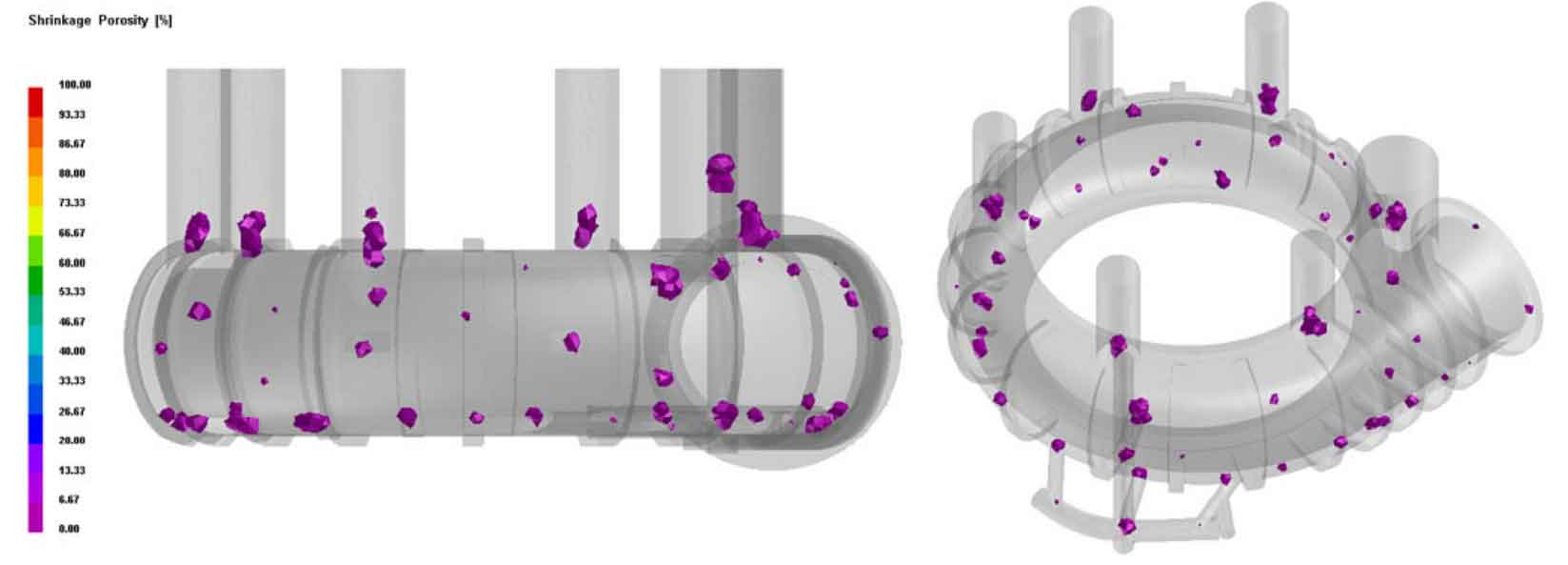
Shrinkage porosity and shrinkage cavity are the most common defects in the process of sand casting, and they are also the main defects in the production of mud pump body of sand casting. The main purpose of numerical simulation of solidification process of sand castings is to predict the distribution of shrinkage porosity and shrinkage cavity defects in the solidification process of sand castings, so as to realize the internal quality control of sand castings.
From the simulation results in the figure, it can be seen that the shrinkage defects generated during the solidification of the mud pump body of sand casting are mainly concentrated in the riser body and the inner sprue, but shrinkage porosity also exists in the main part of sand casting, and the shrinkage porosity at the bottom is significantly more than that at the top, mainly because the mud pump body does not form a bottom-up temperature gradient distribution during solidification, The cooling speed of the bottom of the sand casting is slower than that of the upper part. When the feeding channel of the riser is solidified and blocked, the bottom of the sand casting is not fully solidified, and the feeding of the riser is not obtained at the bottom, forming an isolated hot-melt zone, so shrinkage porosity defects appear.
At #1, #2-1, #2-4 risers, due to the early solidification of the riser neck, the feeding channel was interrupted too early, and the shrinkage porosity defect appeared at the riser root, which is consistent with the above analysis results of solidification process. Due to the chilling effect of chilled iron, there is no shrinkage defect in the stiffener of sand casting mud pump body. Therefore, the design of chilled iron is reasonable. Due to the limited feeding distance of the #1 riser, there are shrinkage defects at the bottom of the flange of the mud pump body of sand casting. It is necessary to set cold iron at the bottom of the flange and combine the #1 riser to eliminate the shrinkage defects in this area.