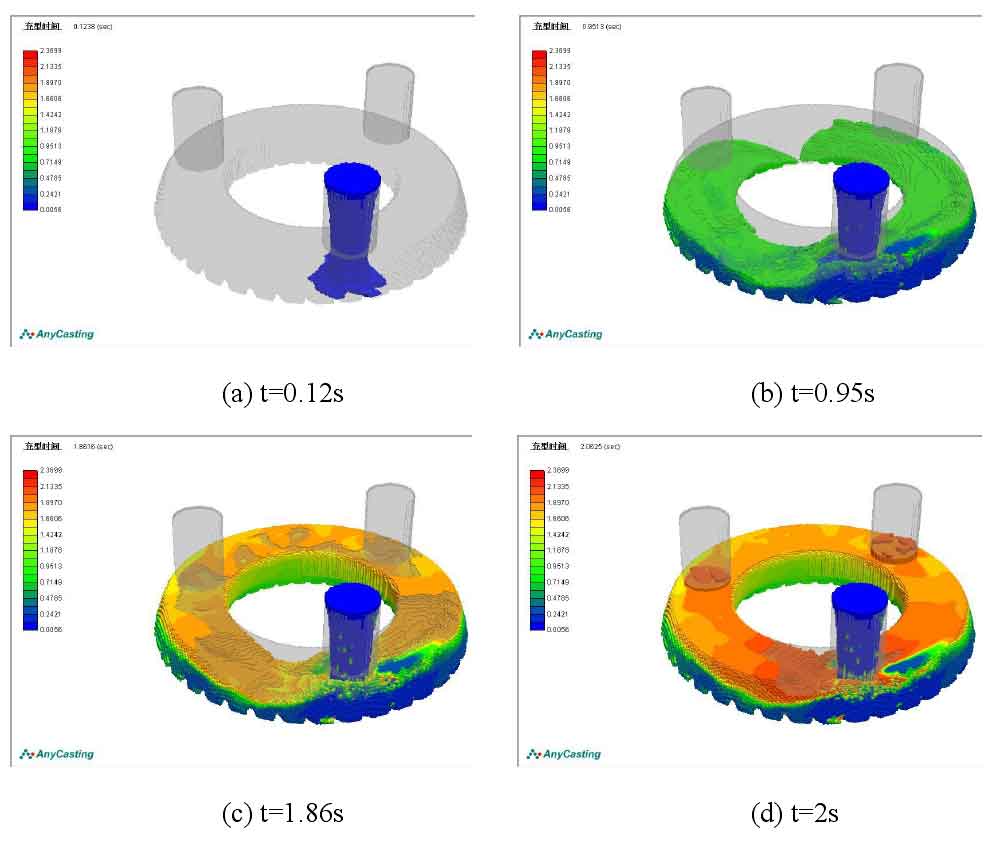
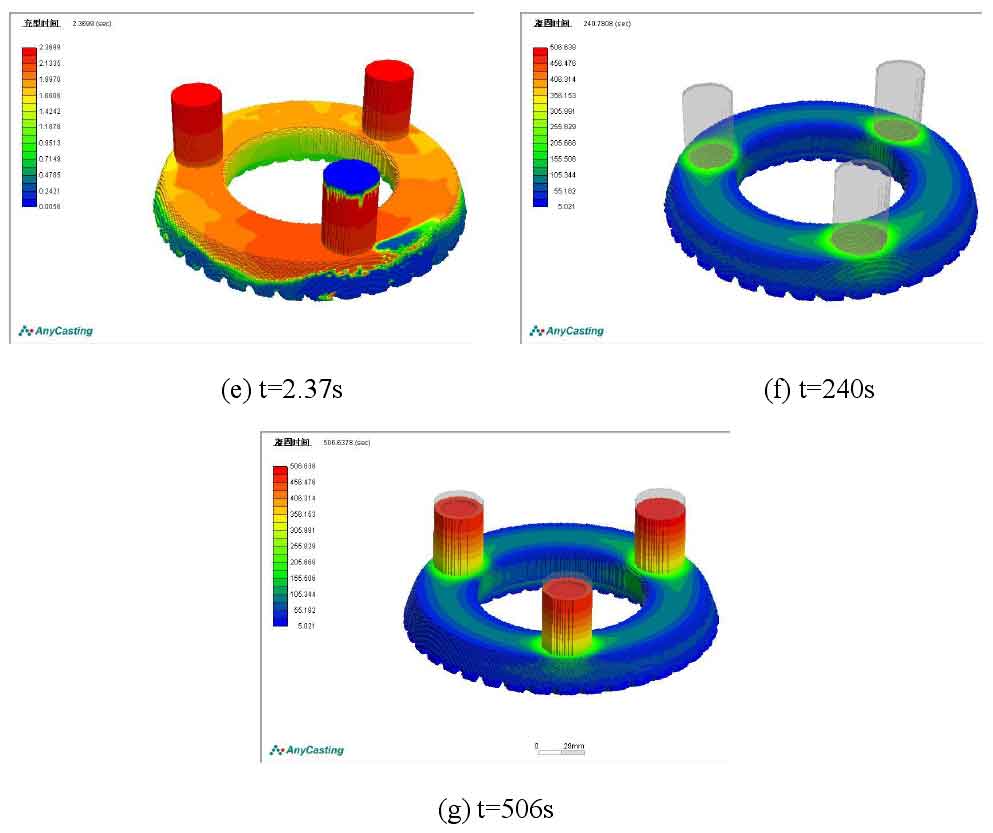
The figure shows the numerical simulation diagram of filling and solidification process of gear blank casting with common gating scheme of gating and riser.
When the pouring time t = 0.12s, the liquid metal has begun to contact the inner wall of the casting cavity through the riser. Since there are no slow flow measures, the impact of the liquid metal on the sand mold cavity is very large, which is easy to cause casting defects such as sand falling and air entrainment; Then, the liquid metal flows in a circular direction along the two channels. When t = 0.95s, the two streams of liquid metal converge. At this time, the mold cavity near the gate has been basically filled with liquid metal; After the two streams of molten metal meet, they begin to flow in reverse and continue to fill the upper end of the cavity. The height of molten metal in different areas of the cavity is inconsistent, but they all rise continuously; When t = 1.86s, there is still residual air pressure in the cavity at the far end of the gate, but it has been basically filled, while the cavities on both sides of the gate have not been filled completely; When the pouring time reaches 2S, the mold cavity at the far end of the gate is completely filled, the liquid metal has begun to flow into the two far end risers, and some areas of the mold cavity near the gate are still not completely filled; When t = 2.37s, the three risers are filled with liquid metal, and the filling process of gear blank casting is completed. When t = 240s, part of the casting solidifies completely; When t = 506s, the riser is solidified.
It can be seen from figures (f) and (g) that the riser well guides the sequential solidification process of the casting, and the feeding effect of the riser is good.