There are two traditional solutions to the shrinkage defects of lost foam casting nodular iron castings. One is to set a riser at the hot spot to provide the liquid metal that needs to be compensated due to the volume change in the forming process of lost foam casting nodular iron castings to eliminate the shrinkage; The second is to use the chilling system. The most commonly used is to use cold iron to form the hot joint into an end zone, which can change the middle zone with almost no temperature difference into a chilling zone with large temperature difference, form sequential solidification and eliminate shrinkage defects. Although these two methods can solve the defects of shrinkage cavity and shrinkage porosity, they are not suitable for lost foam casting reducer shell. Increasing riser reduces the process yield of lost foam casting nodular iron castings of reducer shell and increases the overall process difficulty. In the process of using cold iron, due to the characteristics of lost foam casting, the cold iron is easy to fall off during molding, and may cause the deformation of lost foam casting nodular iron castings, resulting in great process difficulty, which has a great impact on the quality stability of reducer shell, and increases the cost of lost foam casting nodular iron castings.
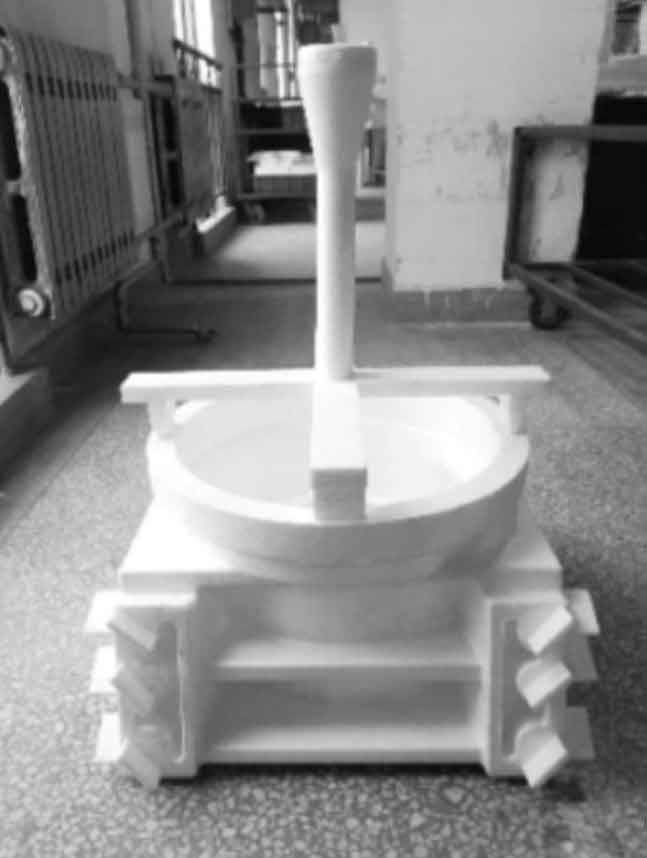
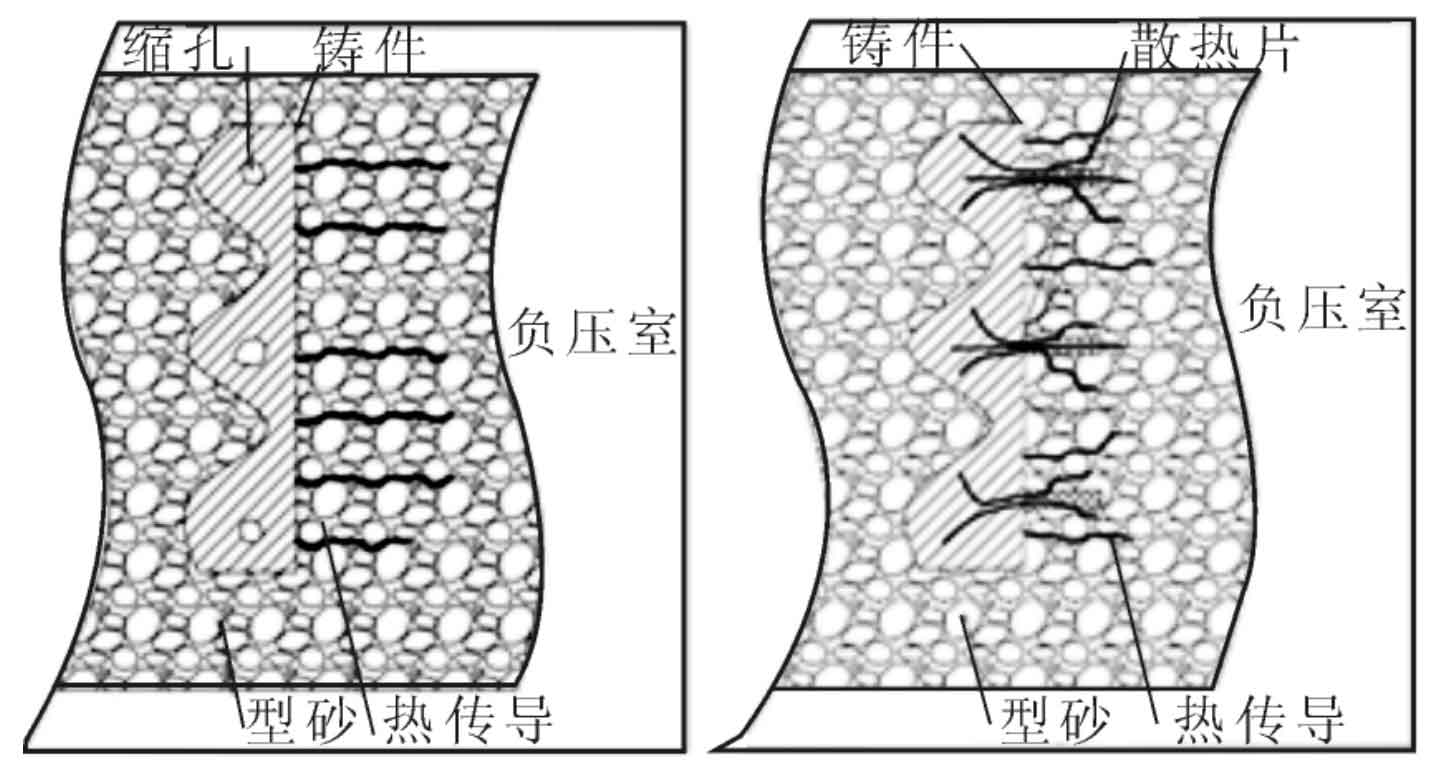
Aiming at the problem of hot shrinkage of nodular cast iron, two new lost foam casting processes were developed: heat dissipation process and flexible chill process. The core purpose of heat dissipation process is to change the structure of lost foam casting nodular iron castings, reduce the