1. Problem description
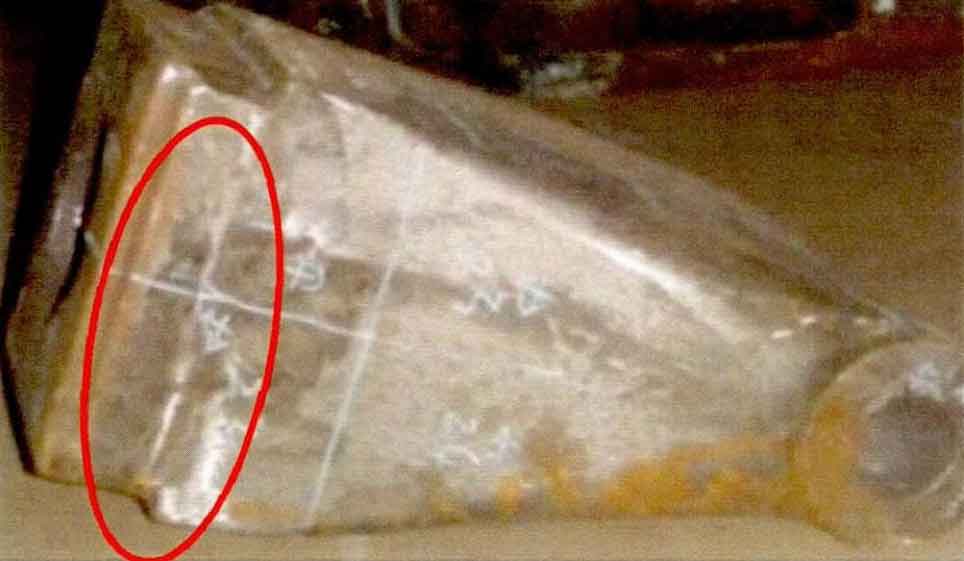
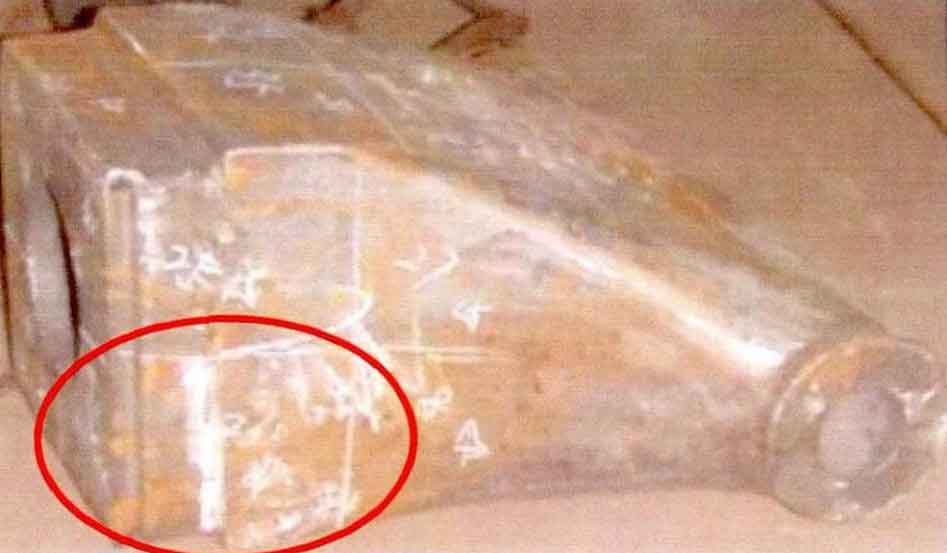
Sand casting bracket steel casting, steel casting No. 20e-70-k1432. The steel casting is a new external product of ZHY casting. In the trial production stage of steel casting, the radiographic inspection of the steel casting is unqualified. The effect is not ideal by adjusting the size and position of riser and adding cold iron. As shown in the table, it is part of the radiographic inspection report. Figure 1 and Figure 2 show the pictures of product area division for radiographic inspection. Radiographic inspection shows that there are shrinkage defects in areas No.21, No.22, No.26 and No.28.
