(1) Effect on hardness of gray cast iron
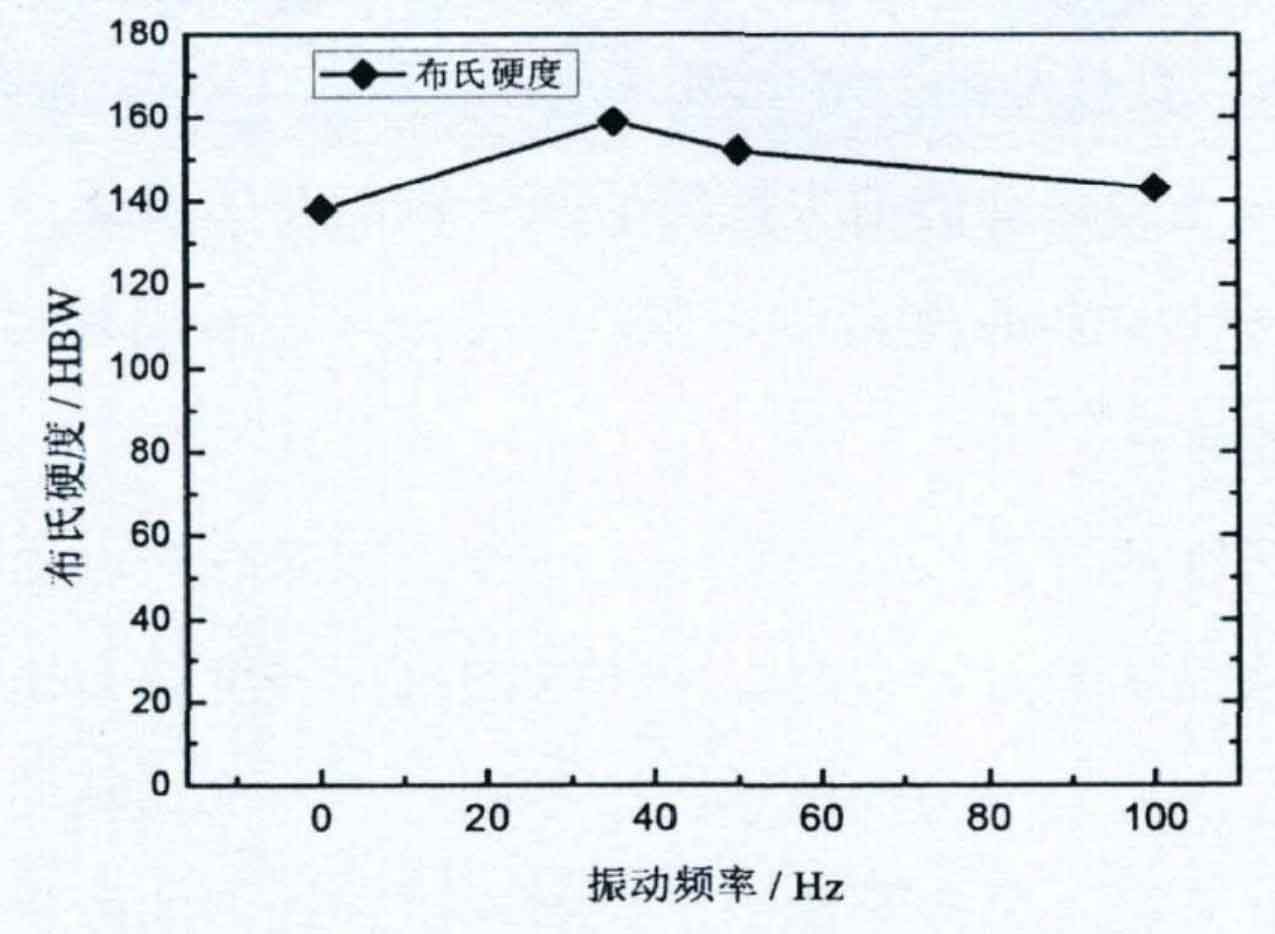
Fig. 1 shows the effect of vibration frequency on the hardness of grey cast iron. It can be seen from Figure 1 that with the increase of vibration frequency, the Brinell hardness of grey cast iron increases first and then decreases. The Brinell hardness value of grey cast iron prepared under the condition of 35Hz vibration frequency is the largest, which is mainly due to the small pearlite flake spacing and primary austenite grain size of grey cast iron prepared under this condition. However, the Brinell hardness values of grey cast iron prepared under the conditions of no vibration and 100Hz vibration frequency have little difference, which is mainly because the microstructure of grey cast iron prepared under the two process conditions has little difference.
