Hydroelectric power generation, which is energy-saving, environmentally friendly, sustainable, and renewable, is an important component of clean energy in China and has made outstanding contributions to the country’s economic development. A certain type of hydroelectric power equipment cast steel ball valve produced by ZHY Casting has a complex structure and high production difficulty. In order to ensure the quality of steel castings for hydroelectric equipment ball valves developed by sand casting manufacturer, SolidWorks software was used for three-dimensional modeling, and the casting process was simulated and optimized using Huazhu CAE casting software.
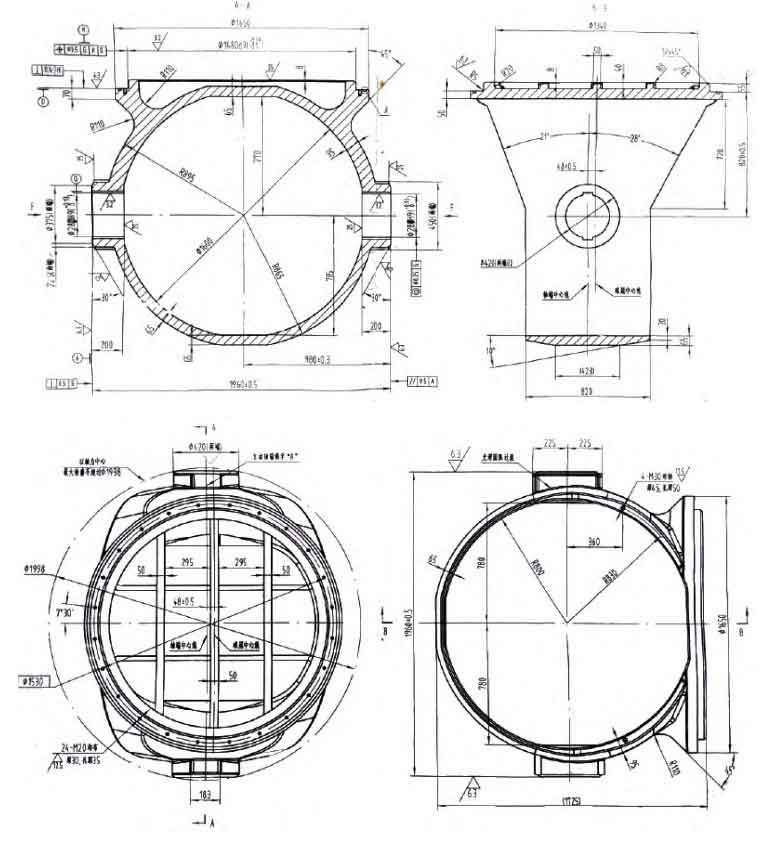
The sand casting manufacturer has developed water and electricity equipment ball valve steel castings made of WCB (equivalent to domestic casting steel grade ZG230-450), with the main chemical composition: ω (C) ≤ 0.30% ω (Si) ≤ 0.60% ω (Mn) ≤ 1.00% ω (P) ≤ 0.004 0% ω (S) ≤ 0.004 5%.
The approximate outline dimensions of the steel castings for water and electricity equipment ball valves developed by sand casting manufacturer are: 2000 mm x 1700 mm x 1500 mm, weighing approximately 5 tons.
