1.Selection and implementation method of inoculant
Aiming at the problems of high pouring temperature and easy decay of inoculant in lost foam casting Castings, it is decided to use the inoculant with high melting point and slow decay plus ordinary inoculant for many times to achieve the best inoculation effect. At the same time, according to the different inoculation effects and anti recession effects of different inoculants, it is decided to use composite inoculants, and add ferrosilicon, silicon barium and silicon barium calcium inoculants in a certain proportion, which are called the first inoculant, the second inoculant and the third inoculant respectively. The addition amount of the first inoculant is 0.15%. 20s after the spheroidizing reaction, sprinkle the second inoculant with the weight of 0.35% ~ 0.45% of the molten iron in the spheroidizing bag, and then sprinkle the third inoculant with the weight of 0.2% ~ 0.4% of the molten iron. By adding three times, the inoculation effect is improved, the incubation decay time is delayed, and the graphite deformity and the amount of non spherical graphite in the casting are reduced, which is conducive to improving the quality of the casting.
2.The spheroidization package with dike is adopted to delay the spheroidization decline
The low spheroidizing grade of losr foam casting of nodular cast iron is mainly due to the high spheroidizing temperature (due to the high pouring temperature). How to improve the spheroidizing rate under the condition of ensuring the pouring temperature, we adopt to set a layer of spheroidizing agent at the bottom of one side of the dam of the dam type spheroidizing package, set a layer of covering agent on the surface of the spheroidizing agent and tamp it, place the cover plate on the covering agent, and then place the spheroidizing agent, the first inoculant and covering agent on the cover plate in turn. The cover plate is stainless carbon steel plate or formed nodular cast iron plate.
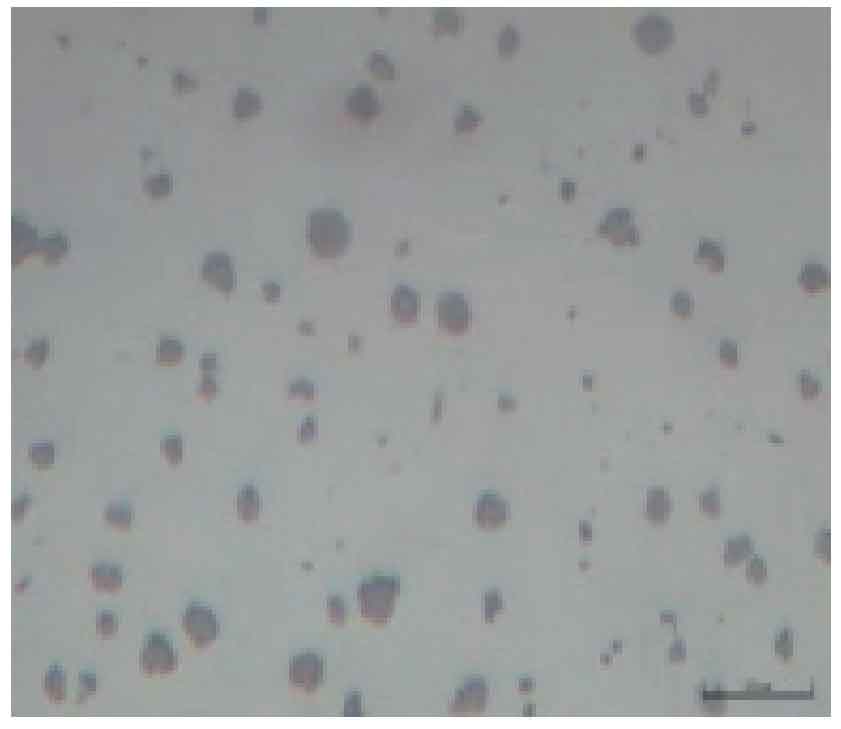
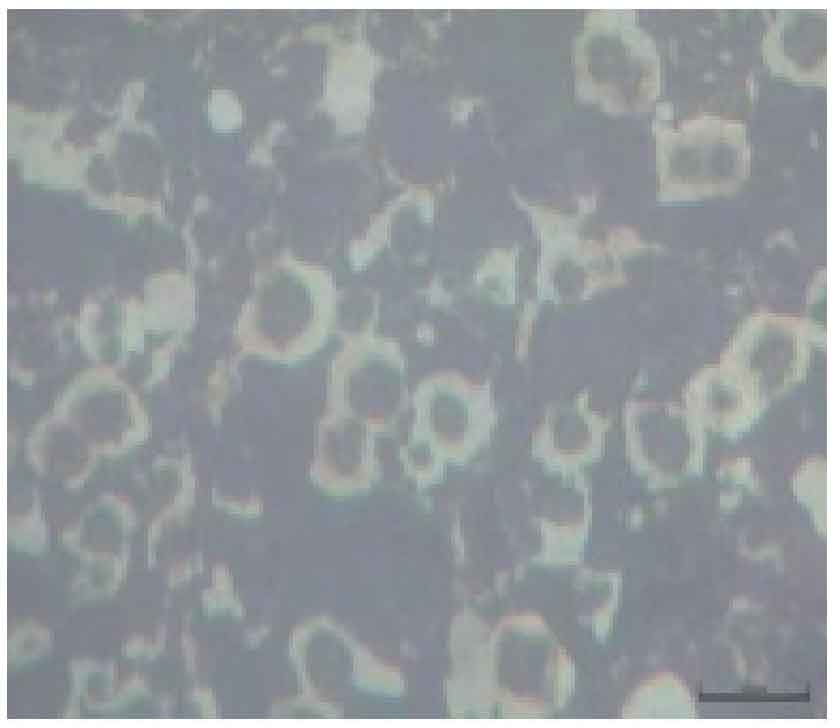
