Spheroidal graphite cast iron (SG iron), also known as ductile iron, is widely recognized for its superior mechanical properties, such as high strength, ductility, and wear resistance. These characteristics make it an ideal material for high-precision engineering applications. However, optimizing the machinability of spheroidal graphite cast iron is crucial to fully harness its potential in precision engineering. This article delves into the factors affecting the machinability of spheroidal graphite cast iron, strategies for optimization, and the future of high-precision engineering applications using this versatile material. Comprehensive tables and lists are included for detailed insights.
Introduction
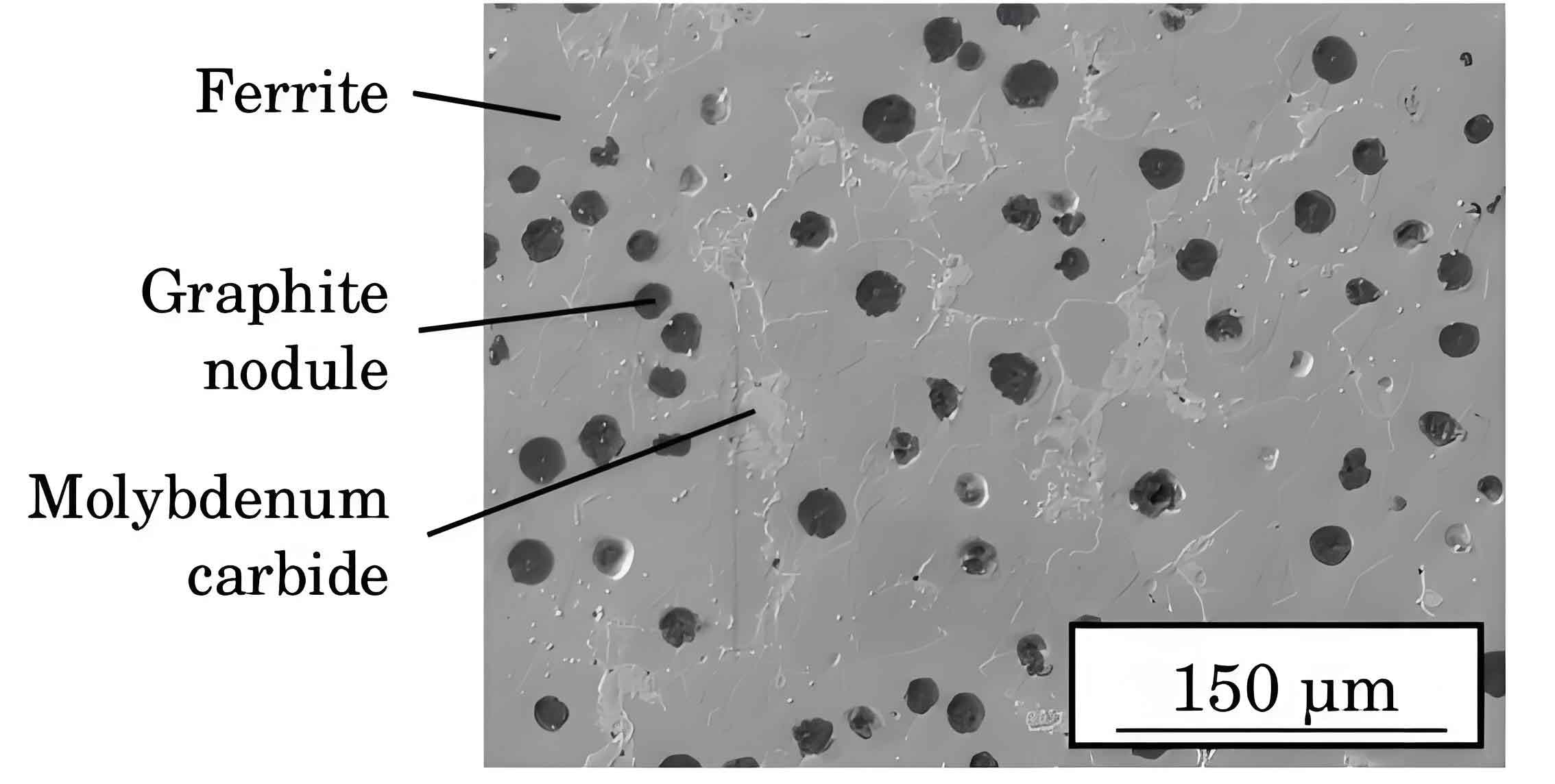
The machinability of a material refers to the ease with which it can be cut, shaped, and finished using machining processes. For spheroidal graphite cast iron, optimizing machinability is essential to achieve the precise tolerances and high surface finishes required in high-precision engineering applications. Factors such as microstructure, hardness, tool material, and cutting conditions play a significant role in determining the machinability of spheroidal graphite cast iron.
Factors Affecting Machinability of Spheroidal Graphite Cast Iron
- Microstructure:
- The presence of spheroidal graphite nodules within the iron matrix enhances machinability by reducing tool wear and improving chip formation.