1. 3D modeling
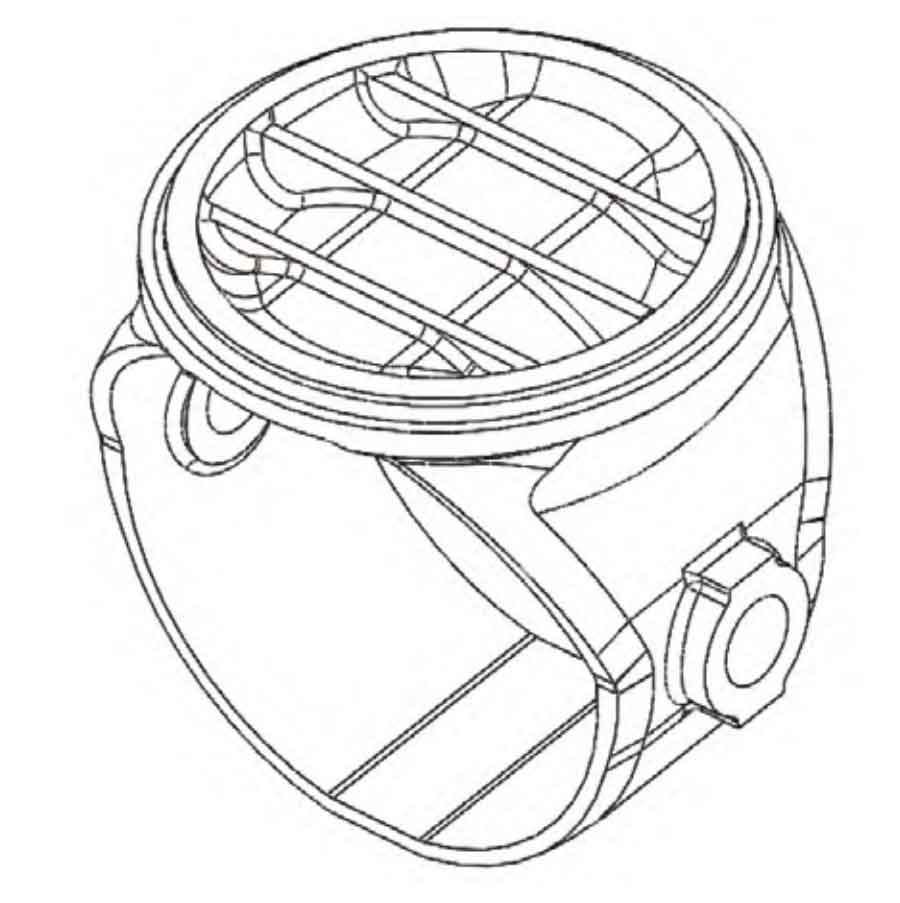
Sand casting manufacturer use Solidworks software to conduct 3D modeling of ball valves (see Figure 2). Through the model, the hot spot ball of the casting can be more directly observed, and the areas where defects may occur can be analyzed, providing more accurate data analysis for process design.
2. Process design
2.1 Setting the Riser
From dimension diagram 1 and 3D model diagram 2, it can be seen that the wall thickness of steel castings for water and electricity equipment ball valves developed by sand casting manufacturer has the characteristic of being thick on the top and thin on the bottom. According to the principle of sequential solidification, in order to facilitate the shaping and subsequent operation, thicker and smoother parts are selected to set up risers. Through specific calculations, the riser is set as follows (see Figure 3):
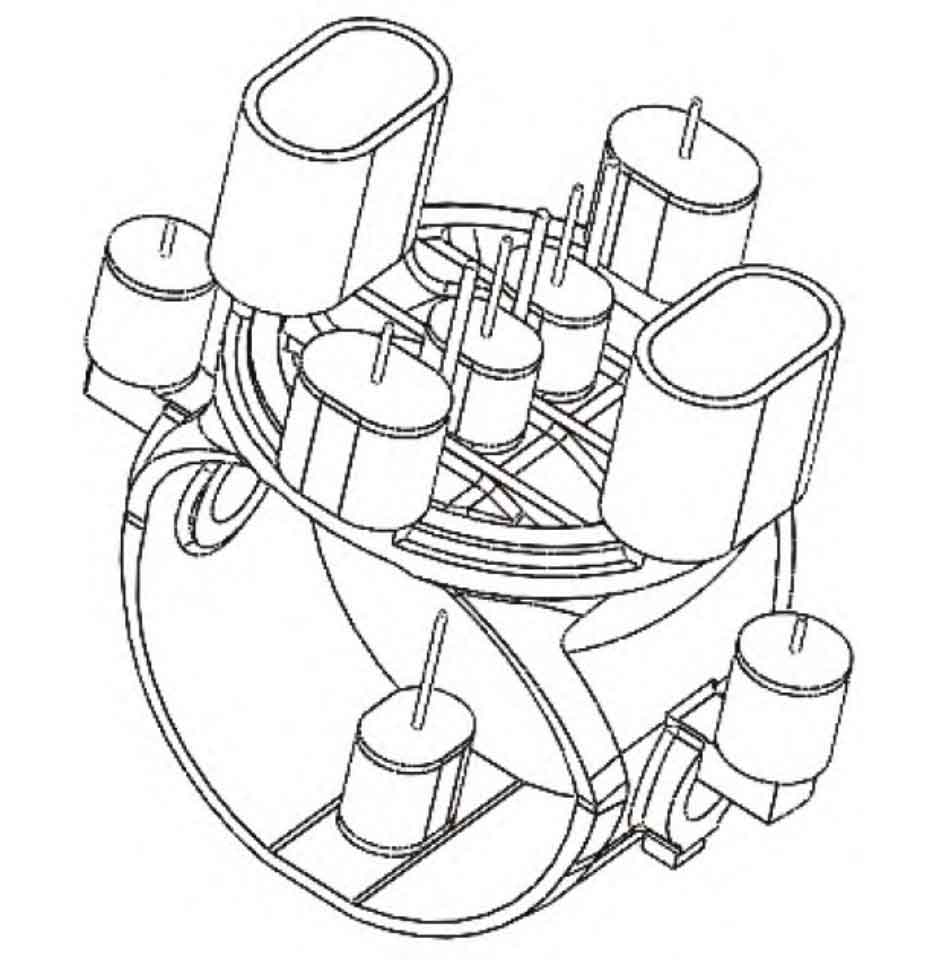
