| Paint | Total mold filling time (s) | Average filling speed (cm/s) |
| Low permeability coating | 1.18 | 17.00 |
| Medium permeability coating | 1.14 | 17.54 |
| High permeability coating | 0.88 | 22.64 |
The test results are shown in Table 1 and table 2.
| Paint | Total mold filling time (s) | Average filling speed (cm/s) |
| Low permeability coating | 0.87 | 22.99 |
| Medium permeability coating | 0.72 | 27.91 |
| High permeability coating | 0.66 | 30.30 |
| No paint | 0.59 | 33.90 |
There are several uses of fire-resistant coating in lost foam casting process. Firstly, the coating provides a barrier between the molten metal and the coarse sand forming the mold, thus improving the surface finish of the casting. Secondly, it ensures the integrity of the cavity during mold decomposition and metal liquid filling in lost foam casting. Especially when the product of pattern decomposition is gas, the cavity is under high pressure, and the strength of dry sand and fire-resistant coating prevents the cavity from collapsing. Thirdly, The fire-resistant coating should have sufficient air permeability to ensure that the gas decomposition products escape from the molten metal like the mold interface, so as to facilitate the filling of molten metal. If the permeability of the coating is not good, the liquid and gaseous decomposition products are not easy to escape, resulting in high pressure in the mold cavity, incomplete filling of molten metal in lost foam casting, and finally casting defects. Under the condition of dry sand lost foam casting, EPS decomposition products enter the surrounding sand through fire-resistant coating under the action of liquid metal pressure and back pressure. Condensation of decomposition products in the diffusion process will block the exhaust channel of the coating and the gap between sand particles, reduce the permeability of the coating and the surrounding dry sand, and further increase the thickness of the impermeable layer. Because the condensate acts as a binder between sand particles, sand shells will appear around the casting. The coating determines the escape rate and escape mode of decomposition products, and has a great impact on the liquid metal filling process and casting quality of lost foam casting.
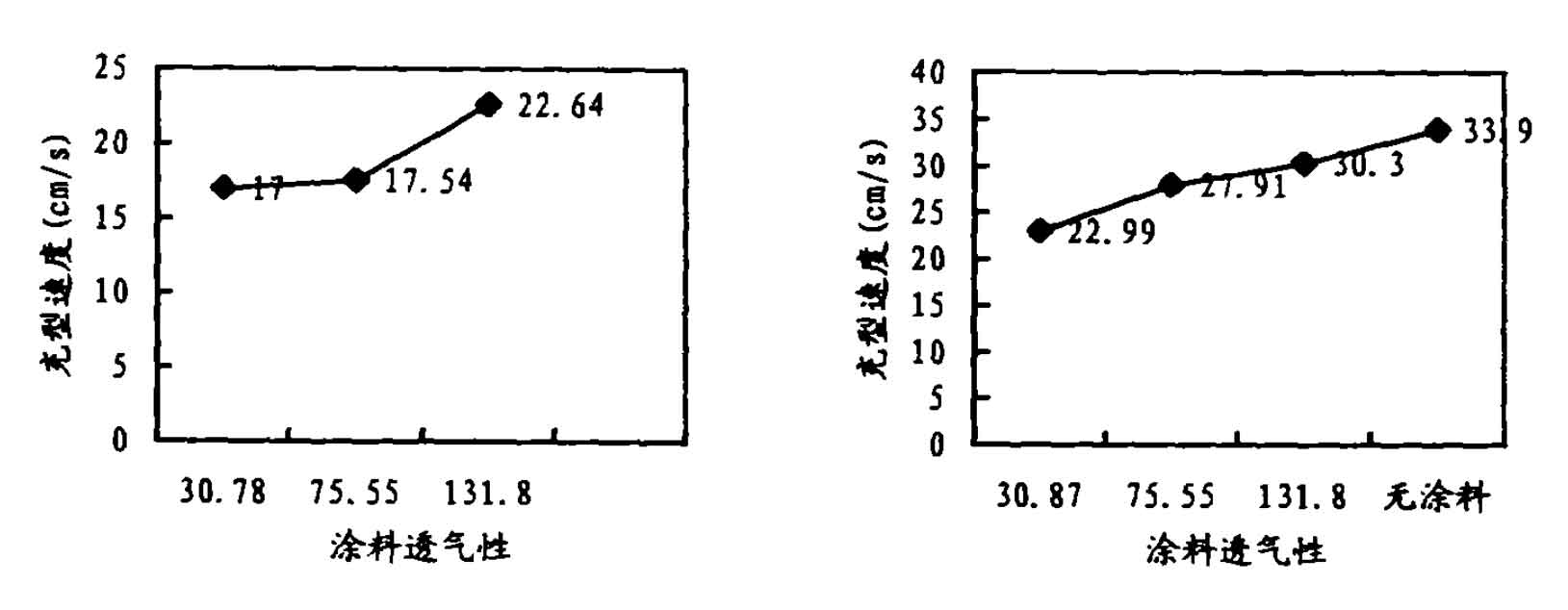
(b) Effect of coating permeability on mold filling speed (no vacuum)
Figure 1 and Figure 2 are the curves of the relationship between the average mold filling speed of liquid metal and the permeability of the coating under the condition of no vacuum and vacuum respectively. It can be seen from the curve that the average mold filling speed of liquid metal in lost foam casting tends to increase with the improvement of the permeability of the coating, whether or not vacuumized. This is because at the pouring temperature of gray cast iron, the pouring temperature is high, forming a large number of gaseous decomposition products and forming an air gap at the liquid metal the first mock examination interface δ, The release rate of back pressure in the air gap affects the filling driving force of liquid metal, which determines the speed of liquid metal filling in lost foam casting. The higher the permeability of the coating, the easier the gaseous decomposition products escape, the faster the release of back pressure, and the faster the liquid metal filling speed in lost foam casting. Under the condition of no vacuum pumping, the average mold filling speed difference between high permeability coating and low permeability coating is 0.33 times; Under vacuum condition, the average filling speed of liquid metal of high permeability coating and low permeability coating is 0.32 times, and without coating, it is equivalent to infinite high permeability of coating, which is 1.47 times of the average filling speed of liquid metal when low permeability coating is used. For high permeability coating, the filling speed under vacuum and no vacuum condition is 0.34 times, while for low permeability coating and medium permeability coating, The difference is 0.35 times and 0.59 times respectively.
During the test, it is found that when the permeability of the coating is too poor or other factors make it too late for the gas generated by the decomposition of the model to be discharged through the coating and molding sand during the pouring process, the liquid metal is blown out of the gate under the action of the back pressure of the pyrolysis gas, and the backflow phenomenon occurs, This further shows that the formation and release of pattern pyrolysis products in dry sand lost foam casting is the key link for the smooth filling process of liquid metal in lost foam casting.
