1.Analysis of the reasons for the failure of the original process
1.1 cause analysis of shrinkage and porosity
The riser used in the original process is not connected with the gating system, and the molten iron enters the casting cavity through the gating system. After the cavity is heated, the temperature is reduced, and then it enters the riser. The molten iron entering the riser is already cold molten iron, and the riser temperature is lower than the casting, so it belongs to the cold riser, which can not play the role of feeding, but solidifies and contracts earlier than the casting, and pulls the molten iron backward from the hot spot of the casting. In addition, due to the use of open riser, graphitization expansion and thermal expansion of sand core in the later stage of solidification can not be solidified and sealed in time, resulting in relaxation of expansion pressure, and can not use expansion for feeding, thus causing shrinkage cavity and shrinkage porosity at the hot spot of casting.
1.2 cause analysis of slag inclusion
The section of the original process is high, and there is no slag retaining effect.
2.Analysis of the reasons for the success of the new process
The large pump body belongs to the large shell casting, and the new technology belongs to the riser free casting technology. According to the report of literature [2], the conditions for adopting the riser free technology to prevent shrinkage cavity and porosity are as follows:
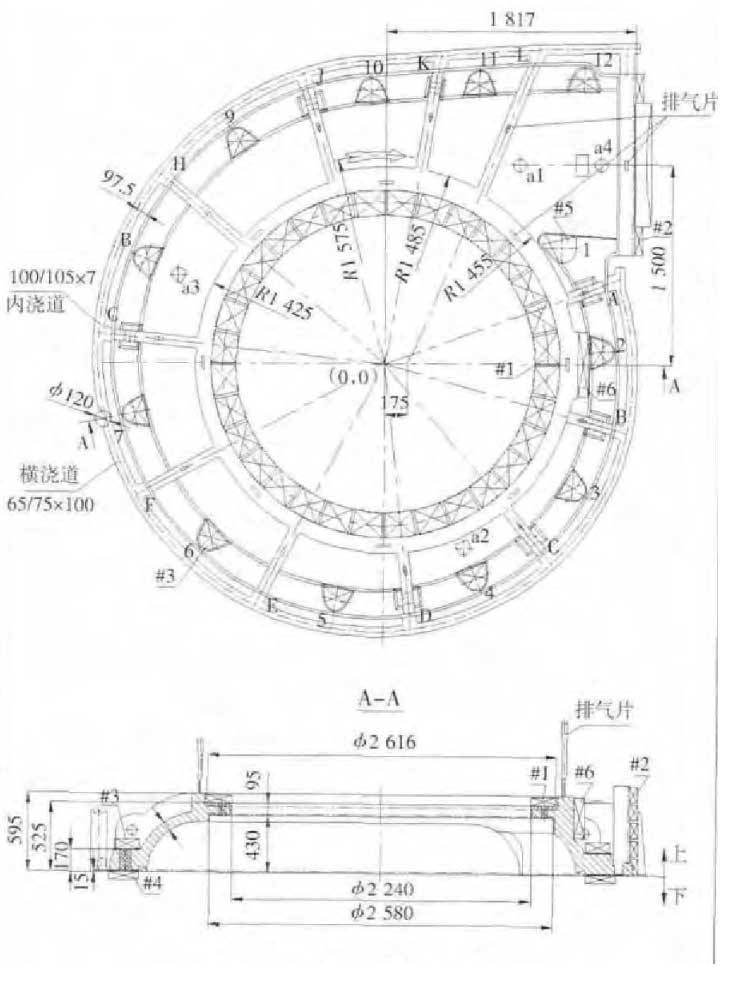
(1) adopt high rigidity mold to prevent the casting from expanding during solidification: 750 pump body adopts furan resin sand mold, and try to improve the compactness, with high rigidity. According to the literature [2], large shell castings can also use the volume expansion generated by the heat of the sand core for feeding. The key is to select the appropriate pouring temperature according to the size and wall thickness of the casting, so that the time of cooling and solidification shrinkage of the casting is exactly the same or close to the time of expansion of the sand core, and the expansion of the sand core can play a feeding role. According to the test, the suitable pouring temperature of 750 pump body is 1 350 ± 10 ℃.
