The cylinder head structure of automotive engines is complex and generally adoptsCast iron or aluminum alloy material, as shown in Figure 1Show. The internal cavity structure of the cylinder block is complex, locally thick and prone to deformationShrink. The cylinder head is installed on top of the cylinder block and sealed from the topThe cylinder forms the combustion chamber. It often ignites with high temperature and high pressureGas phase contact, therefore subjected to significant thermal and mechanical loadsLoad. sand casting Main waste leakage and sand holes, manufacturing process recoveryThere are many miscellaneous parameters and the process is variable. The production process of castings is relatively complexThere are many, and each process has a wide variety of paper-based process dataRecord table, sand casting scattered at different workstations, data queryStatistics and analysis are time-consuming, with an annual production of over 200000 for two types of castingsThe unqualified rate of the product exceeds 5%, and the quality fluctuates greatly.
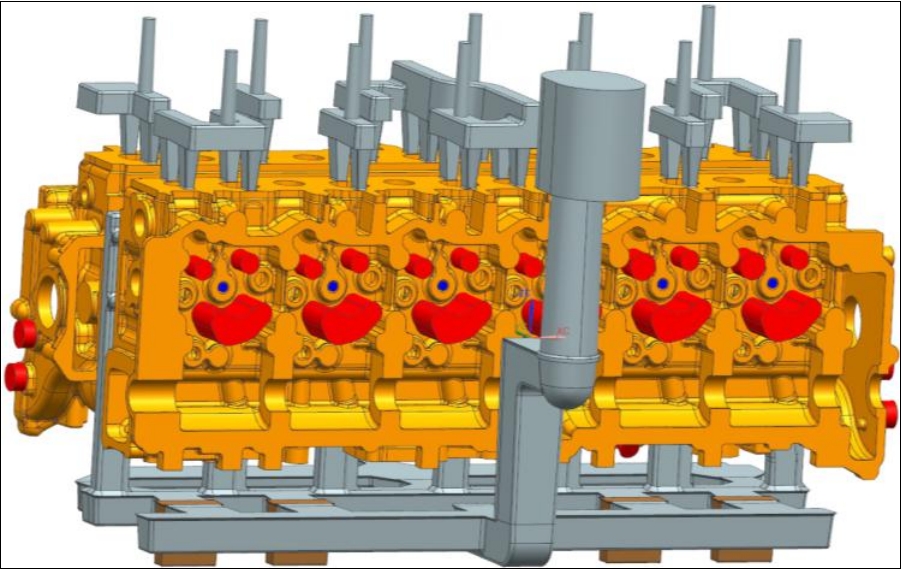
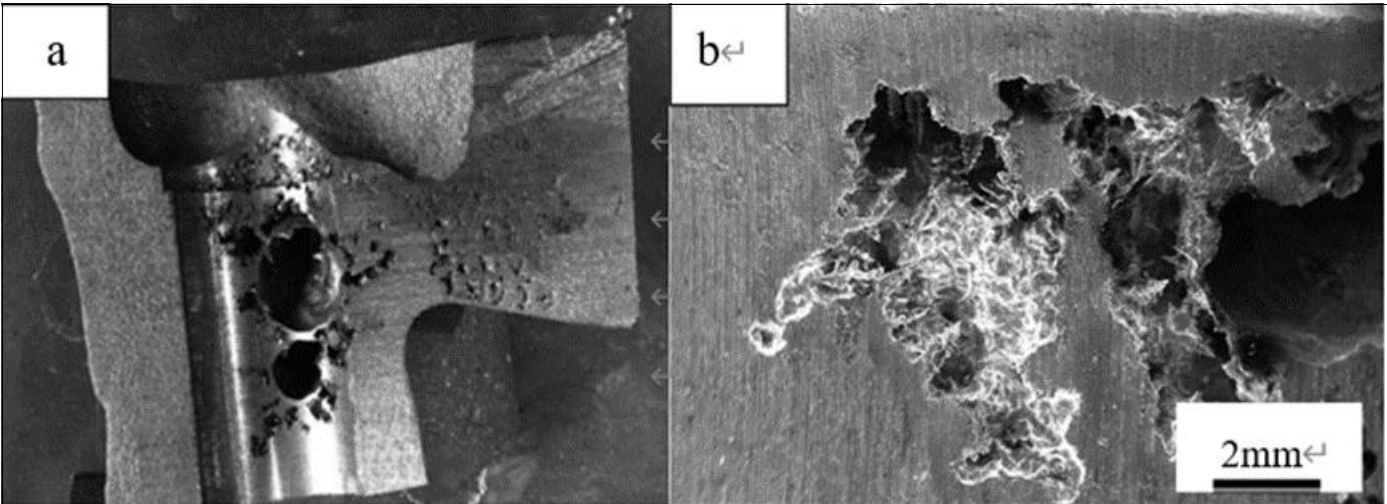
At present, the production of automotive cylinder blocks and cylinder heads in China mainly adopts green sand, resin self hardening sand, and triethylamine cold core forming technology.sand casting After solidification of castingsThe concentration of gas solutes in the liquid phase is highly concentrated, and when contraction occurs at the hot junction, sand casting vacuum pores are formed, which contribute to the precipitation of gasThis creates a strong channel, which in turn hinders the filling and contraction of the metal liquid, exacerbating the formation of shrinkage defects. The common defects of the cylinder head are shown in the figure.
