1. Analysis of cavity layout process
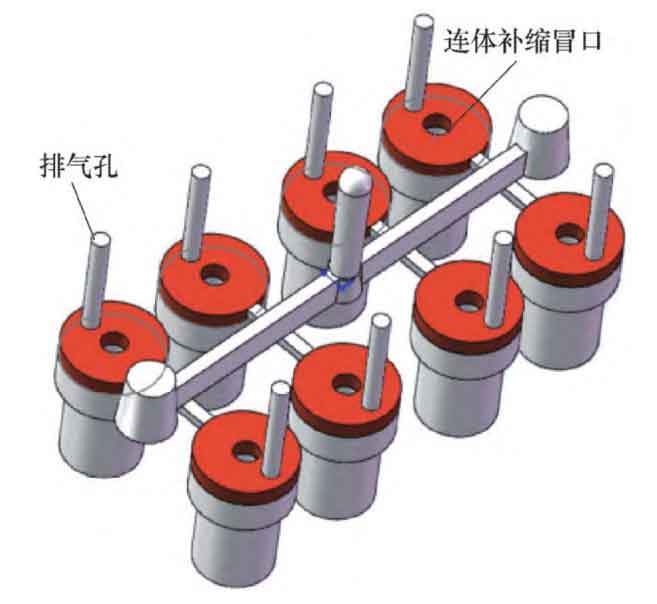
The ductile iron casting process (see Figure) is divided from one end. All the ductile iron castings are in the lower box. There are 8 castings in one box. The left and right rows are arranged in a strip pattern. There are 4 castings in one row. Each casting is basically isolated. There is basically no mutual heat transfer on the outer wall. The resin sand mold is naturally cooled and the cooling speed is relatively fast. The inner hole sand core is surrounded by surrounding metal liquid, the cooling rate is relatively slow, and the heat balance distribution is relatively poor. Due to the influence of the surrounding heat source, the inner hole solidifies late and cannot be effectively fed, so it is easy to have the “fly foot” shaped solidification shrinkage defect. Since the internal hole of the nut is threaded, no casting defects are allowed.
2. Analysis of inner hole sand core
The original process has large heat dissipation area, large temperature gradient and fast cooling speed. The inner hole is formed by furan resin self hardening sand core. Due to the small thermal storage coefficient of silica sand, good thermal insulation performance, small heat dissipation area of the inner hole and small temperature gradient, the cooling speed is relatively slow. According to the solidification characteristics of nodular cast iron, the first solidification area can get the feeding of the later solidification area, and the later solidification area can not get effective feeding or can not reasonably use the graphitization expansion, which is prone to the occurrence of interdendritic shrinkage defects (shrinkage), or the later solidification part will produce concentrated micro shrinkage cavities.
3. Gating system and riser analysis
The function of the exhaust hole is to discharge the gas in the mold cavity and accelerate the cooling speed of the surrounding area. In the original process, the vent hole was placed in the part with fast cooling speed, so that its solidification speed was faster, and the heat distribution was poor. Superimposed by the overheating effect of the ingate, it had the characteristics of sequential solidification, which did not conform to the solidification characteristics of ductile iron, and it would be easier to form shrinkage porosity, shrinkage cavity and other defects in the hole on the side of the ingate. In order to better ensure the quality of castings and summarize the previous production experience of gray cast iron, the top of the nodular cast iron casting process is increased by 30mm as a conjoined feeding riser, and the main function of the nodular cast iron feeding riser is to supplement the liquid shrinkage, so that the top surface shrinkage and centralized shrinkage defects formed by the liquid shrinkage are moved up and removed during processing, which can basically solve the liquid shrinkage defects of castings, The appearance dimensions of nodular cast iron castings also basically meet the requirements.
In the gating system of ductile iron casting process, the high trapezoid section is used in the ingate section. Due to the slow heat dissipation of the ingate, it can not be closed in time at the initial stage of eutectic solidification, so that the molten iron will reflow from the ingate, and the subsequent solidification shrinkage can not be well fed by graphitization expansion. Therefore, the ductile iron castings are prone to appear shrinkage porosity and shrinkage cavity defects in the parts with late solidification. Using this production process of nodular cast iron castings, not only the yield of nodular cast iron castings is low, but also the connecting feeding riser needs to be cut off in the subsequent sequence, and the quality of nodular cast iron castings cannot meet the requirements stably.