- Hardness:
- Optimal hardness levels are crucial; excessive hardness can lead to rapid tool wear, while too low hardness can result in poor surface finish.
- Tool Material:
- The selection of appropriate tool materials, such as carbide or ceramic, is vital for efficient machining.
- Cutting Conditions:
- Parameters such as cutting speed, feed rate, and depth of cut significantly influence the machining performance.
- Coolants and Lubricants:
- The use of appropriate coolants and lubricants can reduce friction, heat generation, and tool wear, enhancing machinability.
Table: Factors Affecting Machinability of Spheroidal Graphite Cast Iron
| Factor | Description | Impact on Machinability |
|---|---|---|
| Microstructure | Presence of spheroidal graphite nodules | Reduces tool wear, improves chip formation |
| Hardness | Optimal levels are crucial | Excessive hardness leads to tool wear; low hardness results in poor finish |
| Tool Material | Selection of appropriate tool materials | Efficient machining with minimal tool wear |
| Cutting Conditions | Parameters like cutting speed, feed rate, and depth of cut | Influences machining performance |
| Coolants and Lubricants | Use of coolants and lubricants | Reduces friction, heat generation, and tool wear |
Strategies for Optimizing Machinability
- Control of Microstructure:
- Graphite Nodule Count and Distribution: Ensuring uniform distribution and optimal count of graphite nodules can enhance machinability.
- Matrix Structure: A predominantly ferritic or pearlitic matrix can be tailored to balance machinability and mechanical properties.
- Heat Treatment:
- Applying appropriate heat treatments, such as annealing or normalizing, can achieve the desired hardness and microstructure.
- Tool Selection:
- Carbide Tools: Offer high wear resistance and longer tool life.
- Ceramic Tools: Suitable for high-speed machining with excellent thermal stability.
- Coated Tools: Applying coatings like TiN or AlTiN can further improve tool life and performance.
- Optimizing Cutting Parameters:
- Cutting Speed: Selecting the appropriate cutting speed to balance productivity and tool life.
- Feed Rate: Adjusting feed rate to ensure efficient chip removal without compromising surface finish.
- Depth of Cut: Maintaining an optimal depth of cut to minimize tool load and wear.
- Use of Advanced Coolants and Lubricants:
- Implementing advanced cooling and lubrication techniques, such as minimum quantity lubrication (MQL) or cryogenic cooling, can significantly improve machinability.
List: Key Strategies for Optimizing Machinability
- Control of Microstructure:
- Graphite nodule count and distribution
- Matrix structure (ferritic or pearlitic)
- Heat Treatment:
- Annealing
- Normalizing
- Tool Selection:
- Carbide tools
- Ceramic tools
- Coated tools (TiN, AlTiN)
- Optimizing Cutting Parameters:
- Cutting speed
- Feed rate
- Depth of cut
- Use of Advanced Coolants and Lubricants:
- Minimum quantity lubrication (MQL)
- Cryogenic cooling
Future Trends in High-Precision Engineering with Spheroidal Graphite Cast Iron
- Advanced Material Engineering:
- Development of new grades of spheroidal graphite cast iron with enhanced properties tailored for specific machining applications.
- Smart Machining Techniques:
- Integration of IoT and AI for real-time monitoring and control of machining processes to optimize performance and quality.
- Sustainable Machining Practices:
- Focus on eco-friendly machining processes and materials to reduce environmental impact.
- Hybrid Manufacturing Processes:
- Combining traditional machining with additive manufacturing techniques to achieve complex geometries and high precision.
- Collaborative Research and Development:
- Partnerships between industry and academia to drive innovation in machining technologies and materials science.
Table: Future Trends in High-Precision Engineering with Spheroidal Graphite Cast Iron
| Trend | Description | Expected Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Advanced Material Engineering | Development of new grades with enhanced properties | Tailored properties for specific applications |
| Smart Machining Techniques | Integration of IoT and AI for real-time process monitoring | Optimized performance, improved quality |
| Sustainable Machining Practices | Focus on eco-friendly processes and materials | Reduced environmental impact |
| Hybrid Manufacturing Processes | Combining traditional machining with additive manufacturing | Complex geometries, high precision |
| Collaborative R&D | Partnerships between industry and academia | Driving innovation in machining technologies |
Conclusion
Optimizing the machinability of spheroidal graphite cast iron is essential for its successful application in high-precision engineering. By understanding and controlling the factors that influence machinability, such as microstructure, hardness, tool materials, cutting conditions, and cooling techniques, manufacturers can achieve superior performance and quality in their machining operations. The future of spheroidal graphite cast iron in high-precision engineering looks promising, with advancements in material science, smart machining techniques, and sustainable practices paving the way for continued innovation and efficiency. As these trends unfold, spheroidal graphite cast iron will remain a cornerstone material in the quest for precision and reliability in engineering applications.
