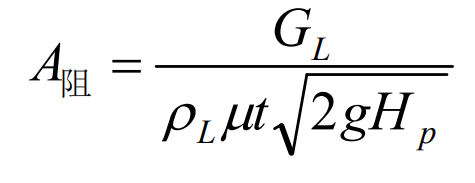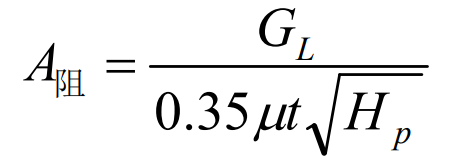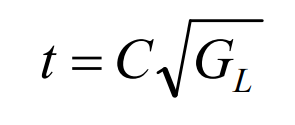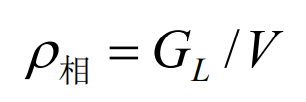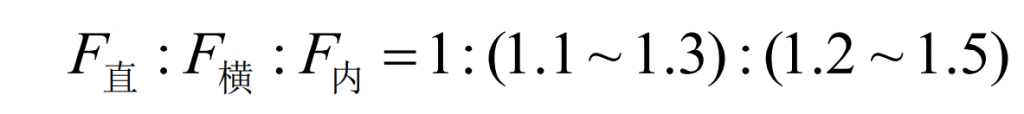According to the analysis of the original process scheme of the valve body, it can be seen that the improper placement of the gate and riser of the original process leads to serious shrinkage cavity and porosity defects in the lost foam casting of the cast steel valve body, so the original process scheme needs to be improved. Firstly, starting with the gating system, Dong Xiuqi and others suggested that the bottom injection type should be preferred in the selection of gating system; However, starting from the characteristics of the alloy metal itself, for the poor fluidity and large shrinkage of cast steel, it is often prone to shrinkage cavity and porosity at the last solidified part. The top injection type should be used for medium and small castings. Therefore, in order to reduce the shrinkage cavity and porosity defects of cast steel valve body lost foam casting, according to the causes of the original process defects and the structural characteristics of cast steel valve body lost foam casting, two new schemes are proposed to compare and select the appropriate Pouring Scheme. The first scheme is the bottom pouring system with liquid metal introduced from the side of the bottom, The second scheme is the top pouring system with liquid metal introduced into the side of the top.
1. Determination of gate position
According to the analysis of the simulation results of the original process scheme, it can be seen that the serious shrinkage cavity and porosity defect is caused by setting the gate of the liquid metal introduced into the mold cavity at a thick part and adding an artificial overflow heat joint at the geometric heat joint, resulting in too high heat and slow heat loss, resulting in final solidification and no feeding of the external liquid metal. Therefore, the new scheme adopts the introduction of molten metal from the outer thin wall, that is, the inner sprue is located at the thin wall, and the number is large and dispersed, so that high-temperature molten metal can be obtained far away from the gate.
2. Runner size design
Compared with the traditional sand casting, the whole lost foam casting process of cast steel valve body is a complex physical and chemical process, and there are many influencing factors, so the design of gating system is still lack of theoretical basis. At present, the gating system of lost foam casting for cast steel valve body is based on the traditional lost foam casting process design of cast steel valve body, and the size is 15% – 20% larger than that of the traditional lost foam casting process of cast steel valve body, which is continuously improved and adjusted through actual production. There are two methods to determine the size of gating system of lost foam casting for cast steel valve body:
1. According to the experience method, taking the traditional sand mold casting process as the sample, after checking the casting manual table or empirical formula for calculation, it will increase by 15% ~ 20% on the basis of the calculation results.
2. The first step is to determine the minimum section (choke section) size in the gating system, and the second step is to obtain the section size of other components according to the proportional relationship.
