The service performance of nodular cast iron is mainly determined by the microstructure and casting defects, among which the microstructure mainly depends on the number of graphite balls, nodularization rate and metal matrix, and the casting defects mainly refer to the macro and micro shrinkage. In the process design of high quality ductile iron products, the most important and key step is to design the feeding system [6]. In the design and research of casting process, the feeding system of casting is mainly composed of riser design, gating system design and chill design, of which riser and gating system design are the most important. In this paper, several advanced technical research results are discussed from the aspects of optimizing riser and gating system design.
1 Riser process study
The riser is mainly used to store the metal liquid in the mold, compensate the possible shrinkage during the formation of the casting, prevent the casting from producing shrinkage cavity and porosity, and also has the function of exhaust, slag collection and guiding mold filling [7]. The shrinkage process of casting after pouring includes liquid shrinkage and subsequent solidification process shrinkage. During the whole metal solidification process, all liquid shrinkage must be effectively supplemented to avoid the shrinkage defects of casting.
Through the comparative experiment shown in Fig. 7, it can be seen from the analysis of the empirical data and the actual experimental results that the effective amount of molten iron feeding for the common sand mold or the riser without insulating sheath is far from that for the heating or insulating riser riser, the feeding efficiency of the former is only 15% of that of the latter, and the feeding is limited. Generally, the most effective solution is to use heating or insulating riser sleeve, which is conducive to increasing or maintaining the temperature of riser molten iron, allowing the molten iron to stay in the riser for a longer time, and facilitating the liquid feeding of castings. The example of casting shrinkage is shown in Figure 1.
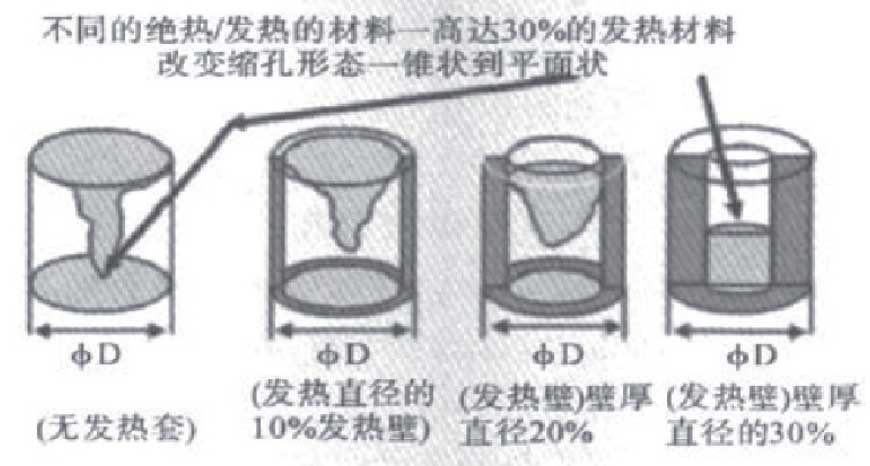
A kind of micro riser is widely used. The riser is made of heating material, and the liquid metal in the riser can be kept for a long time. The advantage of using the riser is that it can not only provide enough liquid metal for feeding, but also accept the metal liquid expanded during the graphitization expansion precipitation process. Usually, this kind of riser which can provide the required feeding metal and receive the expansion liquid is called pressure control riser. Another main function of the riser is to prevent casting deformation by reducing pressure of the riser when the cavity is pressurized due to graphitization expansion.
The main advantages of the micro riser are:
(1) Regardless of pouring temperature, the feeding mode of riser is the same, and the contact area between riser and casting is smaller than that of sand mold riser;
(2) The micro riser can provide the most effective feeding system. The casting with relatively large size can be successfully produced by using this process, and the casting has a high process yield.
2 Research on pouring system technology
The gating system is the general name of the channel in which liquid metal flows into the mold cavity (application examples are shown in Fig. 2 and Fig. 3). Whether the gating system is designed correctly or not has a great impact on the quality of the casting. According to statistics, about 30% of the casting rejects are caused by improper gating system. Although the gating system of nodular cast iron is simpler than that of steel castings, if it is not designed properly, it is easy to cause the molten metal to collide and splash with each other in the mold cavity during the filling process of the mold, resulting in oxidation, inclusion, sand hole and air hole [8]. The gating system is generally divided into pressure type and reverse flow resistance type. The pressure type flow resistance section is set in the inner runner, and the proportion of the gating system is 4:8:3. The reverse flow blocking type is to set the flow blocking between the sprue socket and the transverse sprue, and the ratio of the gating system is recommended to be 3:1:3:2. There are bottom pouring, step pouring and top pouring in the internal sprue. For nodular cast iron, the pressure bottom pouring is better.