Raise the temperature of the molten iron of the electric furnace to 1560 ~ 1600 ℃, after removing the slag on the surface, sprinkle the silicon carbide pretreatment agent with the weight of 0.05% ~ 0.15% of the molten iron, and keep it warm for 9 ~ 11min. Pour the molten iron after removing the scum in the molten iron ladle into the side without spheroidizing agent in the dam type spheroidizing ladle. The inverted spheroidizing and inoculation process of lost foam casting of nodular cast iron is to set a layer of spheroidizing agent with the weight of 0.7% ~ 0.9% of the molten iron at the bottom of one side of the dam, cover the surface of the spheroidizing agent with a layer of covering agent with the weight of 0.05% ~ 0.15% of the molten iron and tamp it, place the cover plate on the covering agent, and then place the spheroidizing agent with the weight of 0.55% ~ 0.65% of the molten iron on the cover plate in turn The weight of the first inoculant is 0.05% ~ 0.15% of the weight of molten iron and the weight of the covering agent is 0.05% ~ 0.15% of the weight of molten iron. The top surface of the cover plate is flat, the shape of the bottom surface is the same as that of the package bottom of the spheroidized package, and the gap between the edge of the top surface of the cover plate and the inner wall of the package is ≤ 5mm. Therefore, when adding molten iron for spheroidizing reaction, due to the existence of the middle cover plate, the whole spheroidizing reaction is carried out in two times. The first layer of spheroidizing reaction is that the spheroidizing agent on the upper layer of the cover plate reacts first to make the molten iron absorb part of rare earth magnesium. With the progress of spheroidization reaction, the cover plate melts gradually. When the cover plate melts, the spheroidizing agent arranged under the cover plate begins to react, that is, the second spheroidizing reaction. Through two spheroidizing reactions successively, the time of spheroidizing reaction is prolonged, the absorption rate of rare earth magnesium is improved, the later burning loss is reduced, the spheroidizing grade is improved, and the final casting quality is guaranteed. After the spheroidizing process is improved, the metallographic structure of nodular iron castings is shown in Fig. 1 and Fig. 2.
It can be clearly seen from Figure 1 and Figure 2 that through the process improvement, the number of graphite and pearlite content have been significantly improved, and the process improvement has achieved obvious results.