1. Sand casting structure and technical requirements
The sand mold casting of the end cover is shown in Figure 1. The maximum size of the part is 2 152 mm outside diameter, 583 mm high, and 1 600 kg net weight The product belongs to thin wall sand casting, with wall thickness between 40 mm and 110 mm. It is made of ZG230-450, and the carbon equivalent is required to be ≤ 0.4. This material has the characteristics of good sand casting performance, relatively high melting point, poor actual fluidity, easy oxidation, etc.
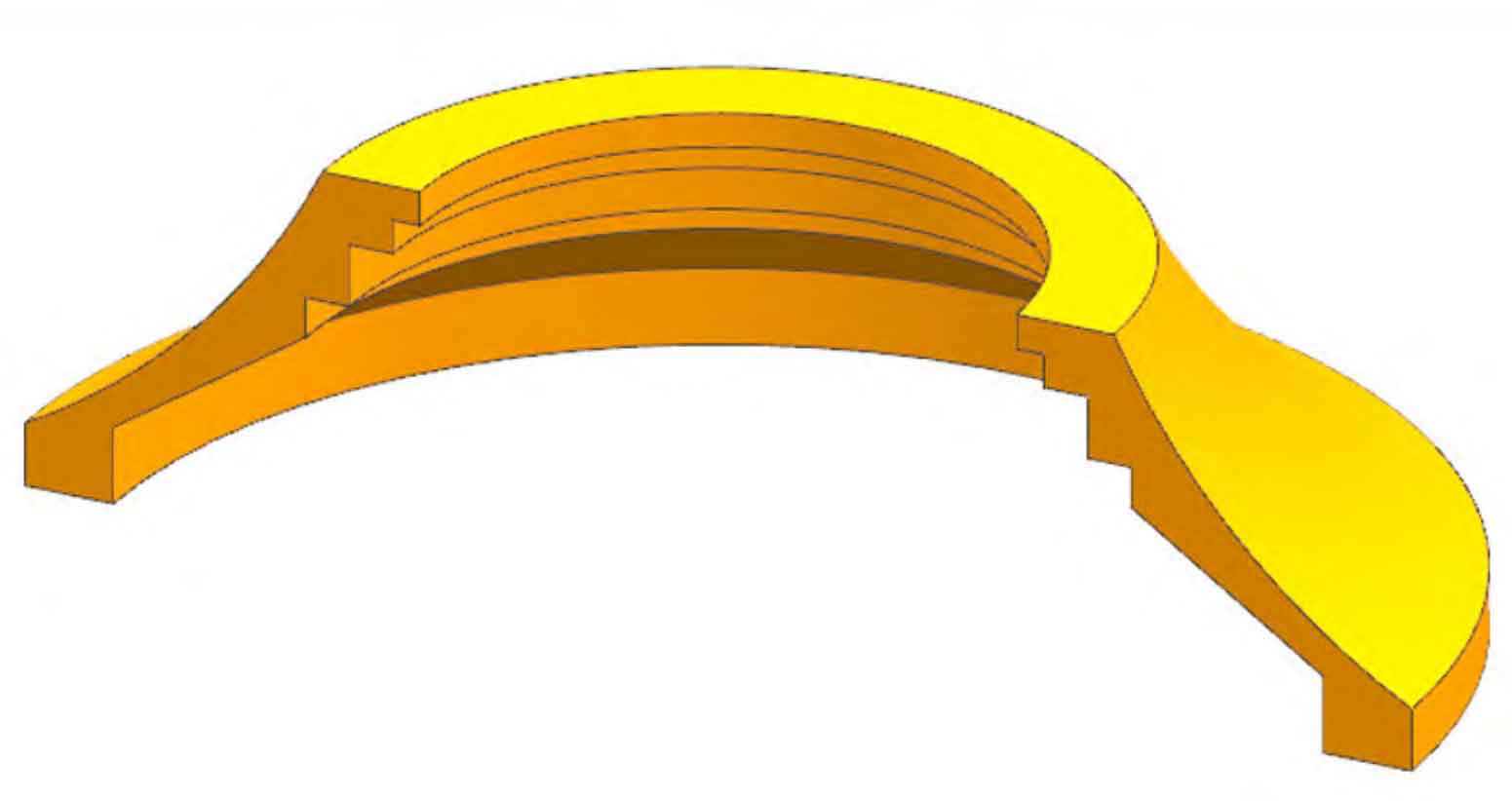
According to the structure and material characteristics of sand casting, the analysis is as follows: the hot spots of the product are scattered, the cooling speed is fast, the wall thickness junction is easy to form shrinkage defects, and the large mouth is easy to deform, which is easy to cause the lack of finish machining during the heat treatment after rough machining.