One concealed riser with a diameter of 230 mm x 340 mm x 300 mm (at the bottom of the ball valve); ϕ Two 290mm x 350mm concealed risers (at the shaft holes at both ends of the ball valve); Two exposed risers with a diameter of 360 mm x 660 mm x 600 mm, and two concealed risers with a diameter of 290 mm x 430 mm x 370 mm (on the circumference of the spherical crown, i.e. on the top circumference of the casting); Two hidden risers with a diameter of 210 mm x 310 mm x 270 mm (at the center of the ball crown, i.e. the top center of the casting).
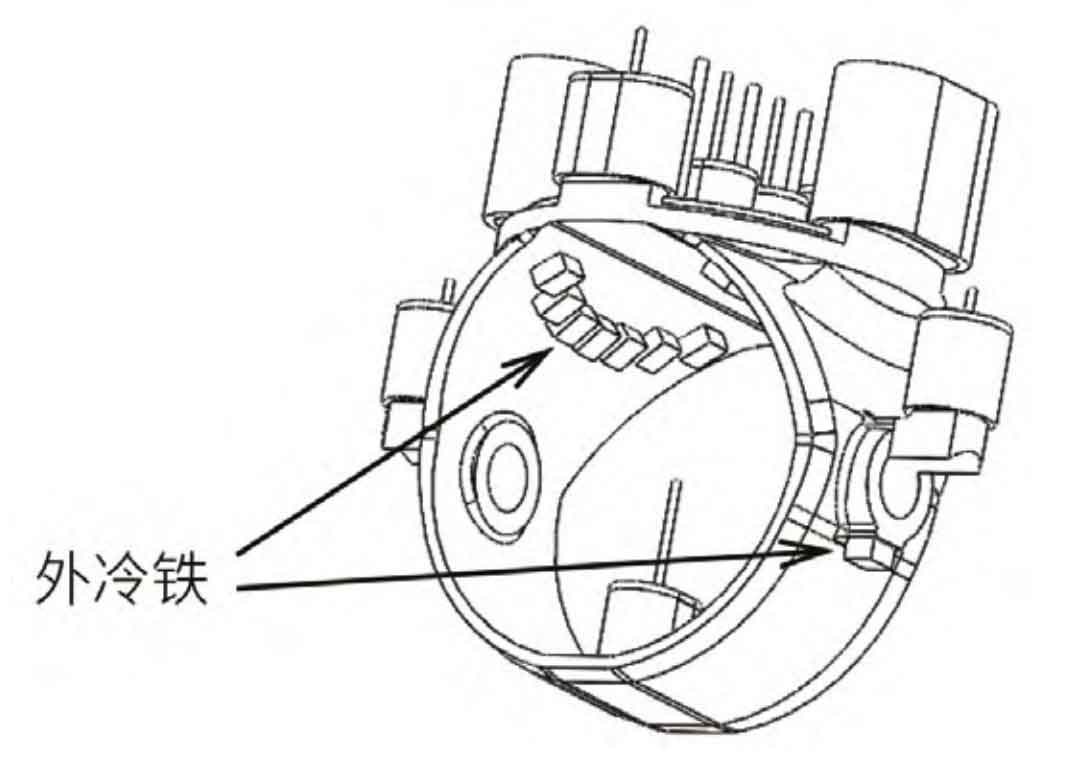
2.2 Add external cold iron
To ensure the sequential solidification of the castings, external cold iron is added locally to the castings where the riser cannot be effectively filled (see Figure 4). One piece is set at the lower part of the shaft hole, and seven pieces of external cold iron are set at the junction of the ball crown and the ball valve body. The size of the external cold iron is 160 mm x 140 mm x 90 mm.
