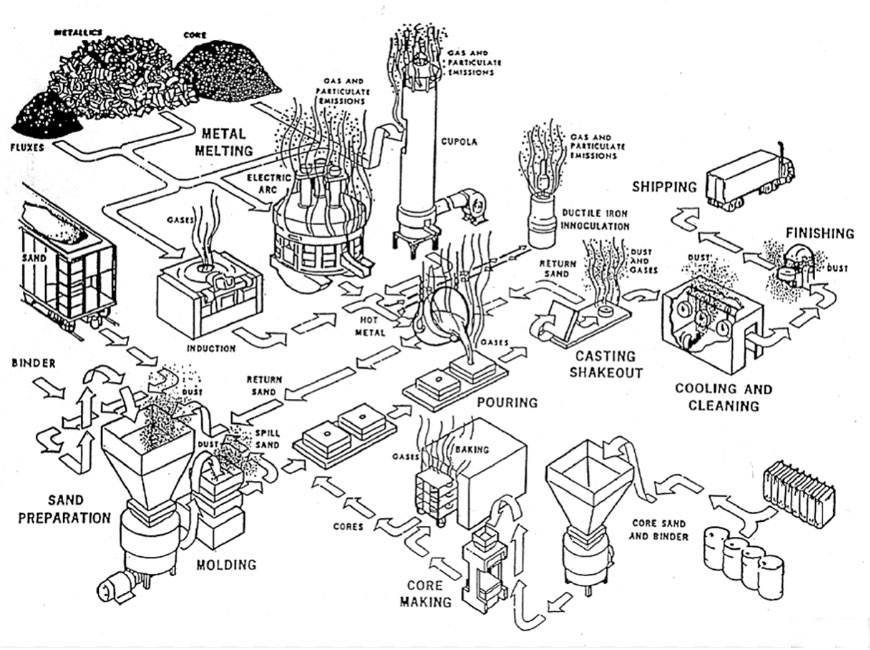
Sand casting is a fascinating and intricate process that transforms raw materials into complex and functional parts. This manufacturing technique has been used for centuries and remains a cornerstone of modern engineering and industrial production. Let’s delve into the step-by-step process of sand casting, where the transformation from grain to glory takes place:
1. Pattern Making:
- The process begins with the creation of a pattern, which is a replica of the final part in the desired shape and size.
- Patterns can be made from wood, plastic, or metal, depending on the complexity and material of the final casting.
2. Mold Preparation:
- A mold cavity is prepared using the pattern. To make the mold, sand is mixed with a binder, such as clay or resin, to give it cohesiveness.
- The mixture is packed around the pattern, creating the mold cavity.
3. Mold Assembly:
- More complex parts may require multiple mold sections. These sections are carefully assembled, and cores (sand shapes used for creating internal features) may also be inserted.
4. Pattern Removal:
- The pattern is then removed, leaving behind a precise impression of the part’s shape in the mold cavity.
5. Metal Melting:
- The chosen metal or alloy is melted in a furnace at temperatures depending on the material’s melting point.
6. Pouring:
- The molten metal is poured into the mold cavity through a sprue, which is a channel designed to allow the metal to flow smoothly and uniformly.
7. Solidification:
- The molten metal cools and solidifies within the mold, taking the shape of the cavity and creating the final casting.
8. Cooling and Solidification:
- After the metal has solidified, the mold is allowed to cool before the casting is removed.
9. Casting Removal:
- The mold is opened, and the casting is carefully removed from the mold cavity. In some cases, sand cores may also be removed at this stage.
10. Finishing:
- The casting may undergo finishing processes such as trimming excess material, machining, grinding, or heat treatment to achieve the desired dimensions and surface finish.
11. Inspection:
- The final casting is thoroughly inspected for any defects or imperfections.
12. Final Product:
- The completed sand casting part is ready for use in its intended application, showcasing the successful transformation from grains of sand to a glorious and functional component.
The sand casting process is highly versatile and widely used in a variety of industries, offering the ability to create parts of different sizes, shapes, and complexities. It allows for cost-effective production of both prototypes and large-scale production runs, making it a fundamental technique in the world of engineering and manufacturing.