(2) Effect on mechanical properties of gray cast iron
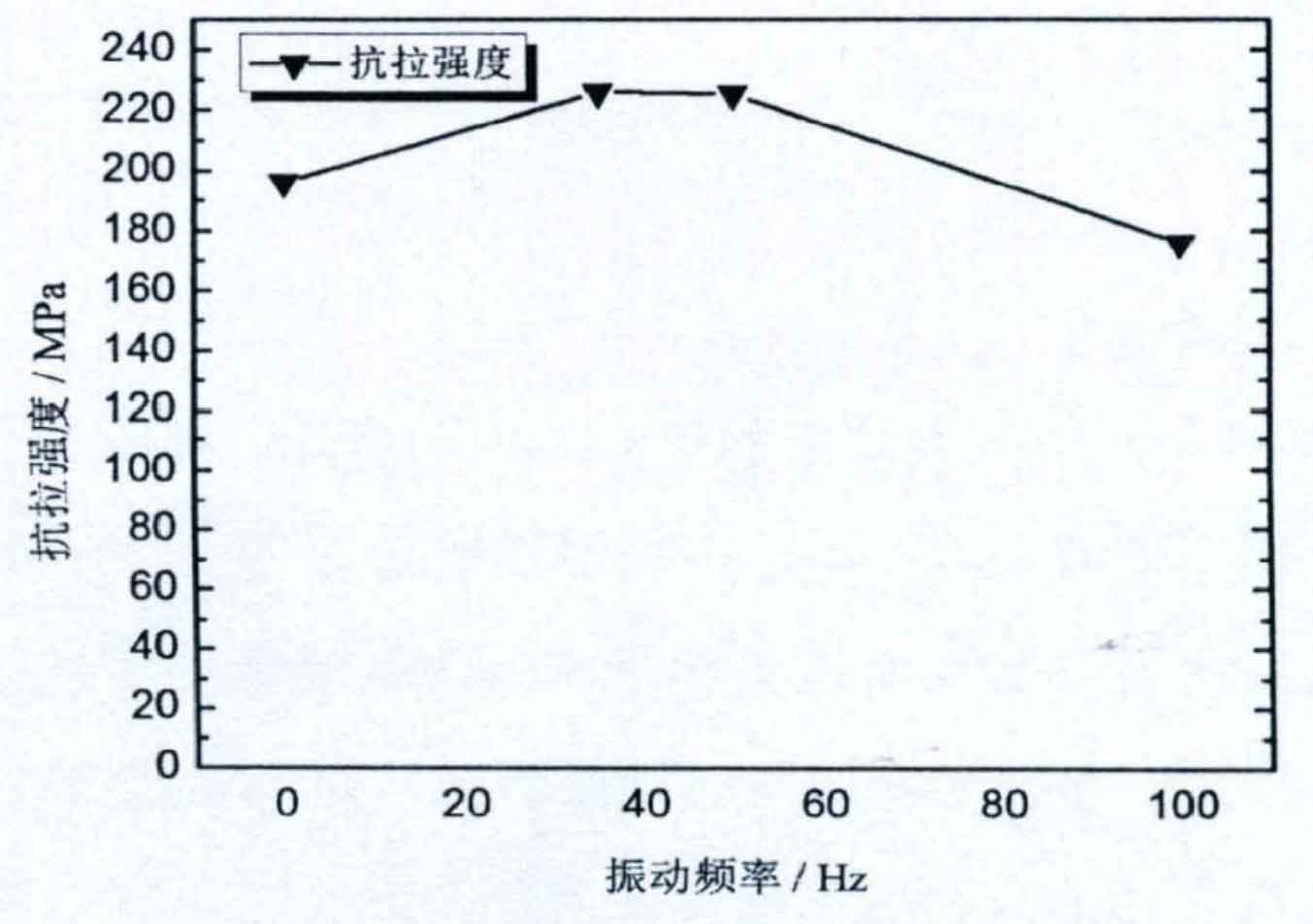
Fig. 2 shows the variation curve of mechanical properties of gray cast iron with vibration frequency. It can be seen from Figure 2 that the tensile strength of grey cast iron increases first and then decreases with the increase of vibration frequency. The tensile strength of grey cast iron prepared at 35Hz is the highest, with a value of 225.99mpa. Compared with 196.04mpa of lost foam casting gray cast iron without vibration, it is increased by 15.28%. Continue to increase the vibration frequency to 50Hz, the strength of the gray cast iron produced under this condition is slightly lower than that of the gray cast iron produced at the vibration frequency of 35Hz, but the reduction is very small. Further increase the vibration frequency to 100Hz, and the tensile strength of the gray cast iron produced at this time is only 175.76Mpa.
The primary phase and graphite in gray cast iron are the main factors affecting its properties. From the above analysis results, it can be seen that the primary austenite grain of lost foam casting gray iron without vibration is coarse, and the primary dendrite is developed. In addition, the length of A-type flake graphite in cast iron is large, and the graphite sheet is also thick. The mechanical properties of gray iron with this structure are poor.
On the other hand, the tensile strength of gray cast iron is also related to the direction of force application. When the number of primary austenite dendrite axes parallel to the tensile stress direction is large, the tensile strength of gray cast iron will be higher. This is because the columnar dendrite has directionality, so the sensitivity to stress is different. When the direction of the primary crystal axis is parallel to the tensile stress, the primary crystal axis has a large bearing capacity. Only when more energy is consumed can the crack pass through the primary crystal axis of the dendrite, which shows that the tensile strength of gray cast iron is large.
