The most common brake drum material in the domestic market is basically ordinary gray cast iron. Its advantages are mainly reflected in low cost (20 ~ 40% lower than steel), good casting performance, high hardness, thermal conductivity and good shock absorption and wear resistance. In the earlier period, the gray cast iron used was mainly HT150 and HT200. These materials had poor strength and were easy to wear and crack during use, so their service life was low. Subsequently, many countries at home and abroad used HT250 to produce brake drums, and its wear resistance was significantly higher than HT200. However, there are still some defects in its thermal conductivity, and the thermal fatigue failure is more serious. In recent years, with the increasing consumption of gray cast iron parts in the automotive industry, the research on gray cast iron has been further deepened, such as using pretreatment process to improve the nucleation conditions of graphite crystallization and precipitation, reduce the fluctuation range of mechanical property parameters of gray cast iron, control the primary austenite and enhance the role of gray cast iron. The mechanical properties of gray cast iron are affected by a series of factors, such as the shape, size, quantity and distribution of graphite, the type of matrix composition phase, the chemical composition of base metal, casting formation process and treatment process, etc.
(1) Effect of graphite on properties of gray cast iron
Gray cast iron contains graphite with low strength and hardness. The existence of graphite destroys the continuity and integrity of its microstructure, and leads to some unique changes in its mechanical properties. Griffith believes that the length (a) of micro crack in material and the normal stress value of brittle fracture( σ ) and considering the unique local plastic deformation energy of gray cast iron and the influence of graphite volume, it is proposed that:
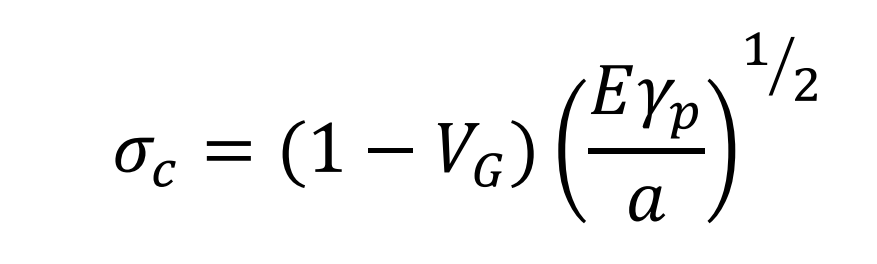
Where e is the modulus of elasticity; is the volume of graphite; plastic deformation energy of fracture surface; α Is the average length of graphite sheet. This formula shows that the increase of graphite volume and average length of graphite sheet or the decrease of plastic deformation energy will reduce the fracture strength of the material. Therefore, the shape, size and quantity of graphite in gray cast iron affect the mechanical properties of gray cast iron. Under the actual solidification conditions, gray cast iron forms a large number of eutectic clusters due to eutectic reaction, while the continuous graphite skeleton precipitates in the eutectic clusters. Therefore, the size, morphology and distribution of graphite depend on the carbon content of gray cast iron, the number of eutectic clusters and the solidification conditions of castings. In the mold with slow cooling speed, such as sand mold, when the casting wall is thick, the number of eutectic clusters is small and the size is large to form coarser graphite. On the contrary, small flake graphite is formed. The size of graphite is also related to the carbon content. When the carbon content is high, the formed graphite is coarser. In the world, the graphite forms in gray cast iron are generally divided into five types: A-type graphite with uniform distribution, chrysanthemum shaped B-type graphite (B-type graphite is actually composed of surrounding A-type graphite and D-type graphite in the central area), C-type primary graphite directly precipitated from molten iron under hypereutectic composition, D-type supercooled graphite formed between primary austenite dendrites at high undercooling, and D-type supercooled graphite at low undercooling and low carbon content, E-type undercooled graphite precipitated between secondary dendrites, and types A, B, D and e exist in hypoeutectic cast iron. The difference of graphite type and distribution leads to significant changes in material properties; Therefore, optimizing the type and distribution of graphite is a shortcut to improve the properties of gray cast iron.
The existence of graphite base in gray cast iron brings many excellent properties to gray cast iron, such as shock absorption, thermal conductivity and so on. Due to the different structure density between graphite and matrix, when gray cast iron vibrates, the vibration is equivalent to alternating transmission in different media. The graphite in gray cast iron buffers the vibration, prevents the transmission of vibration kinetic energy between grains and turns it into heat energy, reducing the transmission of vibration energy; Therefore, gray cast iron has excellent shock absorption and is an excellent material for manufacturing brake drum, metal cutting machine tool, engine cylinder block and other parts. According to the data, the thermal conductivity of graphite crystal is higher than that of base metal. Therefore, the high volume fraction of graphite in cast iron leads to the high thermal conductivity. In terms of thermal conductivity, high carbon has a favorable effect on the thermal fatigue of gray cast iron. Studies have shown that with the increase of carbon content in cast iron, the content of graphite increases and the thermal conductivity becomes better. Graphite has a soft texture and can act as a solid lubricant in the process of dry friction to reduce the wear of materials.
(2) Effect of matrix structure on properties of gray cast iron
In gray cast iron, the matrix structure is mainly composed of pearlite and ferrite. Lamellar pearlite is composed of lamellar cementite and ferrite. Pearlite can be divided into pearlite, sorbite and troostite according to the spacing between pearlite layers. The smaller the spacing between layers, the better the mechanical properties. Ferrite is the melting of carbon α- The solid solution formed by iron has low strength( σ = 170 ~ 250Mpa), and the hardness is about HB 50 ~ 80. A small amount of phosphorus eutectic often appears in gray cast iron. Phosphorus eutectic is a brittle hard phase in cast iron. When it exists in the matrix, it can improve the wear resistance; When the phosphorus eutectic falls off and forms abrasive particles, it will grind the friction surface, which will affect the wear resistance of parts. Phosphorus containing cast iron is often used to manufacture thin-wall wear reducing castings.
(3) Effect of chemical composition on properties of gray cast iron
Because graphite has a great influence on the mechanical properties of gray cast iron, the study of the influence of chemical composition on the structure of gray cast iron mainly lies in the study of the influence of chemical elements on the graphitization process, and then the influence of trace elements on the formation of pearlite. Through a large number of studies, it is found that elements such as silicon, nickel and copper can improve the carbon content in molten iron
The activity of promotes the formation of graphitization in gray cast iron, while manganese, molybdenum, chromium, titanium and other elements will reduce the eutectic transformation temperature, which means that the transformation from carbon to graphite in gray cast iron is reduced; Due to its own chemical composition and cooling rate, gray cast iron will change the cementite content after solidification, which will affect the pearlite content. Among them, silicon, manganese, nickel, chromium and other elements are easy to reduce the pearlite content, while titanium, niobium, vanadium and other elements will increase the pearlite content. It can be seen from the above that the domestic research on brake drum materials mainly focuses on the modification of gray cast iron materials, and the main measures include carbon content, graphite morphology and alloy elements.