(2) adopt high CE and sufficient inoculation to ensure full graphitization. CE (see Table 1) of 750 pump body is close to the eutectic composition, and the inoculant containing Ba CA is used, with a large amount (0.7%), which can achieve full inoculation.
(3) adopt multiple internal sprues to disperse the molten iron, and adjust the coordination with cold iron to make all parts of the casting start at the same time, and simultaneously cool and solidify. In order to prevent the relaxation of graphitizing expansion pressure and improve the utilization ratio of graphitizing expansion, and to prevent the pouring system from sucking the feeding molten iron from the casting before the solidification of the casting in the middle and later stage of solidification, the inner runner and the exhaust piece should solidify quickly after pouring, and the improved process also meets this requirement.
(4) more cold iron is used to strengthen the cooling of the casting, so that the outer layer of the casting cools and solidifies rapidly after the molten iron enters the mold cavity. Before the solidification of the liquid channel in the inner sprue and the core of the casting, a part of the shrinkage is completed in advance, forming a volume vacancy, obtaining the shrinkage liquid from the liquid channel and the inner sprue in time, and increasing the external shrinkage. In addition, the cold iron can make the outer layer of the casting solidify and crust early, and can prevent the appearance of the casting from expanding.
Experimental measurement, production practice and theoretical calculation show that [2], the CE of nodular cast iron is relatively high, with a large amount of graphitization expansion, but under the general pouring temperature, the expansion is not enough to completely offset the liquid and solidification shrinkage, so under the condition of no riser, it is necessary to make full use of the pouring system for feeding. Therefore, “casting without riser” is not “casting without external feeding”. The difference between “riser feeding process” and “no riser process” is that the former is a large number of centralized feeding, so it often adopts sequential solidification; the latter is a scattered multi-point, small amount and rapid feeding, so it is hoped to achieve the simultaneous start and simultaneous surface to interior solidification of each section, so as to prevent each section from drawing molten iron mutually.
In order to verify the feeding effect of the pouring system, Xu Chengzu once poured 80 mm × 80 mm × 100 mm test block [3] without riser. Through the method of cutting off the internal sprue at different times (0 s, 5 s, 10 s) after pouring, the change of shrinkage and porosity of the sample was observed. The results showed that the earlier the sprue was cut off, the more serious the shrinkage and porosity (the shrinkage and porosity volume was 22.0 cm3, 11.4 cm3, 9.5 cm3, respectively), and the non cutting of the internal sprue was 8 Cm3), indicating that the gating system has feeding effect. In fact, this feeding function is already in progress in the pouring process: the molten iron in the first mold starts to cool and solidify in the liquid state under the cooling of the mold wall, because the resulting graphitization expansion can not completely offset the liquid shrinkage and solidification shrinkage, thus generating a net shrinkage and forming a volume vacancy, so that the pouring system can supplement the molten iron in time through the liquid channel of the casting core which has not been blocked, In order to prevent the relaxation of graphitization expansion pressure and increase the utilization rate of graphitization expansion, and to prevent the pouring system in the middle and later stage of solidification from drawing the feeding liquid iron from the casting before the casting solidifies, the section of the internal sprue should not be too thick. In order to improve the feeding capacity of the gating system, it is necessary to strengthen the cooling of the casting, accelerate the solidification and contraction of the outer layer of the casting, produce the volume vacancy in the cavity in advance, and let more molten iron enter the cavity in advance. A large amount of cold iron is laid on the hot spot of 750 pump body, which also meets this condition.
750 pump body casting is a large-scale ductile iron casting with high quality requirements and difficult casting production technology. In the original process, due to the use of cold open riser, many hot spot parts produce shrinkage porosity, because the internal sprue is thick and has poor slag retaining effect, resulting in slag inclusion on the top of the casting; through the use of non riser process, more cold iron is used to improve the compactness of resin sand, improve the mold rigidity and chilling ability; remove cold open riser, Adopting thin inner runner and thin exhaust piece, high CE, sufficient inoculation and proper pouring temperature, the defects of shrinkage porosity and slag inclusion are eliminated, and castings with quality meeting the requirements of customers are produced, which has established quality reputation and brought economic benefits to the enterprise.