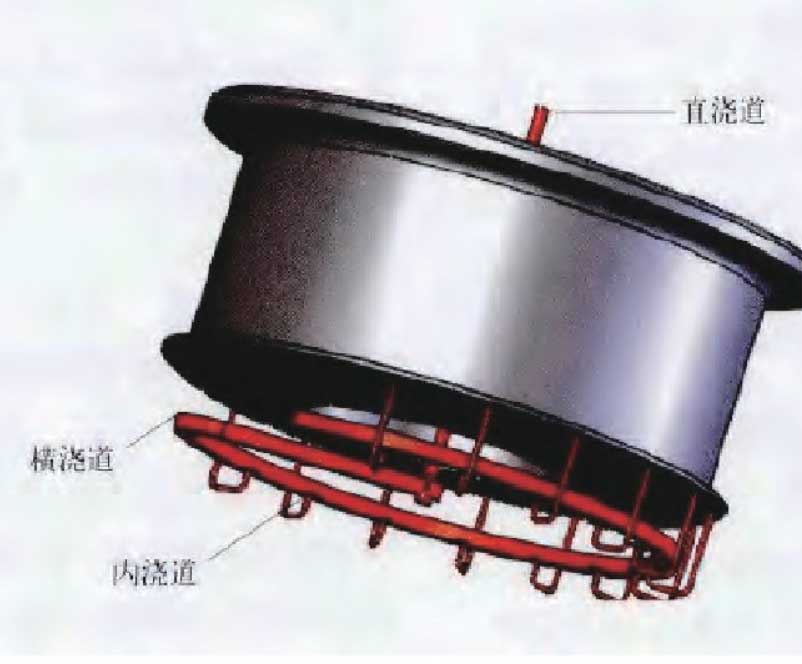
The principle of quick pouring at low temperature is often adopted for large ductile iron castings. Low temperature is beneficial to reduce the total volume of shrinkage cavity, and rapid pouring can effectively prevent the defects of insufficient pouring. According to the experience and calculation, the pouring temperature is about 1350 ℃ and the pouring time is 90 ~ 110 s. A small number of domestic manufacturers have fully implemented the riser free casting process. The characteristics of the riser free casting pouring system should be small internal sprue and scattered Introduction (i.e. multiple and flat thin internal sprue) [9]. For large-scale ductile iron castings, in order to realize riser free casting, the design of gating system should conform to the principle of solidification at the time of contract, which can transport a large amount of molten iron, reduce the temperature difference of different filling parts, and make the temperature distribution of castings uniform. Therefore, according to the principle of “large hole outflow”, the section ratio of each unit of gating system is taken as ∑ f direct ∑ f transverse ∑ f internal = 1:2:1.5. The system has many functions, such as large flow of molten iron, fast and stable filling of mold, uniform temperature field of mold, and closing dirt and gas.
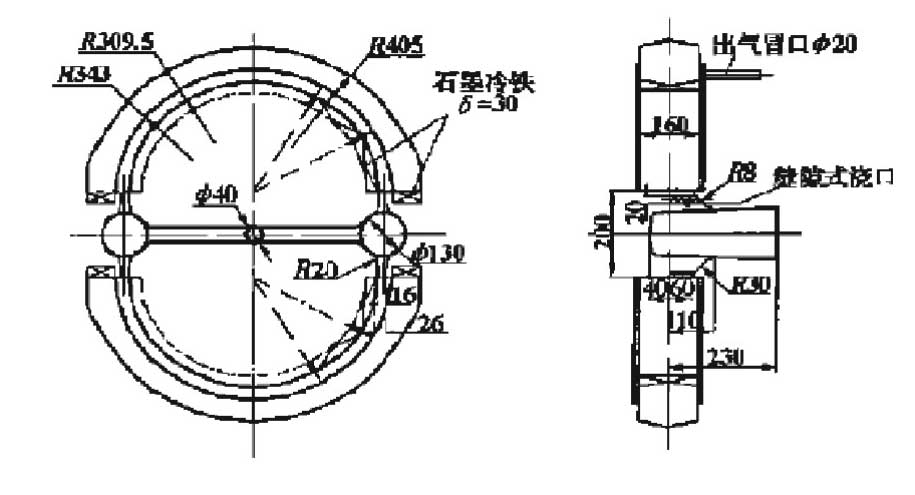
Slot gating system is widely used in the casting of oxidizable materials. In the usual slot gating system, the molten metal flows into the casting cavity from bottom to top along the vertical slot, and the filling process is stable, so as to avoid serious turbulence of the molten iron and no oxide slag, and at the same time, it is conducive to the floating of the slag in the molten iron. As the liquid flow is from bottom to top along the gap layer by layer filling, the temperature of the liquid metal is higher than that of the next layer for each additional layer. In this way, after pouring, the temperature distribution of the whole casting in the height direction is high and low, which is conducive to the sequential solidification of the casting from the bottom to the top [13]. A domestic unit has achieved good results in the application of slot gate in the process improvement of bearing cover casting (FIG. 10). Most of the domestic nodular iron casting manufacturers have widely used the bottom pouring slot gate (Figure 11), its main advantages are: the inner sprue is basically filled in the submerged state, and the filling is stable; it can avoid splashing and oxidation of the liquid metal and the casting defects caused by it, no matter how large the gate ratio is, the transverse sprue is basically working in the full state, which is conducive to slag resistance; It is beneficial to exhaust the gas in the cavity. At the same time, the internal sprue is thin and wide, which effectively reduces the suction area of the internal sprue, which is conducive to the slag blocking of the cross sprue; reduces the possibility of entering the initial slag; reduces the cleaning workload, the internal sprue is thinner than the wall thickness of the casting, which is not easy to damage the casting when removing the sprue [14]; by selecting this type of pouring system, the slag inclusion defects of the casting can be effectively reduced and prevented, and the surface quality of the casting can be improved.
