The comparison of validation results of the three process schemes is shown in the table. Overall, Scheme III has certain advantages in actual production verification: high process yield, small number of sand cores, simple production operation of ductile iron castings, qualified casting at one time, and easier to ensure batch production quality.
| Scheme No | Production rate/% | Sand iron ratio/% | Cold iron utilization rate/% | Verification mode of casting production | Difficulty of production operation | NDT, processing verification |
| Scheme I | 53.3 | 6.7 | 6.9 | 3D printing sand core assembly casting | Complex | The third batch is qualified |
| Scheme II | 71.6 | 8.4 | 26.9 | Not put into production verification | Complex | — |
| Scheme III | 69.6 | 6.4 | 20.2 | 3D printing sand core assembly casting | Simple | First pass |
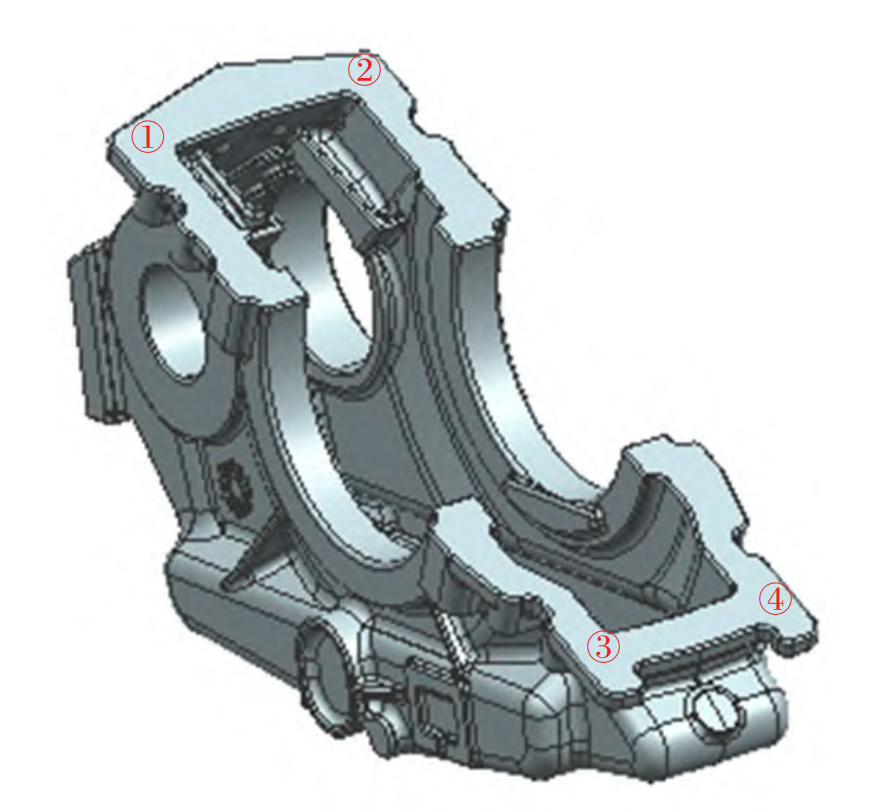
The NDT results of ductile iron castings produced according to Scheme III show that the key areas of ductile iron castings reach UT0~1, RT0~3, and the other areas reach UT1, RT0~3, which meet the NDT requirements of such ductile iron castings. Solid metallographic and hardness testing shall be carried out at four corners of the box joint surface (wall thickness 25 mm), and the testing position is shown in Figure 1.
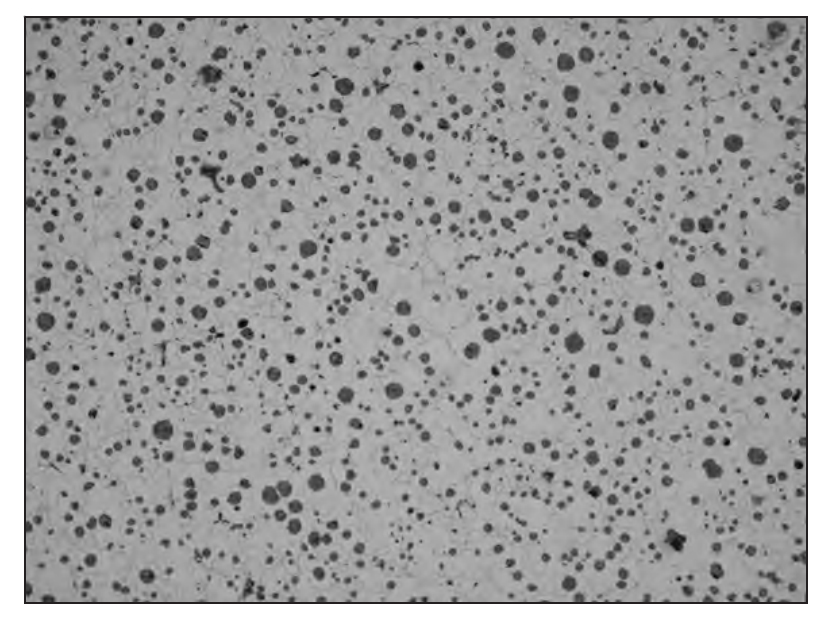
The inspection results show that the number of graphite spheres is 160~320/mm (conducive to the formation of carbon into graphite), and the joint surface is ferrite matrix structure (as shown in Figure 2); The solid hardness of ductile iron castings meets the requirements of 130~210 HB, and the mechanical properties fully meet the performance requirements of EN-GJS-400-15.