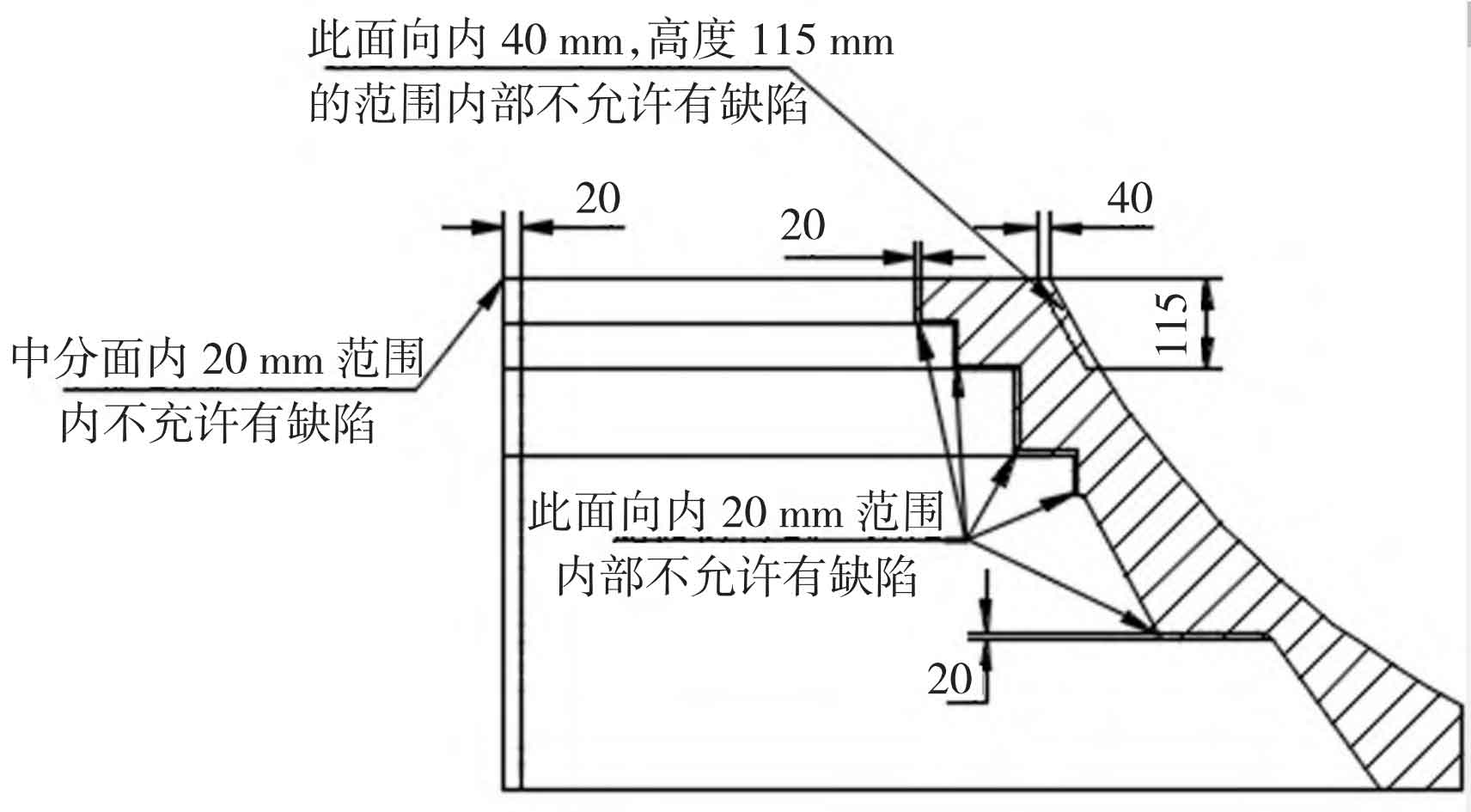
Technical requirements: the products are delivered in rough machining state, all surfaces are required to be machined, and the machining tolerance is accepted according to GB/T1804-m standard. Product requirements MT, UT, RT, VT, PT testing, Figure 2
Except that no defects are allowed in the area, other parts, such as air hole A2, sand slag B2 and shrinkage porosity C2, are acceptable. The specific MT shall be as per ASTM E709SM2/LM2/AM2. The single linear magnetic trace shall not exceed 4 mm, the cumulative amount shall not exceed 6 mm, and the UT shall be greater than A609 φ 2 mm defect is not allowed, RT shall be in accordance with ASTME186/280/446 Grade II, VT and PT shall be in accordance with ASTMA802100 × Within 100 2 × two × 1.5 defects are not allowed to exceed 3 NDT standards for acceptance.
2. Alloy characteristics
According to the customer’s composition requirements, this material is a carbon steel product, and there is no provision for Ni and Cr content in the material. However, in order to ensure that the required low temperature (0 ℃) impact value of the material is ≥ 27 J under the condition of carbon equivalent ≤ 0.4, the Cr and Ni content in the material has been subsequently adjusted. As Ni element can refine the grain, improve the hardening property of the steel, and reduce the quenching temperature during heat treatment, The deformation during heat treatment is reduced, so the Ni mass fraction is controlled within the range of ≤ 0.4%; Since chromium can improve the strength and hardness of steel, but the impact toughness will decrease when the chromium content is high, the chromium content is controlled within the range of ≤ 0.13%.
3. Defects and cause analysis
Sand casting process is used for production. In the past, similar products were produced in a small number, and the process was designed with the big mouth facing up. After actual production, there were many slag inclusions and porosity defects on the surface of the product. Because the product structure belongs to thin wall sand casting, shrinkage porosity is easy to occur at the thin thick junction.
According to the alloy characteristics of the product, the fluidity of the molten steel is poor. During the filling process, the molten steel contacts the sand mold and reacts. It is easy to produce oxidation and gas absorption, and the temperature drops rapidly. The generated gas and slag inclusions are not easy to separate and adhere to the surface, forming a large number of surface slag inclusions or pores, and the defects are not easy to completely process and remove within the range of 0~10 mm.