3. Simulation and optimization
3.1 Simulation analysis
Use Solidworks software to draw a three-dimensional model diagram of the steel casting for the water and electricity equipment ball valve developed by a sand casting manufacturer, convert it into an STL format file, and import it into Huazhu CAE casting simulation software. Perform a 3D model mesh division with a mesh size of 12 532 212, made of WCB material. The liquidus temperature is 1 512 ℃, the solidus temperature is 1 469 ℃, the pouring temperature is 1 580 ℃, the shrinkage rate is 5%, and the initial temperature of the mold and external cold iron is 25 ℃.
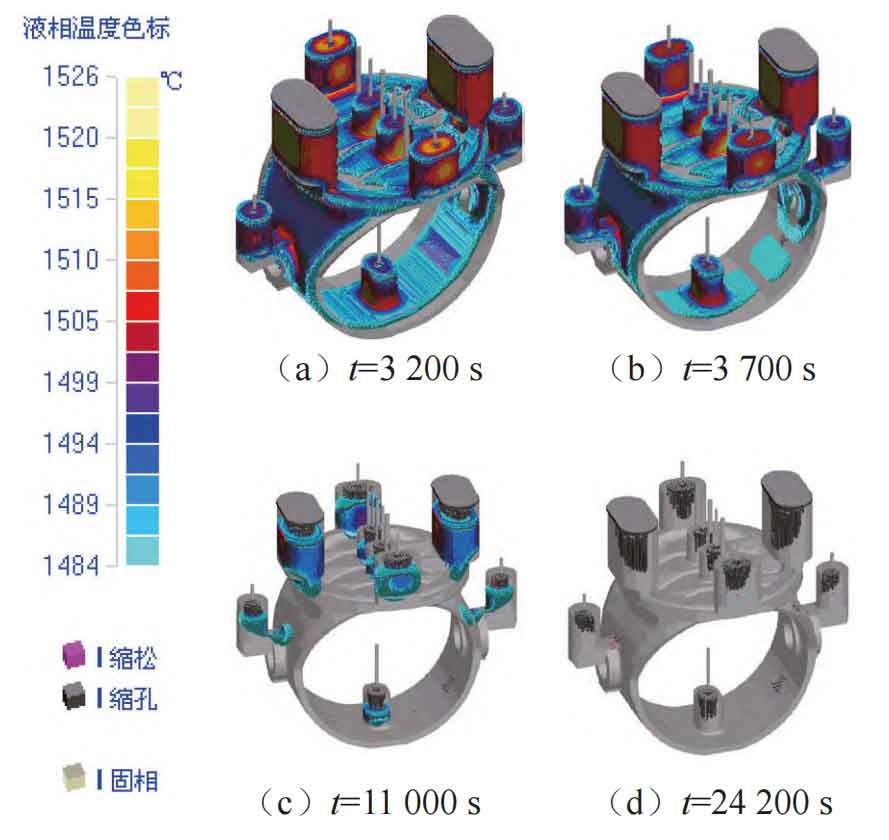
The solidification situation of each time period during the solidification process is shown in Figure 5. It can be observed that when the solidification time t=3700 s, an independent liquid phase is generated between the axial hole position and the bottom riser of the steel casting of the water and electricity equipment ball valve developed by the sand casting manufacturer; When the solidification time t=11000 s, independent liquid phase is also generated at the upper corner of the shaft hole position of the steel casting for water and electricity equipment ball valves developed by sand casting manufacturer. The final simulation results show that shrinkage defects have occurred in all independent liquid phase parts.
The main reasons for the occurrence of shrinkage defects are:
(1) The riser of the shaft holes at both ends of the ball valve is too small;
(2) The through-hole at the axis hole position damages the feeding and contraction channel of the riser;
(3) The distance between the shaft hole position and the bottom riser is too long, and the filling distance is not enough.
3.2 Process optimization
Based on simulation results and cause analysis, the sand casting manufacturer optimized the casting process (see Figure 6).