By using computer numerical simulation technology to simulate the investment casting process, it is possible to understand the casting solidification process in advance and predict the casting processThe defects generated during the manufacturing process can be determined through an ideal process plan before actual production,sand casting to avoid technical risks and improve product quality.The Huazhu CAE/InteCAST software system (referred to as Huazhu CAE system) of Huazhong University of Science and Technology is a powerful and widely used casting system in ChinaOne of the process analysis software, it has reached a quantitative level in predicting shrinkage and porosity defects. Using Huazhu CAE software to generateTaking the process of engine cylinder head castings as an example, this paper introduces the use of CAE simulation software to study the key process parameters of sand casting – pouring temperature and casting moldThe effect of temperature on shrinkage defects.
The casting material is vermicular graphite cast iron, model RU450, and the molding sand is used for wet mold sand castingSand, recycled sand+bentonite+coal powder and other additives. The sand core is mainly made of cold box technology, sand casting silica sandOr recycled sand+cold core resin. As shown in the table, the main process parameters include pouring temperature and castingThe pouring temperature and mold temperature are selected as the main influencing factors, sand casting such as mold temperature and filling timeSu, conduct simulation experiments.
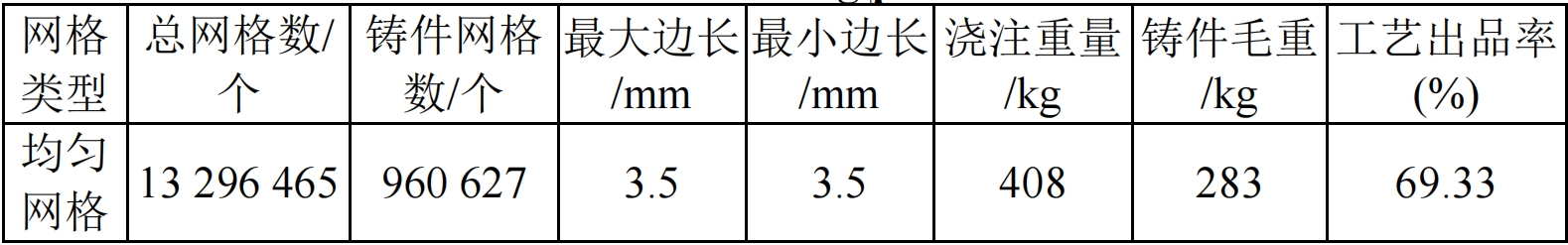
The numerical simulation software used is the Huazhu CAE system, which mainly utilizes its gravity compensation function to predict the shape of shrinkage cavities and porosity during the solidification processCheng.sand casting In the pre-processing stage, mesh generation is performed on three-dimensional models such as castings and pouring systems.
