New energy vehicles are regarded as key projects to alleviate energy consumption and environmental problems, and become a key development goal of strategic emerging industries. The front cover of the motor housing (see Figure 1) is an important part of the motor of a new energy vehicle.
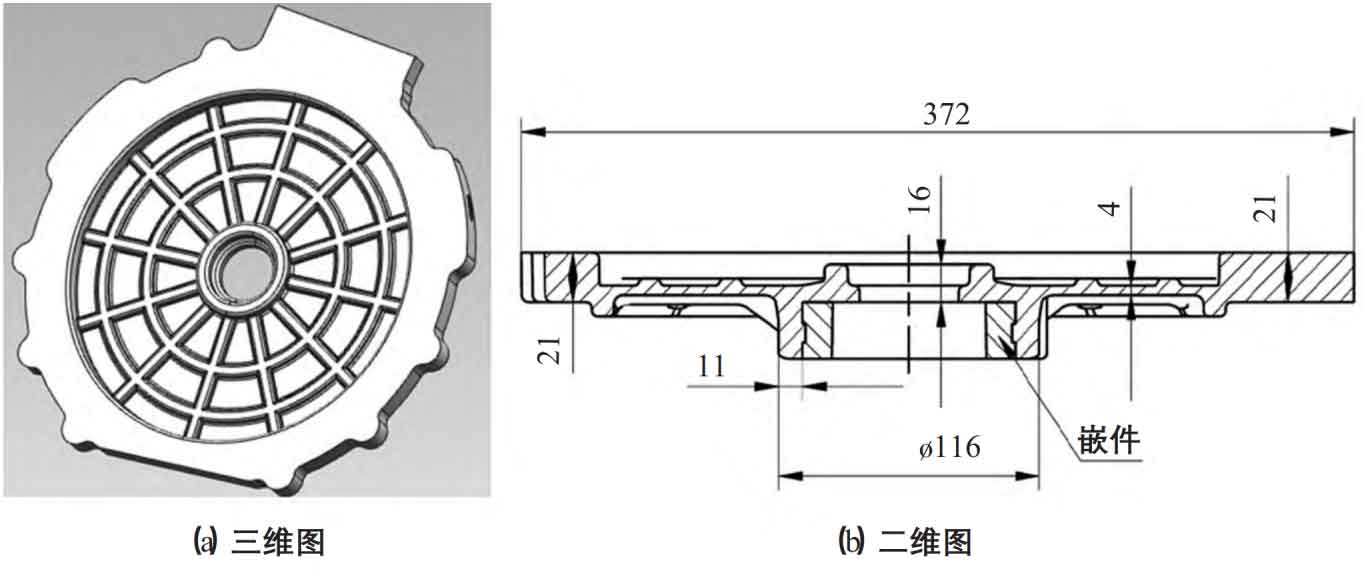
The front cover of the motor housing is made of ZL101A with a mass of 4.5kg. Flange and central through-hole are machined with surface roughness of Ra6.3 μ m. The non machined surface shall be shot blasted. The casting of the front cover of the motor housing shall be free of cold shut, cracks, shrinkage cavities and penetrating defects. Insert shall be pre installed in the casting process, and the insert material shall be 45 # steel. The maximum size of the front cover casting of the motor housing is 372mm, the overall wall thickness is 4mm, the flange wall thickness is 21mm, and the wall thickness of the central through-hole is 16mm. The wall thickness difference is large, so it is difficult to achieve sequential solidification. At the same time, the overall wall thickness of the front cover casting of the motor housing is thin and has a grid rib structure, which is not conducive to the exhaust and the floating of the oxide slag.
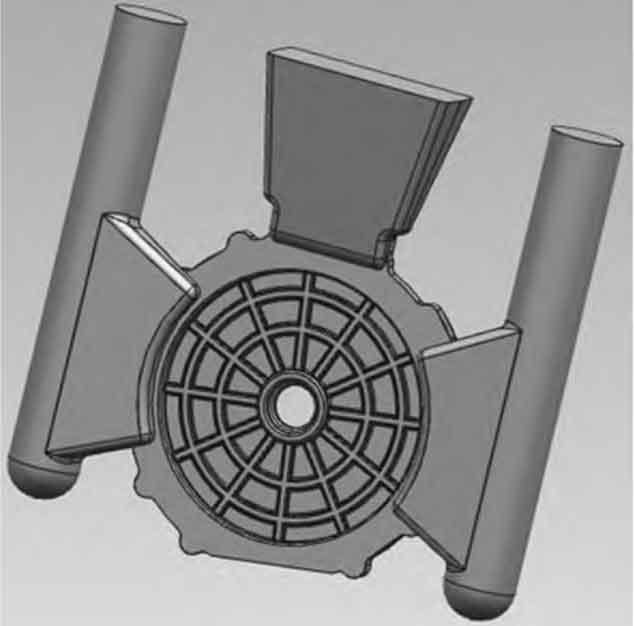
According to the design experience of similar products, metal mold gravity tilting casting is adopted. The tilting process can reduce the drop of aluminum liquid entering the mold cavity and reduce splash and turbulence. A top riser is set at the top of the front cover casting of the motor housing, and a side riser is set at both sides. A gap runner is set between the side riser and the thick wall flange of the front cover casting of the motor housing. The original process scheme is shown in Figure 2.