modulus at the hot joint of lost foam casting nodular iron castings, and the negative pressure gas takes away a lot of heat in the solidification stage, which has the effect of chilling. The specific method is to produce foam plates in the hot spot of lost foam casting (hereinafter referred to as heat sink, figure 1), and then produce the qualified lost foam casting ductile iron castings after coating, drying, packing, molding and pouring. The lost foam casting cast iron process continues to draw negative pressure during pouring and solidification. During the operation of the negative pressure pump, the cold air enters the upper surface of the sand box, completes the heat exchange through the casting and heat sink, and takes away the heat. The specific surface area of the heat sink is large, which reduces the local modulus of lost foam casting nodular iron castings, and the cold air takes away a lot of heat, The local molding sand in contact with the lost foam casting nodular iron casting and the heat sink forms a microchannel flow heat exchange and forms a chilling zone with large temperature difference. The heat sink plays the role of cold iron, which changes the local solidification mode of lost foam casting nodular iron casting into sequential solidification and eliminates the shrinkage cavity and porosity defects of lost foam casting nodular iron casting. See Fig. 2 for the schematic diagram. The technology of heat sink also has advantages: simple and convenient operation; The influence of casting process is small; It hardly affects the production rate of nodular iron castings by lost foam casting of reducer shell; The post-treatment of reducer housing is simple.