Using Huazhu CAE software to simulate the pure solidification process of the cylinder head, the simulation results are shown in the figure. Due to the use of the flat assembly and vertical pouring processThe solidification of the cylinder head is carried out in sequence from the bottom to the top,sand casting in conjunction with the bottom injection and top rising system.
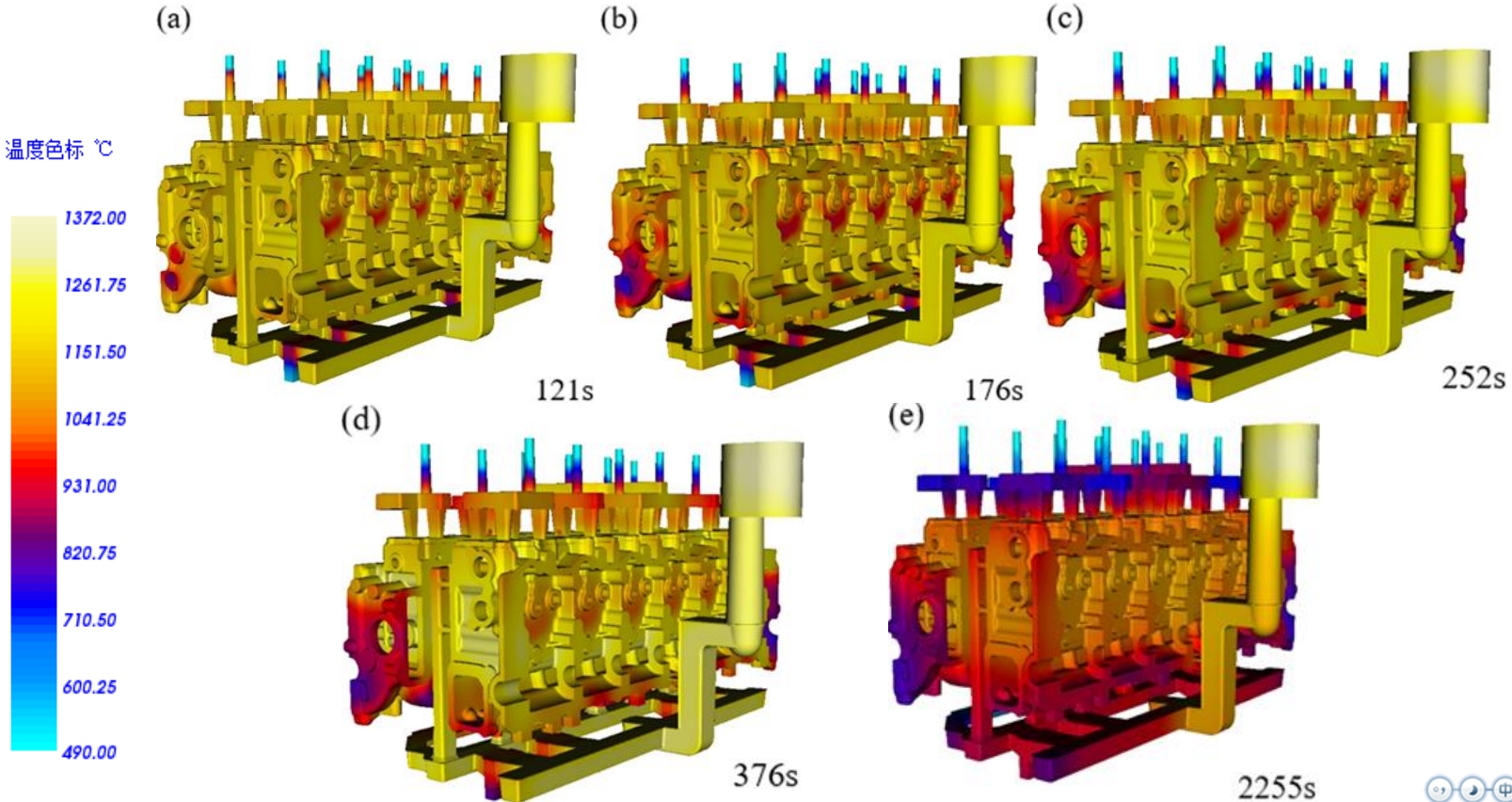
Within the temperature range of the experiment (pouring temperature 1360-1400 ℃, mold temperature 20-40 ℃), sand casting it can be seen from the figure that the internal heat of the cylinder headThere are different quantities of shrinkage and looseness at the node position.