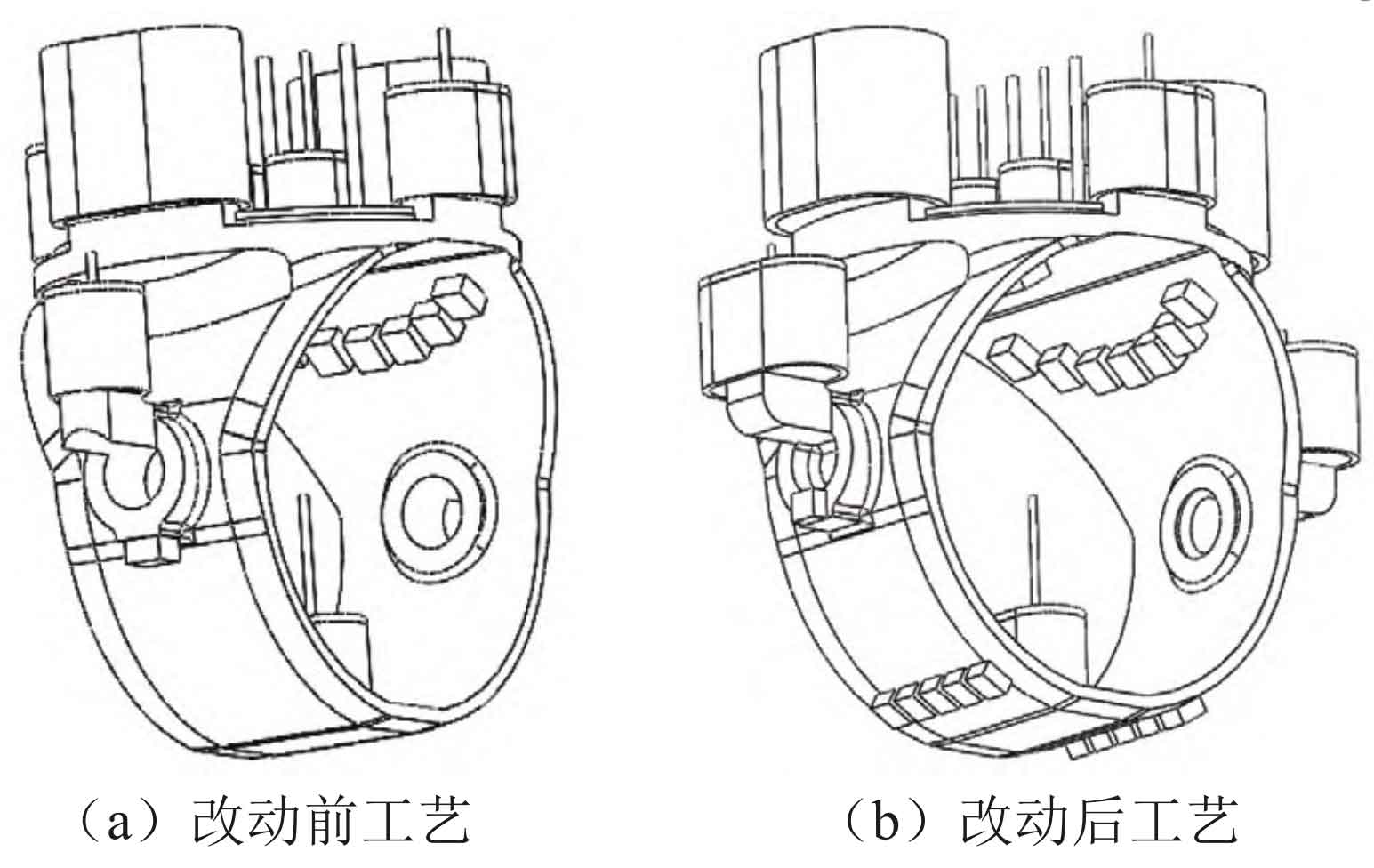
(1) Insert the shaft hole into the riser, starting from the ϕ Change the concealed riser from 290 mm x 350 mm to 290 mm x 430 mm x 370 mm;
(2) Optimize the through-hole structure of the shaft hole position and increase the filling and shrinking channels;
(3) Add an external cold iron between the shaft hole and the bottom riser to artificially cool the end and extend the filling distance;
(4) Change the outer cold iron at the lower part of the shaft hole to the side of the shaft hole to avoid affecting the newly added shaft hole filling channel and avoiding new defect problems.
4. Simulation and actual production after optimization
4.1 Process simulation after optimization
The sand casting manufacturer conducted casting simulation on the optimized process, and the results are shown in Figure 7.