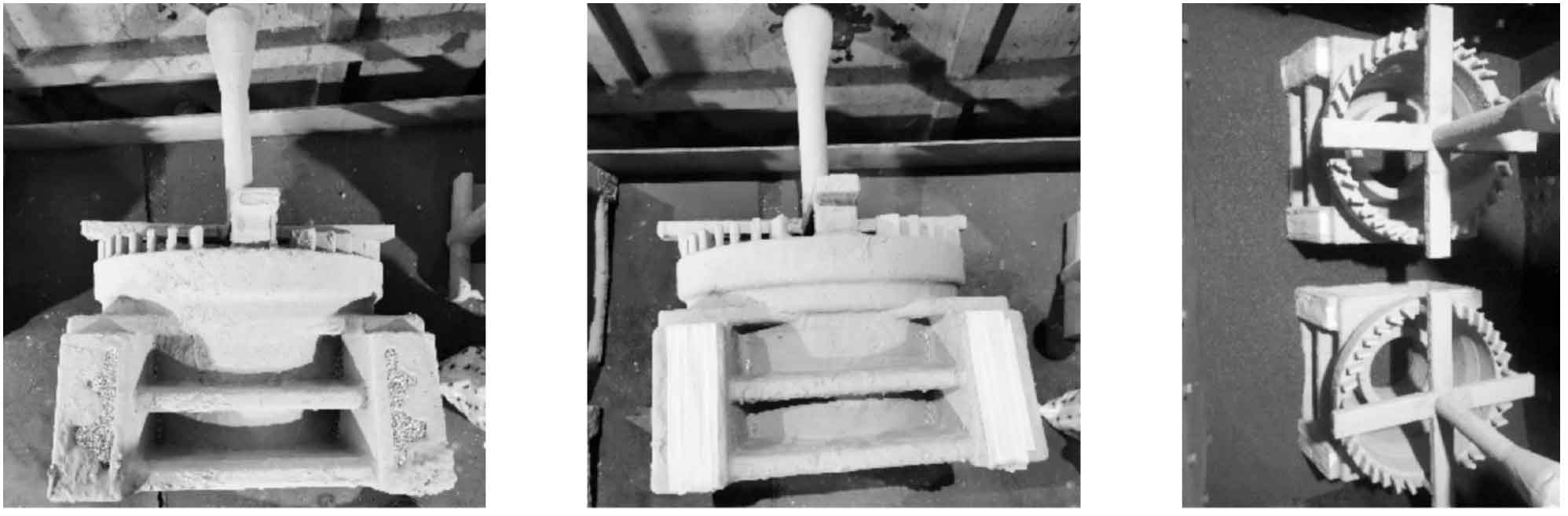
The flexible cold iron process is to use steel shot instead of cold iron to install it at the hot spot of lost foam casting nodular iron castings, eliminate the geometric hot spot of lost foam casting nodular iron castings, and achieve the purpose of eliminating shrinkage defects. The operation method is to add steel shot at the hot joint of lost foam casting nodular iron castings, seal the surface with heat-resistant tape, and then put it into the sand box for vibration molding (Fig. 3). Flexible cold iron is equivalent to setting cold iron at the hot joint of lost foam casting nodular iron castings. Flexible cold iron has certain limitations. It has high requirements for the structure of lost foam casting nodular iron castings. There needs to be a flexible cold iron placement area, otherwise it is difficult to complete.
The reducer shell casting produced by the original process has shrinkage defects in the bolt through hole, as shown in Figure 4. By analyzing the structure of lost foam casting nodular iron castings, it is found that the shrinkage position of reducer shell belongs to geometric hot spot, where there is a large shrinkage tendency, which is consistent with the shrinkage defect in mass production. Considering various factors comprehensively, the heat dissipation process is used. The specific process is shown in Figure 5. In the blanking and bonding process, the bonding size in the hot spot area of lost foam casting nodular iron castings is 50 mm × 30 mm × 7 mm, 12 fins in total. Other processes remain unchanged. Machining after trial production verifies that the bolt hole of reducer housing is normal and there is no quality problem (Fig. 6). The heat dissipation process is mass-produced, and 2000 reducer shells are continuously produced. After processing, there is no shrinkage defect at the bolt hole. The operation process of flexible cold iron process is difficult, and the setting amount of cold iron is difficult to control. Small batch trial production has been carried out, which proves the feasibility of this process.