Application Statistics of cold iron in cylinder block iron castings.
It can be seen from the statistical cases that HT200 and HT250 are widely used in the production of cylinder block iron castings. The main reason is that the material source is wide, the production process is simple, the cost is low, and it is easy to use. At the same time, the thermal conductivity of gray cast iron ranges from 0.054 to 0.058w / (m ·℃), and its chilling ability is strong. In addition, the use frequency of gray cast iron chill should be strictly controlled in order to reduce or even eliminate the adverse effect of oxidation of gray cast iron chill on cylinder body iron castings.
In order to prevent the oxidation and corrosion of gray cast iron chill caused by high temperature and high humidity, and reduce or even eliminate the adverse effect of easy oxidation of gray cast iron cold iron, resulting in air holes and cracks in cylinder body iron castings, coating is needed on the surface of cold iron.
Statistical results of material, length (unit: mm), width (unit: mm), thickness (unit: mm) and average wall thickness (unit: mm) and mass (unit: kg) of cast iron cylinder block.
The relationship between the thickness of cold iron δ and the average wall thickness t of iron castings adjacent to the cylinder block is
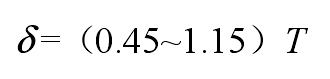
The relationship between the length L of cold iron and the thickness δ of cold iron is
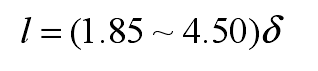
The relationship between the width of cold iron and the thickness of cold iron is
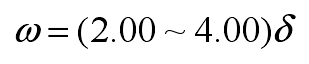
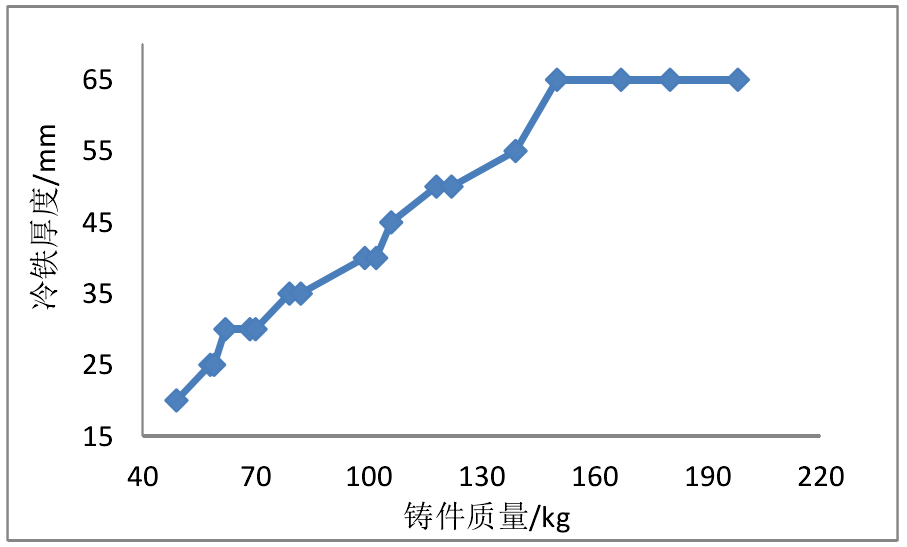
The variation curve of chill thickness and casting quality is shown in Fig. It can be seen from the figure that cold iron is mainly used for small cylinder block iron castings, and the greater the quality of cylinder block iron castings, the thickness of chill iron will also increase, and finally tend to be stable. This is mainly because the larger the cast iron, the more need to control the solidification mode, so the chilling effect of cold iron is required to be stronger; but when the thickness increases to a certain extent, the chilling effect does not increase significantly. Therefore, in actual production, it is not necessary to use the cold iron with excessive wall thickness. If necessary, the number of cold irons can be increased to control the solidification mode of iron castings.
In addition, during the use of cold iron, the following matters should be noted:
(1) Based on the effective feeding distance of riser, the location and chilling capacity of external chill can not affect the solidification condition and feeding channel of cylinder block iron castings;
(2) The size of cold iron should not be too large or too long. There should be enough clearance between the cold irons. To avoid mold damage, casting cracks;
(3) The external cold iron should be placed at the bottom and side of the cylinder body, and the surface of the external cold iron should be smooth and smooth without rust and oil stain; the material of the internal cold iron should be consistent with the casting material.
(4) The practical frequency of external cold iron should be strictly limited. The number of cold irons used in cylinder type iron castings ranges from 5 to 10 times. The upper limit is taken for small and medium-sized cylinder blocks, and the lower limit is taken for large-scale cylinder blocks. Before use, the oxidation of cold iron should be strictly checked to avoid porosity defect caused by repeated use of cold iron.