| Negative No | Shrinkage cavity size | Shrinkage grade | Thickness | Qualified |
| 21 | 100*20 | 4 | 20 | Yes |
| 22 | 100*30 | 5 | 20 | No |
| 26 | 50*20 | 4 | 25 | No |
| 28 | 140*25 | 5 | 25 | No |
2. Cause analysis
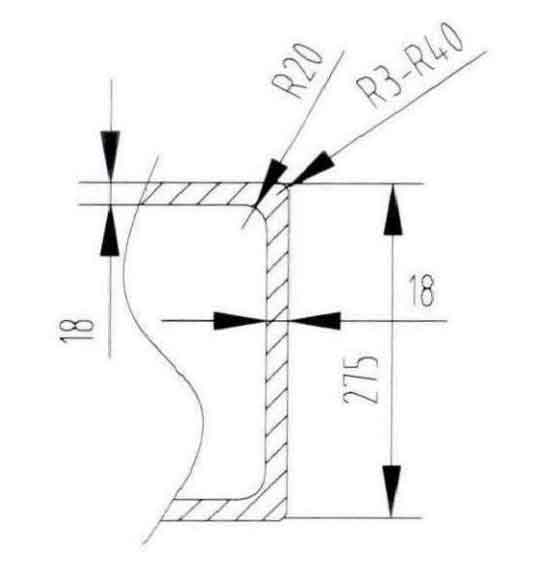
Conduct air gouging and visual confirmation for the casting defect parts. As shown in Figure 3, there are linear shrinkage defects at the connecting corner between the top surface and the side of the sand casting. The partial section of steel casting is shown in Figure 4.
3. Countermeasure formulation and verification
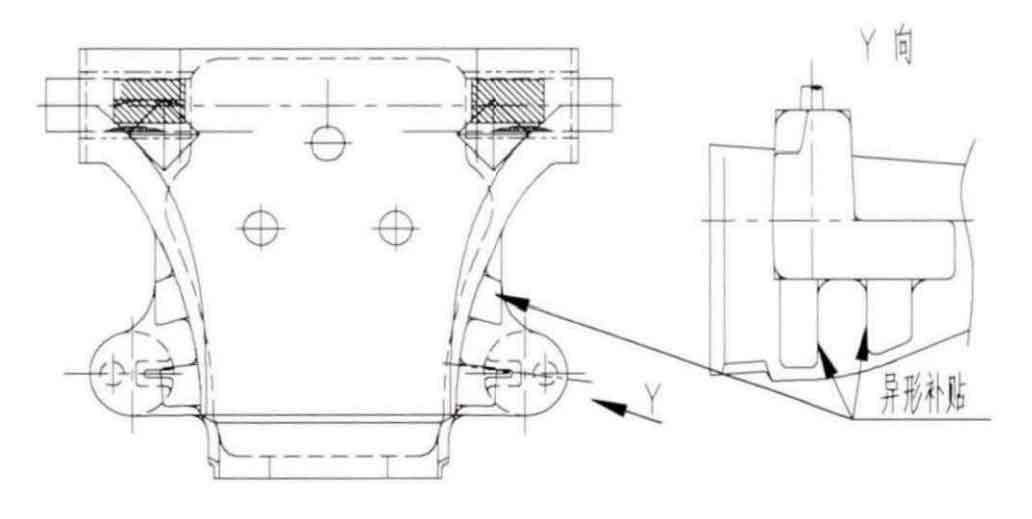
For this kind of steel castings with thin-walled structure, countermeasures should be formulated. In addition to setting risers at the top, side risers should also be set at the side, and special-shaped subsidies should be set at the side risers according to the shape of steel castings. We should not only control the subsidy, which can effectively promote the feeding of riser to steel castings, but also minimize the weight of subsidy.
The sand casting process is changed, and the riser subsidy shape in the sand casting process diagram is shown in Figure 5. The special-shaped subsidy makes the side riser, riser neck, special-shaped subsidy and steel casting form a feeding channel from large to small, which can ensure the internal quality of the product.