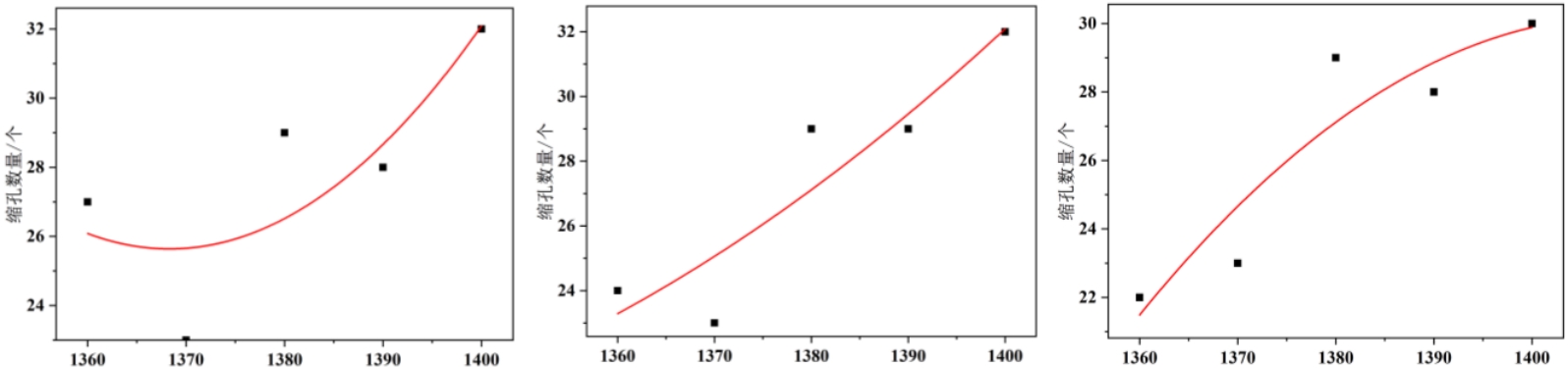
The number of shrinkage defects at different pouring temperatures is shown in the figure. When the casting temperature of the cylinder head is 20 ℃,sand casting the number of shrinkage defects increases with the increase of pouring temperatureThe quantity decreases first and then increases. When the pouring temperature is 1370 ℃, the minimum number of shrinkage cavities is 22. When the casting temperature is 30 ℃ and 40 ℃, as the pouring temperature increasesAs the pouring temperature increases, the number of shrinkage pores increases. sand casting When the pouring temperature is 1360 ℃, the minimum number of shrinkage pores is 24 and 22, respectively.