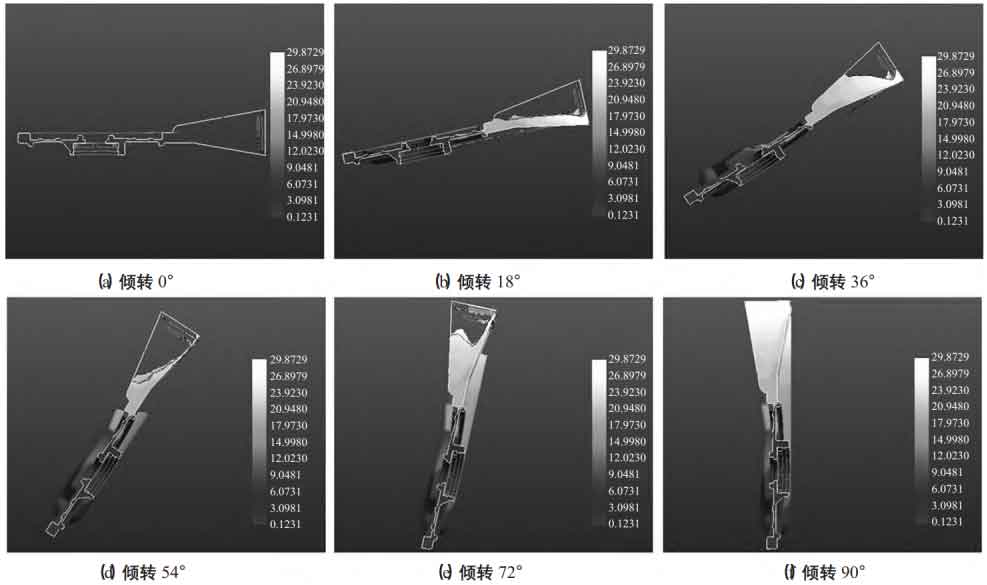
Simulate the original scheme, and the filling process is shown in Figure 3. With the tilting of the die, the aluminum liquid enters the cavity. When tilting 18 °, the gas at the filling end and the oxide slag at the front end of the liquid surface need to float up through the mold cavity and return to the top riser. Because the wall thickness of the mold cavity area is thin and the solidification time is short, the gas and oxide slag in the mold cavity cannot float smoothly to the top riser, but will remain in the mold cavity, causing the defects of air holes and slag inclusions in the front cover casting of the motor housing.
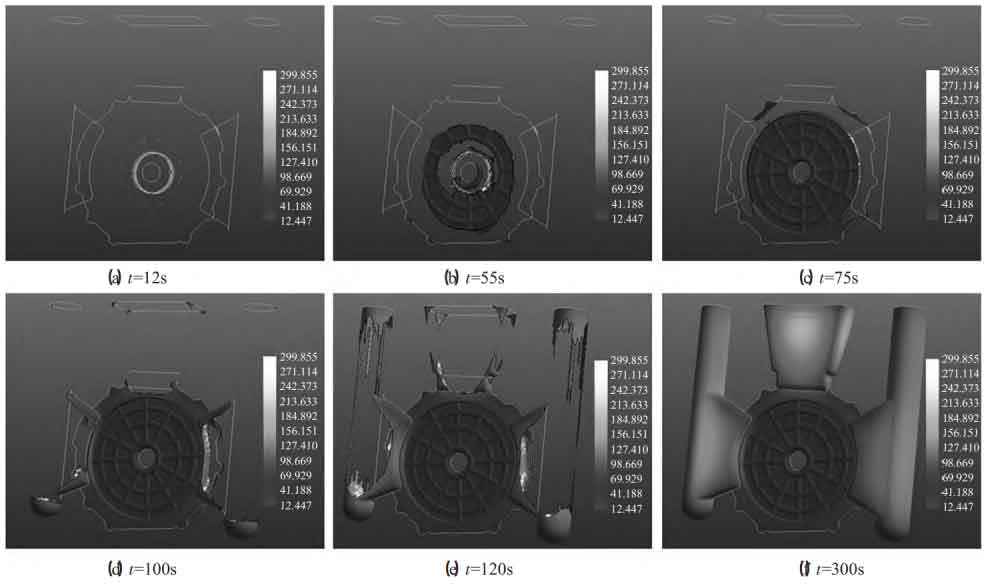
The solidification process is shown in Fig. 4. When t=12s, the front cover casting of motor housing starts to solidify, and when t=300s, the front cover casting of motor housing completely solidifies. The casting flange and central through-hole of the front cover of the motor housing are hot spot areas. When t=55s, the central through-hole has not solidified yet, while the surrounding thin-walled areas have solidified, the feeding channel is interrupted, a closed liquid phase area is formed at the central hot spot, and shrinkage defects are easily formed at the central through-hole.