The section size of each element of the gating system is calculated by combining the two methods. The specific steps are as follows:
(1) The first is to determine the minimum section (choke section) size in the lower gating system, and deduce the choke section area according to the principle of hydrostatic formula, as shown in the formula:
Where, a resistance represents the minimum cross-sectional area in the gating system, cm2; GL is the weight of liquid metal flowing through resistance a, kg; ρ L density of molten metal, where the density of molten steel is ρ L = 7.8g / cm3 ; μ Is the flow coefficient, which can generally be taken according to the small resistance, and the value of steel castings is 0.03-0.05; HP is the height of the indenter, cm; T is pouring time, S. Simplified formula:
(2) For steel castings, the pouring time t can be determined according to the formula:
Where, C is the coefficient, which is determined by the relative density of the lost foam casting of the studied cast steel valve body ρ L decision.
Where, GL is the casting quality; V is the contour volume of lost foam casting of cast steel valve body.
(3) The weight of lost foam casting of single cast steel valve body is about 33.6kg, the contour volume is 23460cm3, and G is about 53kg, μ Take 0.04 and HP 295mm. According to the above formula, t is about 5S and a resistance = 14.8cm2. For lost foam casting, the size of gating system shall be enlarged by 15% ~ 20% based on the calculation results, and the cross-sectional area at the contact between lost foam casting of cast steel valve body shall be twice the minimum flow blocking cross-sectional area.
The lost foam casting of cast steel valve body is made of carbon steel, which is easy to oxidize, so the open gating system is adopted, and the proportion relationship of each component is shown in the formula:
(4) Gating system structure: different from the traditional casting process, it is better to have a simple structure and facilitate pattern assembly. It is not recommended to adopt ox horn type, flow blocking type, centrifugal type and other complex structural forms. The complex structure will lengthen the flow distance of liquid metal, consume a lot of heat before pouring into the cavity, and reduce the filling capacity of liquid metal.
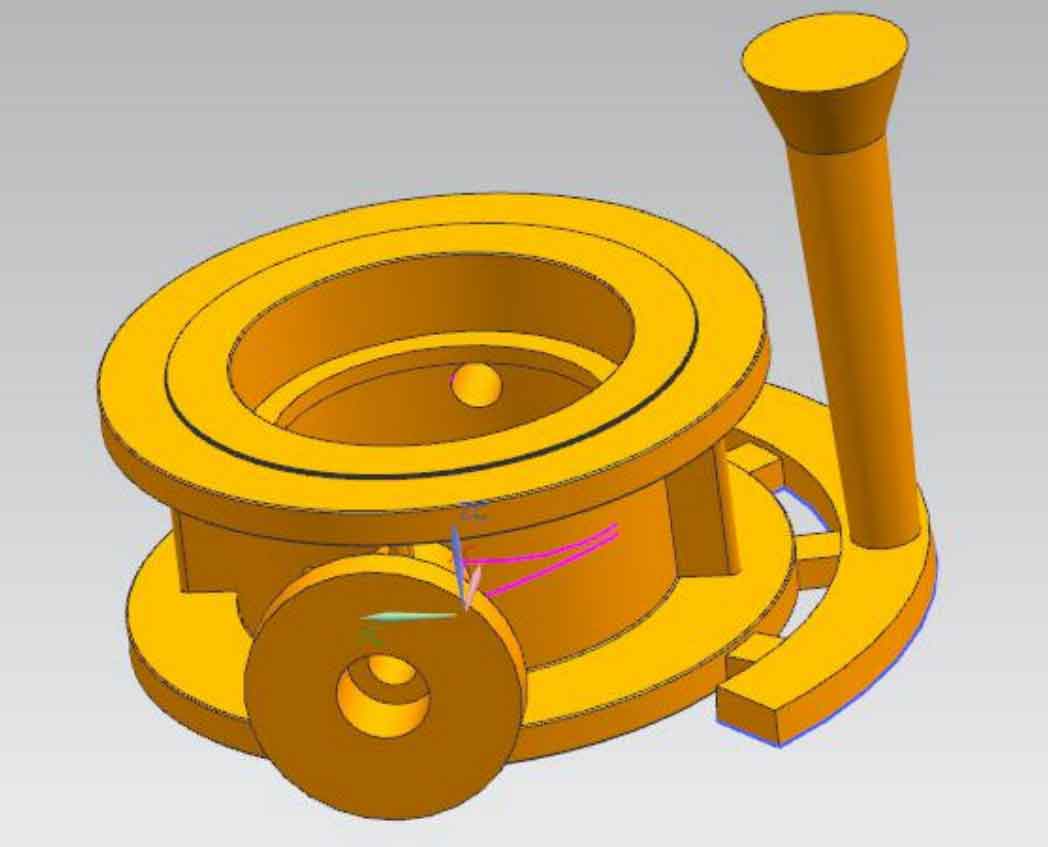
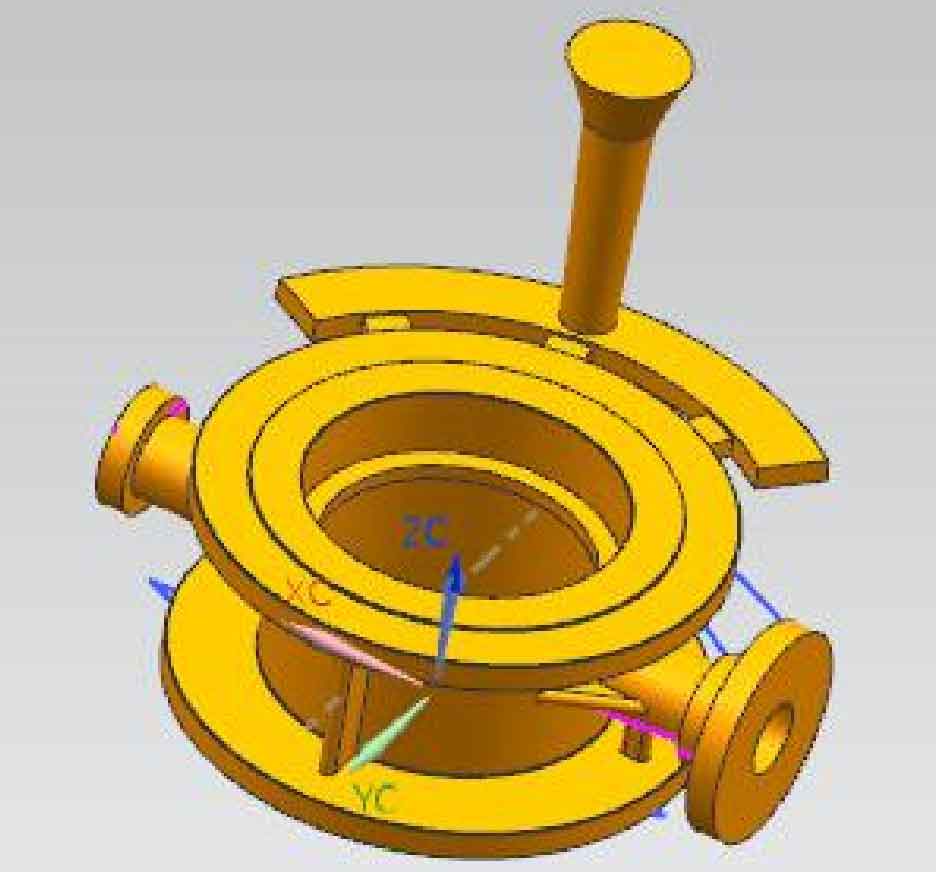
Figures 1 and 2 are the three-dimensional structure diagrams of bottom injection and top injection gating systems respectively. The sectional dimension of the gating system refers to the minimum flow blocking sectional area of 18cm2 calculated above. Three internal sprues are set, with a cross-sectional area of 30mm × 12mm, the cross-sectional area of the runner is 45mm × 15mm, the sprue is a cylinder with a diameter of 32mm and a slope of 2 °.