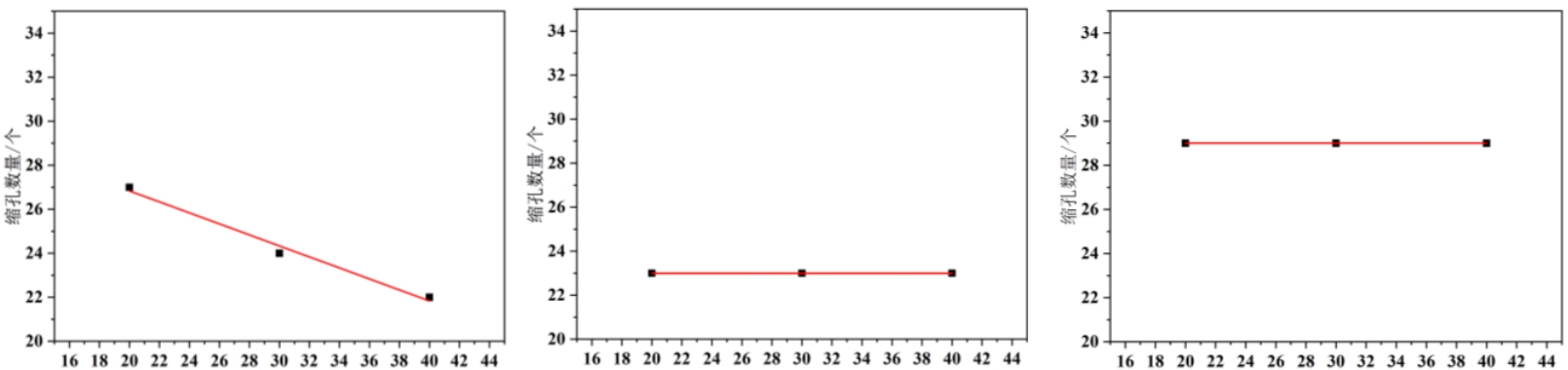
The number of shrinkage defects at different casting temperatures is shown in the figure. When the pouring temperature is between 1370-1400 ℃, sand casting the number of shrinkage defects affects the casting temperatureNot sensitive within the range of 20~40 ℃.
It is easy to see from the figure that there is an approximate linear relationship between the number of shrinkage holes and the pouring temperature, as well as the mold temperature. The number of shrinkage holes and the pouring temperature can be calculatedThe linear correlation coefficient r between temperature and mold temperature.
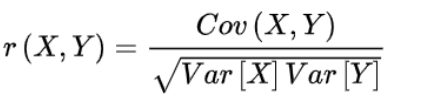
When the casting temperature is 20 ℃, the correlation coefficient r1 between the number of shrinkage holes and the pouring temperature is 0.725 1; sand casting When the casting temperature is 30 ℃, the number of shrinkage pores andThe correlation coefficient r2 of pouring temperature is 0.919 9; When the casting temperature is 40 ℃, the correlation coefficient r3 between the number of shrinkage cavities and the pouring temperature is 0.910 5;sand casting PouringWhen the temperature is 1360 ℃, the correlation coefficient r4 between the number of shrinkage cavities and the mold temperature is -0.993 4; When the pouring temperature is 1370 ℃,sand casting the number of shrinkage poresIf the variance is 0, it is considered uncorrelated; When the pouring temperature is 1380 ℃, the variance of the number of shrinkage pores is 0, which is considered unrelated; Pouring temperature is 1At 390 ℃, the correlation coefficient r5 between the number of shrinkage cavities and the mold temperature is considered to be 0, indicating no correlation; When the pouring temperature is 1400 ℃, sand casting the number of shrinkage cavities and the casting moldThe correlation coefficient of temperature r6=-0.866.In summary, it can be seen that the effect of pouring temperature on the number of shrinkage pores is more significant when the mold temperature is between 20~40 ℃ and the pouring temperature is between 1360~1400 ℃The casting temperature is more pronounced, indicating that the number of shrinkage pores is more sensitive to the pouring temperature.
Epilogue
(1) The cylinder head uses vermicular graphite cast iron Ru450, which has a complex internal cavity structure and is locally thick and prone to shrinkage,sand casting resulting in shrinkage holes and defects at the thick internal wallsSink.When the temperature of the cylinder head mold is 20 ℃, as the pouring temperature increases, the number of shrinkage holes first decreases and then increases, and the pouring temperature is 1370 ℃When the casting temperature is 30 ℃ and 40 ℃, the minimum number of shrinkage holes is 22. As the pouring temperature increases, the number of shrinkage holes increasesWhen the temperature is 1360 ℃, the minimum number of shrinkage pores is 24 and 22, respectively.When the pouring temperature is between 1370-1400 ℃,sand casting the number of shrinkage pores is not sensitive to the casting temperature between 20-40 ℃.When the casting temperature is between 20~40 ℃ and the pouring temperature is between 1360~1400 ℃,sand casting the effect of pouring temperature on the number of shrinkage pores is more apparent than that of casting temperatureThe number of shrinkage holes is more sensitive to the pouring temperature.