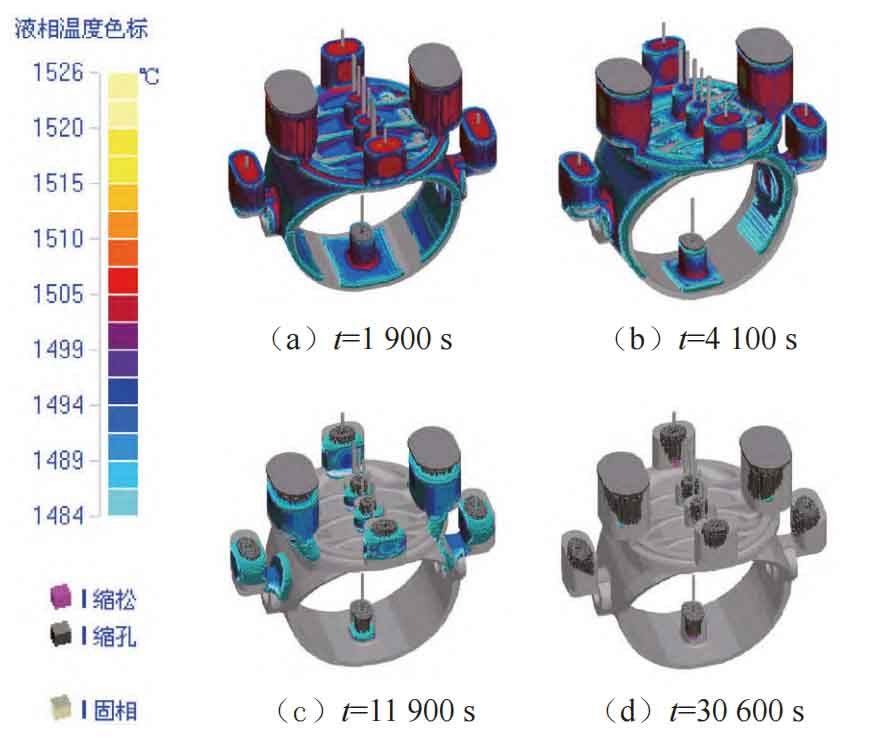
From Figure 7, it can be seen that:
(1) When the solidification time t=1900 s, the added external cold iron effectively plays a role in artificially cooling the end, prolonging the feeding distance of the riser;
(2) When the solidification time t=4 100 s, the additional filling and contraction channels at the axial hole position avoid the formation of an independent liquid phase between the axial hole position and the bottom riser;
(3) When the solidification time t=11 900 s, the increased riser at the axial hole position provides sufficient molten steel for the upper corner position of the axial hole, avoiding the occurrence of shrinkage porosity.
4.2 Actual production effect
Sand casting manufacturer determine the casting process based on simulation results, put it into actual production, and develop operating instructions for each process, strictly control each link in the production process, and ensure that the process is effectively executed.
The sand casting manufacturer uses optimized casting technology to produce ball valve steel castings with dense interior, smooth surface, and good quality. According to the customer’s requirements, according to GB/T 7233.1-2009 “Ultrasonic Testing of Steel Castings – Part 1: General Purpose Steel Castings”, UT testing was carried out on the steel castings of water and electricity equipment ball valves developed by manufacturers of rough machined sand castings. The results showed that they were qualified at level 2, and no defects exceeding the standard were found. The UT of the entire casting body was 100% qualified. The optimized process plan can effectively remove shrinkage defects, meet the customer’s requirements for sand casting manufacturer to develop steel castings for water and electricity equipment ball valves, pass the acceptance smoothly, and obtain customer recognition after delivery.
5. Conclusion
(1) The simulation results optimized by the sand casting manufacturer show that process optimization such as increasing the riser at both ends of the shaft hole position, increasing the shrinkage channel at the through-hole of the shaft hole position, and adding external cold iron can effectively solve shrinkage porosity defects.
(2) The sand casting manufacturer determined the casting process based on simulation results, strictly controlled the production process, ensured the effective execution of the process, and produced dense castings with good quality that met customer requirements, verifying the effectiveness of the process.
(3) The use of SolidWorks 3D modeling and Huazhu CAE casting simulation analysis provides important references for the design and optimization of casting processes, changes the traditional experience based design mode, reduces the occurrence of casting shrinkage defects, and improves the quality of steel castings for water and electricity equipment ball valves developed by sand casting manufacturer.