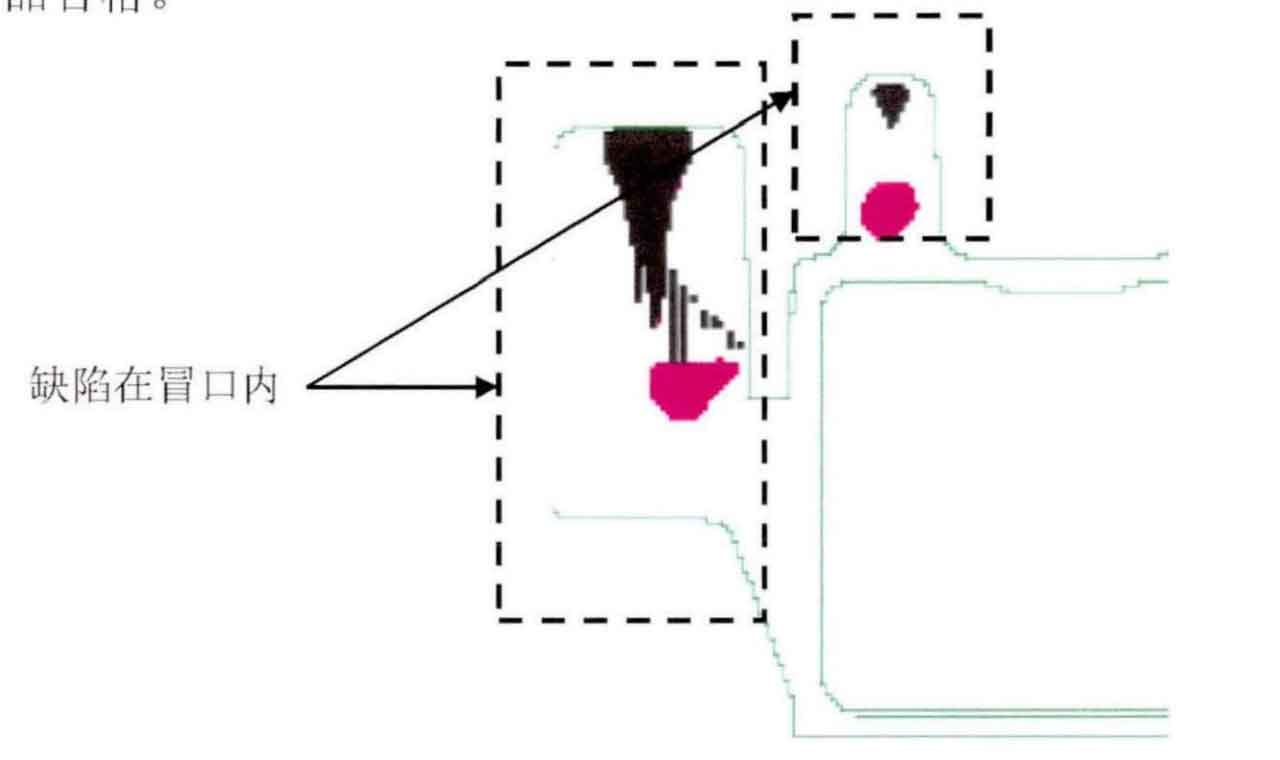
The three-dimensional simulation of the new sand casting process is carried out, and the simulation results are shown in Figure 6. The simulation results show that there are no shrinkage and porosity defects at the unqualified parts of the original radiographic inspection. The defect is controlled inside the riser.
After process change, model modification, trial production and small batch trial production, the steel castings are subject to ultrasonic flaw detection and radiographic flaw detection, and the steel castings are qualified.
The qualified processed steel castings are shown in Figure 7 and have been recognized by customers.
4. Improving harvest
When encountering steel castings with thin-walled structure, special attention should be paid to feeding and chilling at the corner. In this case, the defects of shrinkage cavity and porosity are eliminated by reasonably setting risers and subsidies. This improvement method can be popularized and applied in thin-walled steel castings.