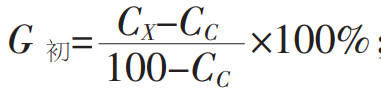In the solidification process of Hypereutectic nodular iron casting, when the temperature is lower than the graphite liquidus, the primary graphite ball will precipitate. In the growth process of primary graphite ball, due to the direct contact between graphite and molten iron, the diffusion of carbon atoms is much easier. The growth of graphite ball is affected by the diffusion rate of carbon atoms in molten iron. When it grows to a certain size, the graphite ball is surrounded by an austenitic shell, Then the spheroidal graphite cast iron and graphite balls will continue to grow until the end of Eutectic Transformation.
Therefore, the condition of graphite expansion of nodular cast iron at the initial stage cex-ce0 > 0; Ce0 is the CE value of eutectic point and CEX is the actual CE value of ductile iron.
Calculation of primary carbon precipitation:
CX is the carbon content of nodular iron castings, and CC is the eutectic carbon content.
The density of carbon is about 2.25g/cm3. For every 1% carbon precipitated, the volume of nodular iron will expand by 2.05% ~ 3.4%. Therefore, the volume expansion caused by the amount of primary carbon precipitated can be calculated from the above formula.
As hypereutectic nodular iron precipitates primary graphite balls first, and the density of graphite is less than that of molten iron, the graphite balls will float upward during the growth process. If the nodular iron castings are too thick, the cooling speed is slow, and the graphite has enough time to float, a lot of graphite will float to the near upper surface, This is the main reason for graphite floating in hypereutectic thick nodular iron castings.
Therefore, the main measures to control graphite floating: ① reduce the CE value of nodular iron castings, and the CE value should be less than the eutectic point; ② Speed up the cooling rate of nodular iron castings, especially the cooling rate of thick parts.